PPT - UCLA Health
... There is persistent disease involving the ant wall of the frontal sinus or the sinus itself ...
... There is persistent disease involving the ant wall of the frontal sinus or the sinus itself ...
ch_06_lecture_with_notes
... cells are called ________, and ________ are boneresorbing cells. 6. If the activity of osteoclasts exceeds that of osteoblasts in a bone, how will the mass of the bone be affected? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... cells are called ________, and ________ are boneresorbing cells. 6. If the activity of osteoclasts exceeds that of osteoblasts in a bone, how will the mass of the bone be affected? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Cranial Nonmetric Trait Database User Guide
... classification as either 4 hypostotic or 5 hyperostotic, while certain traits classed primarily as hyperostotic also have a relationship to nerves or blood vessels. Some well-known traits have been excluded from the files. These are the tori (maxillary, mandibular, palatal and auditory) likely to be ...
... classification as either 4 hypostotic or 5 hyperostotic, while certain traits classed primarily as hyperostotic also have a relationship to nerves or blood vessels. Some well-known traits have been excluded from the files. These are the tori (maxillary, mandibular, palatal and auditory) likely to be ...
Anatomy Mnemonics Inner Wall Bones of Orbit (7) Bones of the Wrist
... S2, S3, S4 Keep the ass up off the floor Innervation of the Diaphragm C3, C4, C5 Keep the diaphragm alive. Spatial Relations Position of the Mitral Valve The mitral (bicuspid) valve is so named because its two cusps resemble a bishop’s crown, or mitre. ...
... S2, S3, S4 Keep the ass up off the floor Innervation of the Diaphragm C3, C4, C5 Keep the diaphragm alive. Spatial Relations Position of the Mitral Valve The mitral (bicuspid) valve is so named because its two cusps resemble a bishop’s crown, or mitre. ...
Joints - El Camino College
... b. The interior of the capsule is lined with a ___________ membrane of loose CT, which produces a lubricating fluid (___________ fluid) that reduces friction 2. Articulating surfaces of the bones are covered with articular (_________) cartilage 3. The articular capsule is usually reinforced with ___ ...
... b. The interior of the capsule is lined with a ___________ membrane of loose CT, which produces a lubricating fluid (___________ fluid) that reduces friction 2. Articulating surfaces of the bones are covered with articular (_________) cartilage 3. The articular capsule is usually reinforced with ___ ...
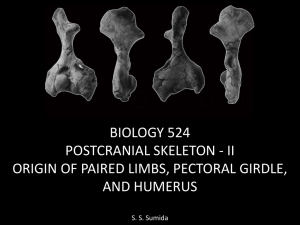
Week 6 Powerpoint - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... have had a continuous , laterally directed stabilizing structure one each side of the body. It is further hypothesized that the pectoral (fore) and pelvic (hind) fins were pieced out of these elongate, transsegmental structures. ...
... have had a continuous , laterally directed stabilizing structure one each side of the body. It is further hypothesized that the pectoral (fore) and pelvic (hind) fins were pieced out of these elongate, transsegmental structures. ...
Microsurgical anatomy of the retroauricular
... Published online 3 September, 2003 © neuroanatomy.org ...
... Published online 3 September, 2003 © neuroanatomy.org ...
ch_06_lecture_presentation
... cells are called ________, and ________ are boneresorbing cells. 6. If the activity of osteoclasts exceeds that of osteoblasts in a bone, how will the mass of the bone be affected? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... cells are called ________, and ________ are boneresorbing cells. 6. If the activity of osteoclasts exceeds that of osteoblasts in a bone, how will the mass of the bone be affected? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Ch 6 notes-
... • Houses brain and sense organs for sight, smell, taste, and balance • Total of 22 bones • 8 form the cranium • Forming cranial cavity, which houses brain • 14 are facial bones • Also includes associated bones, 6 auditory ossicles, and one hyoid bone © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Houses brain and sense organs for sight, smell, taste, and balance • Total of 22 bones • 8 form the cranium • Forming cranial cavity, which houses brain • 14 are facial bones • Also includes associated bones, 6 auditory ossicles, and one hyoid bone © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Maxillary Reconstruction
... The space between the restored anterior, superior, and inferior walls of the maxilla can usually be filled with soft tissue (muscle/fat) nasal lining may or may not be necessarily restored. The temporalis flap covers bone effectively in these types of reconstruction but does not close the pala ...
