Lesson 6
... disorders are the simple type, catatonia, paranoia and hebephrenia; while effective reactions are the manic-depressive type. If emotional stress is not given proper management, it may result to abnormal behavior such as: a. Personality Aberrations. The behavior shown in the mild forms of maladjustme ...
... disorders are the simple type, catatonia, paranoia and hebephrenia; while effective reactions are the manic-depressive type. If emotional stress is not given proper management, it may result to abnormal behavior such as: a. Personality Aberrations. The behavior shown in the mild forms of maladjustme ...
- Journal of Affective Disorders
... and Cloninger et al. (1997) model of depressive types have some empirical backing, it is not clear that these two conceptualizations are assessing the same construct. Specifically, in a mixed sample of mood and non-mood disorder patients, Strong et al. (2007) found that the self-directedness, Dysthym ...
... and Cloninger et al. (1997) model of depressive types have some empirical backing, it is not clear that these two conceptualizations are assessing the same construct. Specifically, in a mixed sample of mood and non-mood disorder patients, Strong et al. (2007) found that the self-directedness, Dysthym ...
Mood Disorders and Suicide
... includes cognitive symptoms (worthlessness, indecisiveness) and physical symptoms (altered sleeping pattern, changes in appetite and weight, loss of energy) ...
... includes cognitive symptoms (worthlessness, indecisiveness) and physical symptoms (altered sleeping pattern, changes in appetite and weight, loss of energy) ...
Mood and Anxiety Disorders
... • Depression can be considered across a spectrum, with symptoms and severity assessed on a continuum – Unitary Theory of Depression (Akiskal & McKinney, 1973) – Severe, moderate, and mild depressions may not be points on a single spectrum • Depression can be a symptom or a disorder • Mood is disprop ...
... • Depression can be considered across a spectrum, with symptoms and severity assessed on a continuum – Unitary Theory of Depression (Akiskal & McKinney, 1973) – Severe, moderate, and mild depressions may not be points on a single spectrum • Depression can be a symptom or a disorder • Mood is disprop ...
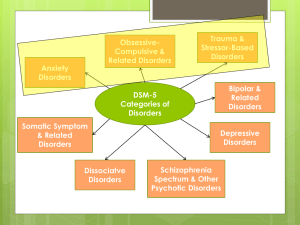
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth
... • “DSM is a medical classification of disorders and as such serves as a historically determined cognitive schema imposed on clinical and scientific information to increase its comprehensibility and utility.” • “Conditions for Further Study,” described in Section III, are those for which it was deter ...
... • “DSM is a medical classification of disorders and as such serves as a historically determined cognitive schema imposed on clinical and scientific information to increase its comprehensibility and utility.” • “Conditions for Further Study,” described in Section III, are those for which it was deter ...
Document
... Kleinman’s theory – somatization and depression are different manifestations of the same problem – cross-cultural research • pattern of somatoform disorders affected by cultural beliefs ...
... Kleinman’s theory – somatization and depression are different manifestations of the same problem – cross-cultural research • pattern of somatoform disorders affected by cultural beliefs ...
Abnormal Psych (Ch 3..
... Culture-bound syndromes - Patterns of abnormal behavior found within only one or a few cultures. Culture-bound syndromes may reflect exaggerated forms of common folk superstitions and belief patterns within a particular culture. Culture-bound syndromes in the United States include anorexia nervosa a ...
... Culture-bound syndromes - Patterns of abnormal behavior found within only one or a few cultures. Culture-bound syndromes may reflect exaggerated forms of common folk superstitions and belief patterns within a particular culture. Culture-bound syndromes in the United States include anorexia nervosa a ...
Psychological Disorders
... • Mental disorders are a psychological response to stress & inhumane conditions • Genetic components of many disorders • Acceptance of phys cause & search for med treatment ...
... • Mental disorders are a psychological response to stress & inhumane conditions • Genetic components of many disorders • Acceptance of phys cause & search for med treatment ...
8th Edition
... Antisocial Personality Disorder - individual shows a pervasive disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others. Borderline Personality Disorder - individual shows a generalized pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and observable emotions, and significant impulsive ...
... Antisocial Personality Disorder - individual shows a pervasive disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others. Borderline Personality Disorder - individual shows a generalized pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and observable emotions, and significant impulsive ...
Spectrum of cases seen by Clinical Psychologist
... Behavior problems in children are outcome of three factors ...
... Behavior problems in children are outcome of three factors ...
Anxiety Disorders
... can serve as a diversion from a person’s real fears, so it may reduce anxiety. Provide the person with evidence that they are doing something well, even if it is only avoiding cracks on a sidewalk. Genetic ...
... can serve as a diversion from a person’s real fears, so it may reduce anxiety. Provide the person with evidence that they are doing something well, even if it is only avoiding cracks on a sidewalk. Genetic ...
Ch. 15 Abnormal Psychology/Psychopathology Take Home Test
... at people as they walk by, and he is known for his ever-present greeting of “Good Luck!” In fact, the students at this campus have come to refer to him as “Good Luck Nick.” Nobody knows if he has a home or if he is destitute, but Nicholas never asks for anything. Which of the four criteria of mental ...
