Head and Neck Embryology and Anatomy
... to form the frontal sinuses. The orbital part of the frontal bone forms most part of the roof of the orbits. The orbital cavity is a vital anatomical part of the facial skeleton; it contains the eye and important neural and vascular elements and connective tissues. It is formed between the cranial t ...
... to form the frontal sinuses. The orbital part of the frontal bone forms most part of the roof of the orbits. The orbital cavity is a vital anatomical part of the facial skeleton; it contains the eye and important neural and vascular elements and connective tissues. It is formed between the cranial t ...
The Skeletal System: - North Seattle College
... IV. Pelvic Girdle Continue 2. The greater (false) and lesser (true) pelvis are anatomicaly separated by a plane at the pelvic brim. ...
... IV. Pelvic Girdle Continue 2. The greater (false) and lesser (true) pelvis are anatomicaly separated by a plane at the pelvic brim. ...
HUMAN SKELETAL REMAINS
... pterion. The frontal bones typically consist of a single plate of bone, the squamosal portion of the frontal bone, although in some adults it is divided into two halves by the metopic suture, whi ...
... pterion. The frontal bones typically consist of a single plate of bone, the squamosal portion of the frontal bone, although in some adults it is divided into two halves by the metopic suture, whi ...
Period 7 Lower Limb
... extend laterally from juncture of neck and shaft. Develop where large tendons attach to femur. ...
... extend laterally from juncture of neck and shaft. Develop where large tendons attach to femur. ...
bone quiz - Sinoe Medical Association
... A. Introduction 1. A human skull usually consists of ____________________________________ 2. The moveable bone in the skull is the _________________________________ 3. Some cranial and skull bones together form the ________________ of the eye. B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects ________ ...
... A. Introduction 1. A human skull usually consists of ____________________________________ 2. The moveable bone in the skull is the _________________________________ 3. Some cranial and skull bones together form the ________________ of the eye. B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects ________ ...
unit 1.1
... chicken wing and how do they compare to a human arm? Although many differences exist between the anatomy of humans and chickens, one structure that shows similarities in muscle pairing and range of motion is a bird’s wing. In this activity you will study chicken wing structure and function, which is ...
... chicken wing and how do they compare to a human arm? Although many differences exist between the anatomy of humans and chickens, one structure that shows similarities in muscle pairing and range of motion is a bird’s wing. In this activity you will study chicken wing structure and function, which is ...
1-BonesUpperLimb
... scapula. Anatomical neck: formed by a groove separating the head from the tubercles. Greater tubercle: at the lateral margin of the humerus. Lesser tubercle: projects anteriorly. The two tubercles are separated by Intertubercular Groove. Surgical Neck: a narrow part distal to the tubercles. It is a ...
... scapula. Anatomical neck: formed by a groove separating the head from the tubercles. Greater tubercle: at the lateral margin of the humerus. Lesser tubercle: projects anteriorly. The two tubercles are separated by Intertubercular Groove. Surgical Neck: a narrow part distal to the tubercles. It is a ...
kumc 26 suboccipital triangle student
... Anterior arch. Transverse process with foramina. Lateral masses: Articulation with occipital condyles. Articulation with axis. ...
... Anterior arch. Transverse process with foramina. Lateral masses: Articulation with occipital condyles. Articulation with axis. ...
Bones of upper limb
... Because the radius & ulna are firmly bound by the interosseous membrane, a fracture of one bone is commonly associated with dislocation of the nearest joint. Colle’ s fracture (fracture of the distal end of radius) is the most common fracture of the forearm. It is more common in women after mi ...
... Because the radius & ulna are firmly bound by the interosseous membrane, a fracture of one bone is commonly associated with dislocation of the nearest joint. Colle’ s fracture (fracture of the distal end of radius) is the most common fracture of the forearm. It is more common in women after mi ...
Frontal Bone
... to articulate with the zygomatic process of the maxilla, forming the lateral portion of the infraorbital rim. This concavity projects superiorly to form the frontal process that articulates with the frontal bone. Posteriorly, a temporal process articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal ...
... to articulate with the zygomatic process of the maxilla, forming the lateral portion of the infraorbital rim. This concavity projects superiorly to form the frontal process that articulates with the frontal bone. Posteriorly, a temporal process articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal ...
Skeletal System – Part 6
... the thigh bones, are deep and heavily reinforced by ligaments that attach the limbs firmly to the girdle. Functions of the Girdle: ...
... the thigh bones, are deep and heavily reinforced by ligaments that attach the limbs firmly to the girdle. Functions of the Girdle: ...
The laterl wall of the nose consists of medial surface of maxilla
... The sphenopalatine foramen is situated just behind the posterior end of the middle turbinate, which is part of the ethmoid. This foramen is formed by two processes of the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone and body of the sphenoid bone. This foramen serves as a communication between nasal cavi ...
... The sphenopalatine foramen is situated just behind the posterior end of the middle turbinate, which is part of the ethmoid. This foramen is formed by two processes of the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone and body of the sphenoid bone. This foramen serves as a communication between nasal cavi ...
lateral - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... – The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle – The Upper limb – The Pelvic (Hip) Girdle – The Lower limb • Developmental Aspects (Ch 7b) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... – The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle – The Upper limb – The Pelvic (Hip) Girdle – The Lower limb • Developmental Aspects (Ch 7b) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Paraxial mesoderm
... tibia are preaxial bones. -Ventral & dorsal surfaces: flexor muscles are ventral. During 7th week, adduction of limb buds occurs with 90° ...