... The space between the restored anterior, superior, and inferior walls of the maxilla can usually be filled with soft tissue (muscle/fat) nasal lining may or may not be necessarily restored. The temporalis flap covers bone effectively in these types of reconstruction but does not close the pala ...
Soft Tissue of the Back
... and, if they reach anywhere on the skull, they are called capitis. E.G., Iliocostalis lumborum ...
... and, if they reach anywhere on the skull, they are called capitis. E.G., Iliocostalis lumborum ...
Bones of the Upper Limb Bone Structure Description Notes clavicle an
... an "S" shaped bone located it articulates medially with the manubrium of the between the sternum and sternum and laterally with the acromion process of the scapula the scapula; it forms a strut that supports the upper limb; it is frequently fractured; it is the first bone to begin ossification durin ...
... an "S" shaped bone located it articulates medially with the manubrium of the between the sternum and sternum and laterally with the acromion process of the scapula the scapula; it forms a strut that supports the upper limb; it is frequently fractured; it is the first bone to begin ossification durin ...
Surgical approaches
... vii. This can be accomplished by reapproximating the suprahyoid musculature or with non-absorbable suspension sutures from the mandible. 2. Subhyoid approach a. useful for lesions of the tongue base that have either directly invaded the hyoid bone, or have neck metastases that involve the hyoid bone ...
... vii. This can be accomplished by reapproximating the suprahyoid musculature or with non-absorbable suspension sutures from the mandible. 2. Subhyoid approach a. useful for lesions of the tongue base that have either directly invaded the hyoid bone, or have neck metastases that involve the hyoid bone ...
13anat1
... Temporal Bone • Petrous portion (not shown). Located at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Houses inner ear and internal auditory canal (IAC connects inner ear with brainstem). Levator palatini muscle is attached to Petrous portion. • Styloid Process (not shown). Locate ...
... Temporal Bone • Petrous portion (not shown). Located at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Houses inner ear and internal auditory canal (IAC connects inner ear with brainstem). Levator palatini muscle is attached to Petrous portion. • Styloid Process (not shown). Locate ...
Understanding the Fascial planes of head and Neck
... Sternothyroid, Omohyoid, Thyrohyoid • Runs between hyoid bone and clavicle • Thickens to form a pulley through which the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle passes, suspending the hyoid bone ...
... Sternothyroid, Omohyoid, Thyrohyoid • Runs between hyoid bone and clavicle • Thickens to form a pulley through which the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle passes, suspending the hyoid bone ...
Ossification - Evolutionary Morphology of Vertebrates
... skull reinforcement occurs almost simultaneously, with a whole set of perichondral bones arising especially at places of high mechanical load. The suspensorium becomes protected against dislocation in an anteroposterior direction through a ligamentous connection, which even becomes partially ossifie ...
... skull reinforcement occurs almost simultaneously, with a whole set of perichondral bones arising especially at places of high mechanical load. The suspensorium becomes protected against dislocation in an anteroposterior direction through a ligamentous connection, which even becomes partially ossifie ...
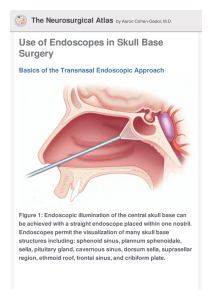
Use of Endoscopes in Skull Base Surgery
... face can be removed with kerrison punches and a drill. Bone excision can be extended laterally on each side of the sella to the anterior face of the cavernous sinus. Dural incision can be made superior and inferior to the intercavernous sinus, and the sinus can then be coagulated and removed. Proxim ...
