Bone-Axial Skeleton - Indian Hills Community College
... Also in the skull you will find two big jaw bones. The top jaw bone is the Maxillae. And the bottom jaw bone is the Mandible. There will be features on each of these bones but we will talk about those in just a bit. Starting with the markings or features you will see a circle around something above ...
... Also in the skull you will find two big jaw bones. The top jaw bone is the Maxillae. And the bottom jaw bone is the Mandible. There will be features on each of these bones but we will talk about those in just a bit. Starting with the markings or features you will see a circle around something above ...
outline ear and senses - Social Circle City Schools
... 3. What are the locations and the functions of the 3 parts of the outer ear? Pinna (auricle) External auditory meatus (auditory canal) Tympanic Membrane ...
... 3. What are the locations and the functions of the 3 parts of the outer ear? Pinna (auricle) External auditory meatus (auditory canal) Tympanic Membrane ...
Review of Skeletal System (PDF)
... c. Tympanic portion of the Temporal Bone -- the area surrounding the External Auditory Meatus (ear) -- Lateral View: T-3 d. Mastoid ("rock-like") Process of the Temporal Bone -- a hard, rounded portion that can be felt right behind your earlobe -- inside is the mastoid air sinus, an air-filled cavit ...
... c. Tympanic portion of the Temporal Bone -- the area surrounding the External Auditory Meatus (ear) -- Lateral View: T-3 d. Mastoid ("rock-like") Process of the Temporal Bone -- a hard, rounded portion that can be felt right behind your earlobe -- inside is the mastoid air sinus, an air-filled cavit ...
lateral nasal wall comprising narrow, mucosal lined channels and
... mobile cilia projecting into the mucus, beating 12–15 times a second. The direction of ciliary beats is organized into well-defi ned pathways, present at birth. These mucociliary pathways ensure drainage of the sinuses through their physiological ostium into the nasal cavity ...
... mobile cilia projecting into the mucus, beating 12–15 times a second. The direction of ciliary beats is organized into well-defi ned pathways, present at birth. These mucociliary pathways ensure drainage of the sinuses through their physiological ostium into the nasal cavity ...
01-Introduction2008-10
... We hope that you will enjoy this course, as well as learn some morphology and histology. If you have any problems with the course work, please come and see one of us right away: we can often help you find a solution ...
... We hope that you will enjoy this course, as well as learn some morphology and histology. If you have any problems with the course work, please come and see one of us right away: we can often help you find a solution ...
Name: Investigation of a Chicken Wing Purpose The purpose of this
... 15. Name the two human bones most like the forelimb bones of the chicken wing. Radius, ulna 16. How many joints are there between the upper limb and the forelimb? one 17. What do we call the tissue that holds the bones together at the joints? tendons 18. What color is this connective tissue at the j ...
... 15. Name the two human bones most like the forelimb bones of the chicken wing. Radius, ulna 16. How many joints are there between the upper limb and the forelimb? one 17. What do we call the tissue that holds the bones together at the joints? tendons 18. What color is this connective tissue at the j ...
Vertebral Column and Thoracic Cage Lab
... 7. The pedicles, laminae, and spinous process of a vertebra form the _______________. 8. The intervertebral foramina provide passageways for _______________. 9. Transverse foramina of cervical vertebrae serve as passageways for _______________ leading to the brain. 10. The first vertebra is also cal ...
... 7. The pedicles, laminae, and spinous process of a vertebra form the _______________. 8. The intervertebral foramina provide passageways for _______________. 9. Transverse foramina of cervical vertebrae serve as passageways for _______________ leading to the brain. 10. The first vertebra is also cal ...
An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton
... • Are bound by dense fibrous connective tissue • Are found only in skull ...
... • Are bound by dense fibrous connective tissue • Are found only in skull ...
notes#10 - DENTISTRY 2012
... - inferior surface of greater wing of sphenoid is the floor of infratemporal fossa, that is related to the middle cranial “fossa superior view” , consists of : * foramen ovale mandibular nerve * foramen spinosum middle meningeal artery - inferatemporal part of maxilla (posterior surface of maxil ...
... - inferior surface of greater wing of sphenoid is the floor of infratemporal fossa, that is related to the middle cranial “fossa superior view” , consists of : * foramen ovale mandibular nerve * foramen spinosum middle meningeal artery - inferatemporal part of maxilla (posterior surface of maxil ...
Bones of upper limb
... Because the radius & ulna are firmly bound by the interosseous membrane, a fracture of one bone is commonly associated with dislocation of the nearest joint. Colle’ s fracture (fracture of the distal end of radius) is the most common fracture of the forearm. It is more common in women after mi ...
... Because the radius & ulna are firmly bound by the interosseous membrane, a fracture of one bone is commonly associated with dislocation of the nearest joint. Colle’ s fracture (fracture of the distal end of radius) is the most common fracture of the forearm. It is more common in women after mi ...
Brain Stem Gross Anatomy
... Blood Flow to Brain two sources #1 via Internal Carotid Arteries (ICAs) extends up into the skull via the carotid canal projects up to the cavernous sinus gives rise to opthalmic artery (OA) located at the origin of the optic nerve at the base of the brain gives rise to anterior choroidal artery (A ...
... Blood Flow to Brain two sources #1 via Internal Carotid Arteries (ICAs) extends up into the skull via the carotid canal projects up to the cavernous sinus gives rise to opthalmic artery (OA) located at the origin of the optic nerve at the base of the brain gives rise to anterior choroidal artery (A ...
Page 0 of 41
... visualized from neither any surface of the skull& y see it will form things . for example, ethmoid bone , y see that this bone contribute to forming part of the anterior cranial fossa , it will form the part of the septum of the nose &part of the lateral wall of the nose , sometimes y will be able t ...