... tibia are preaxial bones. -Ventral & dorsal surfaces: flexor muscles are ventral. During 7th week, adduction of limb buds occurs with 90° ...
anatomy of the ear
... is variably aerated, it is an area that can become infected and inflamed just as any of these anatomic areas can. Inflammation of this structure is called mastoiditis. There is a nerve for taste which goes through the middle ear without a bony covering which makes it somewhat susceptible to disease ...
... is variably aerated, it is an area that can become infected and inflamed just as any of these anatomic areas can. Inflammation of this structure is called mastoiditis. There is a nerve for taste which goes through the middle ear without a bony covering which makes it somewhat susceptible to disease ...
File
... Protraction is moving in an anterior (forward) direction. For example, sticking out your chin. Retraction is moving in a posterior (backward) direction. For example, squeezing your shoulder blades together. ...
... Protraction is moving in an anterior (forward) direction. For example, sticking out your chin. Retraction is moving in a posterior (backward) direction. For example, squeezing your shoulder blades together. ...
Document
... the frontalis inserts into the skin and subcutaneous and does not attach to the bone. Consequently, black eyes result from injury to the scalp/forehead. Most blood enter the upper eyelid, but some may also enter the lower one. ...
... the frontalis inserts into the skin and subcutaneous and does not attach to the bone. Consequently, black eyes result from injury to the scalp/forehead. Most blood enter the upper eyelid, but some may also enter the lower one. ...
Mnemonics
... Mnemonics The dictionary defines Mnemonics as a device, such as a formula or rhyme, used as an aid in remembering. Mnemonics are extremely useful in remembering hierarchal materials or for tests that require that the study remember definitions or descriptions of a term. Here are a few examples from ...
... Mnemonics The dictionary defines Mnemonics as a device, such as a formula or rhyme, used as an aid in remembering. Mnemonics are extremely useful in remembering hierarchal materials or for tests that require that the study remember definitions or descriptions of a term. Here are a few examples from ...
Temporomandibular joint
... • It has NO BONY ARTICULATION!!! • It is suspended from the styloid process of the temporal bone by the stylohyoid ligament • Main Function: attachment site for tongue muscles and muscles that open/close the jaw Lippert, p201 ...
... • It has NO BONY ARTICULATION!!! • It is suspended from the styloid process of the temporal bone by the stylohyoid ligament • Main Function: attachment site for tongue muscles and muscles that open/close the jaw Lippert, p201 ...
Bones of upper limb
... Because the radius & ulna are firmly bound by the interosseous membrane, a fracture of one bone is commonly associated with dislocation of the nearest joint. Colle’ s fracture (fracture of the distal end of radius) is the most common fracture of the forearm. It is more common in women after mi ...
... Because the radius & ulna are firmly bound by the interosseous membrane, a fracture of one bone is commonly associated with dislocation of the nearest joint. Colle’ s fracture (fracture of the distal end of radius) is the most common fracture of the forearm. It is more common in women after mi ...
Minneapolis Community and Technical College (MCTC): Biology
... Central canal: contains artery, vein, lymph vessel and nerve Concentric lamella (lamellae = plural) Osteocyte Lacuna (lacunae = plural) Canaliculus (canaliculi = plural) The Axial Skeleton Before you begin your study of the skeletal system, first study the definitions of general bone markings. The a ...
... Central canal: contains artery, vein, lymph vessel and nerve Concentric lamella (lamellae = plural) Osteocyte Lacuna (lacunae = plural) Canaliculus (canaliculi = plural) The Axial Skeleton Before you begin your study of the skeletal system, first study the definitions of general bone markings. The a ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepepharmanatomy.wordpress.com Bones
... The vertebral column in an adult typically consists of 33 vertebrae arranged in five regions: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal. The vertebrae gradually become larger as the vertebral column descends to the sacrum and then become progressively smaller toward the apex of th ...
... The vertebral column in an adult typically consists of 33 vertebrae arranged in five regions: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal. The vertebrae gradually become larger as the vertebral column descends to the sacrum and then become progressively smaller toward the apex of th ...
Bones (Osteology)
... The vertebral column in an adult typically consists of 33 vertebrae arranged in five regions: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal. The vertebrae gradually become larger as the vertebral column descends to the sacrum and then become progressively smaller toward the apex of th ...
... The vertebral column in an adult typically consists of 33 vertebrae arranged in five regions: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal. The vertebrae gradually become larger as the vertebral column descends to the sacrum and then become progressively smaller toward the apex of th ...
HEAD , FACIAL BONES, SINUSES, AND ORBITS
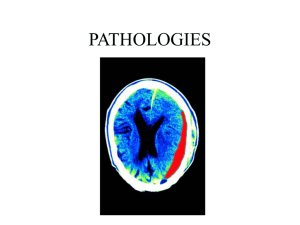
... Optic nerve gliomas are found in or around the nerves that send messages from the eyes to the brain. They are frequently found in persons who have neurofibromatosis, a condition a child is born with that makes him/her more likely to develop tumors in the brain. Persons usually experience loss of vis ...
... Optic nerve gliomas are found in or around the nerves that send messages from the eyes to the brain. They are frequently found in persons who have neurofibromatosis, a condition a child is born with that makes him/her more likely to develop tumors in the brain. Persons usually experience loss of vis ...
anatomy team
... C1 rotates. The most distinctive characteristic of this bone is (dens) odontoid process that rises perpendicularly from the upper surface of the body. ...
... C1 rotates. The most distinctive characteristic of this bone is (dens) odontoid process that rises perpendicularly from the upper surface of the body. ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.