... face can be removed with kerrison punches and a drill. Bone excision can be extended laterally on each side of the sella to the anterior face of the cavernous sinus. Dural incision can be made superior and inferior to the intercavernous sinus, and the sinus can then be coagulated and removed. Proxim ...
Assiut university researches Functional Morphological Study of the
... kinesis due to the presence of immovable naso-frontal hinge. However, the quadrate can glide antero-posteriorly and vice versa. While, in the budgerigar, the brain case exhibits a high kinesis due to the presence of movable naso-frontal hinge. 2) The brain case of the budgerigar is characterized by ...
... kinesis due to the presence of immovable naso-frontal hinge. However, the quadrate can glide antero-posteriorly and vice versa. While, in the budgerigar, the brain case exhibits a high kinesis due to the presence of movable naso-frontal hinge. 2) The brain case of the budgerigar is characterized by ...
Growth and Development 3
... Growth of the Lips The lips trail behind the growth of the jaws prior to adolescence, and then undergo a growth spurt to catch up. Because lip height is relatively short during the mixed dentition years, lip separation at rest (often termed lip incompetence) is maximal during childhood and decreases ...
... Growth of the Lips The lips trail behind the growth of the jaws prior to adolescence, and then undergo a growth spurt to catch up. Because lip height is relatively short during the mixed dentition years, lip separation at rest (often termed lip incompetence) is maximal during childhood and decreases ...
Meninges (singular Meninx)
... 1. Infraorbital artery gives branches to anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries. Their distribution to the maxillary incisors and cuspid teeth and to the maxillary sinuses. 2. Posterior superior alveolar artery. Its distribution is to the maxillary molar and premolar teeth and gingiva. 3. In ...
... 1. Infraorbital artery gives branches to anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries. Their distribution to the maxillary incisors and cuspid teeth and to the maxillary sinuses. 2. Posterior superior alveolar artery. Its distribution is to the maxillary molar and premolar teeth and gingiva. 3. In ...
9-Ear Final (2o15-16)
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
Skull Base Forgotten Foramina: A CT Pictorial Review
... This persistent bony canal can occasionally be detected in the sphenoid bone extending from the sella turcica to the pharynx (Fig. 5 on page 10 ). It is best referred to as an intrasphenoidal canal. The incidence of the craniopharyngeal canal has been calculated as 0.42% from a retrospective analysi ...
... This persistent bony canal can occasionally be detected in the sphenoid bone extending from the sella turcica to the pharynx (Fig. 5 on page 10 ). It is best referred to as an intrasphenoidal canal. The incidence of the craniopharyngeal canal has been calculated as 0.42% from a retrospective analysi ...
Veins of the Face and the Neck The facial vein is formed at the
... maxillary veins .On leaving the parotid salivary gland, it divides into an anterior branch, which joins the facial vein, and a posterior branch, which joins the posterior auricular vein to form the external jugular vein. ...
... maxillary veins .On leaving the parotid salivary gland, it divides into an anterior branch, which joins the facial vein, and a posterior branch, which joins the posterior auricular vein to form the external jugular vein. ...
The Primitive Cynodont Procynosuchus: Functional Anatomy of the
... The upper left dentition consists of five incisors within the premaxilla, an incisiform tooth whose alveolus is formed from the premaxilla internally and the maxilla externally, two incisiform teeth within the maxilla, a canine, and ten postcanine teeth. As the distinction between an incisor and a p ...
... The upper left dentition consists of five incisors within the premaxilla, an incisiform tooth whose alveolus is formed from the premaxilla internally and the maxilla externally, two incisiform teeth within the maxilla, a canine, and ten postcanine teeth. As the distinction between an incisor and a p ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.