... at people as they walk by, and he is known for his ever-present greeting of “Good Luck!” In fact, the students at this campus have come to refer to him as “Good Luck Nick.” Nobody knows if he has a home or if he is destitute, but Nicholas never asks for anything. Which of the four criteria of mental ...
AXIS II - DAV College For Girls, Yamunanagar
... studying plants, planets and people. With an agreed upon classification system we can be confident that we are communicating clearly. If someone says to you “ I saw a coolie running down the street, you probably have an accurate idea of what the coolie looked like- not from seeing it but rather from ...
... studying plants, planets and people. With an agreed upon classification system we can be confident that we are communicating clearly. If someone says to you “ I saw a coolie running down the street, you probably have an accurate idea of what the coolie looked like- not from seeing it but rather from ...
Chapter Outline
... complete. Depersonalization disorder is characterized by feelings of unreality or distorted perceptions of the body or environment. It is more common than the other dissociative disorders, tends to be chronic, is often accompanied by mood or anxiety disorders, and can be precipitated by stress. In d ...
... complete. Depersonalization disorder is characterized by feelings of unreality or distorted perceptions of the body or environment. It is more common than the other dissociative disorders, tends to be chronic, is often accompanied by mood or anxiety disorders, and can be precipitated by stress. In d ...
DSM-IV-TR Invalidities - Professionaltrainingresourcesinc.com
... thus be treated as though they had attachment responses indicative of a disorder, rather than having their real attachment needs addressed. DSM-IV suggests, for most diagnoses, that the condition must cause “clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important ar ...
... thus be treated as though they had attachment responses indicative of a disorder, rather than having their real attachment needs addressed. DSM-IV suggests, for most diagnoses, that the condition must cause “clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important ar ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The sociocultural model suggests that to fully explain psychopathology we need to pay attention to the social and cultural factors that form the context, or background, of abnormal behavior. Sociocultural factors such as gender, age, marital status; physical, social, and economic situations; and the ...
... The sociocultural model suggests that to fully explain psychopathology we need to pay attention to the social and cultural factors that form the context, or background, of abnormal behavior. Sociocultural factors such as gender, age, marital status; physical, social, and economic situations; and the ...
Slide 1
... Rule-out Schizoaffective and Mood Disorder with Psychosis: 1. No significant mood symptoms during active phase 2. If mood symptoms present during active phase, their duration is brief relative to active and residual phases Not due to a medical condition or a substance ...
... Rule-out Schizoaffective and Mood Disorder with Psychosis: 1. No significant mood symptoms during active phase 2. If mood symptoms present during active phase, their duration is brief relative to active and residual phases Not due to a medical condition or a substance ...
Social and Familial Factors in the Course of Biplar Disorder: Basic
... How do you see these variables interacting with each other to influence the course of BD? Future research to focus on replication, looking at the interactions of risk and protective factors at different phases of the life cycle, cost effective methods for training clinicians and the identification o ...
... How do you see these variables interacting with each other to influence the course of BD? Future research to focus on replication, looking at the interactions of risk and protective factors at different phases of the life cycle, cost effective methods for training clinicians and the identification o ...
Anxiety Disorders and Somatoform Disorders
... Observational learning can produce fear which results in anxiety. ...
... Observational learning can produce fear which results in anxiety. ...
A Survival Guide to the DSM-5
... Situation • Child referred for counseling because of numerous disciplinary problems at school. Upon assessment, child is found to meet criteria for ADHD ...
... Situation • Child referred for counseling because of numerous disciplinary problems at school. Upon assessment, child is found to meet criteria for ADHD ...
CHAPTER 13 Long PRACTICE TEST
... Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the distinction between normal and abnormal behavior? a. A person might be considered normal in one culture and abnormal in another. b. Not all people whose behavior is abnormal experience personal distress. c. The most widely used criterion fo ...
... Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the distinction between normal and abnormal behavior? a. A person might be considered normal in one culture and abnormal in another. b. Not all people whose behavior is abnormal experience personal distress. c. The most widely used criterion fo ...
Psychological Disorders
... The DSM-5 lists known causes of these disorders, statistics in terms of gender, age at onset, and prognosis as well as some research concerning the optimal treatment approaches. Mental Health Professionals use this manual when working with patients in order to better understand their illness and pot ...
... The DSM-5 lists known causes of these disorders, statistics in terms of gender, age at onset, and prognosis as well as some research concerning the optimal treatment approaches. Mental Health Professionals use this manual when working with patients in order to better understand their illness and pot ...
Obsessive Compulsive disorder for medical students
... picking were more prevalent in women and girls with OCD, whereas tics, Tourette’s syndrome and alcohol dependence were more common in men and boys with OCD ...
... picking were more prevalent in women and girls with OCD, whereas tics, Tourette’s syndrome and alcohol dependence were more common in men and boys with OCD ...
Ch 12 Big Review backup.tst
... 84. An anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, inappropriate fears connected with public situations or performances in front of other people is ________. A) a specific phobia B) a social phobia C) agoraphobia D) generalized anxiety disorder 85. Feeling fearful but not knowing why is characteris ...
... 84. An anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, inappropriate fears connected with public situations or performances in front of other people is ________. A) a specific phobia B) a social phobia C) agoraphobia D) generalized anxiety disorder 85. Feeling fearful but not knowing why is characteris ...