... visualized from neither any surface of the skull& y see it will form things . for example, ethmoid bone , y see that this bone contribute to forming part of the anterior cranial fossa , it will form the part of the septum of the nose &part of the lateral wall of the nose , sometimes y will be able t ...
Axial skeleton
... • air-filled spaces connected to nasal cavity • named for bones in which they occur – frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary ...
... • air-filled spaces connected to nasal cavity • named for bones in which they occur – frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary ...
Lower Limb
... • AKA “articulations” – functional junctions between bones • Functions: – Bind parts of the skeletal system – Make bone growth possible – Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth – Enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions ...
... • AKA “articulations” – functional junctions between bones • Functions: – Bind parts of the skeletal system – Make bone growth possible – Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth – Enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions ...
Pathology Codes - Museum of London
... The bilateral, symmetrical nature of the new bone plaques observed in the lower legs suggests some kind of systemic infection. It’s possible the changes in the feet may be related to this possible infection. The compact new bone to the anterior vertebrae is suspicious; given the marked retro-auricul ...
... The bilateral, symmetrical nature of the new bone plaques observed in the lower legs suggests some kind of systemic infection. It’s possible the changes in the feet may be related to this possible infection. The compact new bone to the anterior vertebrae is suspicious; given the marked retro-auricul ...
The Skeletal System: Bones and Joints
... Each long bone consists of a shaft, called the (1) , and a(n) (2) at each end of the bone. A long bone that is still growing has a(n) (3) , composed of cartilage, between each epiphysis and the diaphysis. When bone growth stops, the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone, and is called the (4) . The l ...
... Each long bone consists of a shaft, called the (1) , and a(n) (2) at each end of the bone. A long bone that is still growing has a(n) (3) , composed of cartilage, between each epiphysis and the diaphysis. When bone growth stops, the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone, and is called the (4) . The l ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... Arches transfer weight from 1 part of the foot to another ...
... Arches transfer weight from 1 part of the foot to another ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... Arches transfer weight from 1 part of the foot to another ...
... Arches transfer weight from 1 part of the foot to another ...
The Skull - OpenStax CNX
... The frontal bone is the single bone that forms the forehead. At its anterior midline, between the eyebrows, there is a slight depression called the glabella (see Figure 3 (Lateral View of Skull )). The frontal bone also forms the supraorbital margin of the orbit. Near the middle of this margin, is t ...
... The frontal bone is the single bone that forms the forehead. At its anterior midline, between the eyebrows, there is a slight depression called the glabella (see Figure 3 (Lateral View of Skull )). The frontal bone also forms the supraorbital margin of the orbit. Near the middle of this margin, is t ...
Movement
... between the sphenoid ahead and the occipital one behind. The end of its behind going thumb, in inside in top creates a movement of inflection, whereas its thenar eminence going ahead, in inside and top creates the opposite movement. ...
... between the sphenoid ahead and the occipital one behind. The end of its behind going thumb, in inside in top creates a movement of inflection, whereas its thenar eminence going ahead, in inside and top creates the opposite movement. ...
Movement
... between the sphenoid ahead and the occipital one behind. The end of its behind going thumb, in inside in top creates a movement of inflection, whereas its thenar eminence going ahead, in inside and top creates the opposite movement. ...
... between the sphenoid ahead and the occipital one behind. The end of its behind going thumb, in inside in top creates a movement of inflection, whereas its thenar eminence going ahead, in inside and top creates the opposite movement. ...
Face Morphology
... International nomenclature committee, similar to ISCN, Human Genome Variation Society nomenclature, with periodic discussion and revision ...
... International nomenclature committee, similar to ISCN, Human Genome Variation Society nomenclature, with periodic discussion and revision ...
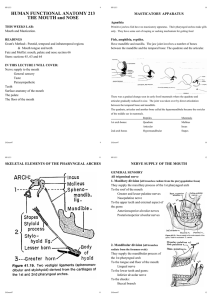
HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY 213 THE MOUTH and NOSE
... There was a gradual change seen in early fossil mammals where the quadrate and articular gradually reduced in size. The joint was taken over by direct articulation between the temporal bone and mandible. The quadrate, articular and another bone called the hypermandibula became the ossicles of the mi ...
... There was a gradual change seen in early fossil mammals where the quadrate and articular gradually reduced in size. The joint was taken over by direct articulation between the temporal bone and mandible. The quadrate, articular and another bone called the hypermandibula became the ossicles of the mi ...
Skeletal Packet
... bones! The traditional lyrics are listed below. Fill in the blanks that follow to make the song more scientific. Your toe bone connected to your foot bone Your foot bone connected to your ankle bone Your ankle bone connected to your leg bone Your leg bone connected to your knee bone Your knee bone c ...
... bones! The traditional lyrics are listed below. Fill in the blanks that follow to make the song more scientific. Your toe bone connected to your foot bone Your foot bone connected to your ankle bone Your ankle bone connected to your leg bone Your leg bone connected to your knee bone Your knee bone c ...
L1-Nose, Nasal cavity & Paranasal sinuses & Pharynx 2014
... Nose, is the only visible part of the respiratory system and serves as the entrance to the respiratory tract The nose has two cavities, separated from one another by a wall called the septum. The external openings, known as external (anterior) nares or nostrils, lead to the nasal cavities. F ...
... Nose, is the only visible part of the respiratory system and serves as the entrance to the respiratory tract The nose has two cavities, separated from one another by a wall called the septum. The external openings, known as external (anterior) nares or nostrils, lead to the nasal cavities. F ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.