Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes (9/28-29/2016)
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
PEKE - Science
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... faster it rotates the wider the spectral lines are • Measuring rotation speed allows us to estimate luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
... faster it rotates the wider the spectral lines are • Measuring rotation speed allows us to estimate luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
Work and Energy - mrweaverphysics
... •Identify the types of energy that make up the total energy of a system •Predict changes in mechanical energy when positive or negative work is done on the center of mass •Analyze a system and categorize the internal energy as potential, kinetic, or some combination of potential and kinetic. •Solve ...
... •Identify the types of energy that make up the total energy of a system •Predict changes in mechanical energy when positive or negative work is done on the center of mass •Analyze a system and categorize the internal energy as potential, kinetic, or some combination of potential and kinetic. •Solve ...
Ch. 26.5: The Expanding Universe
... Dark Matter = Does not give off radiation & cannot be detected Exerts gravitational force on visible matter Universe may be 90% + dark matter Why do we think Dark Matter exists? Galaxies are accelerating faster than they should be (based on the observable matter in the Universe). The acceleration du ...
... Dark Matter = Does not give off radiation & cannot be detected Exerts gravitational force on visible matter Universe may be 90% + dark matter Why do we think Dark Matter exists? Galaxies are accelerating faster than they should be (based on the observable matter in the Universe). The acceleration du ...
review
... from measuring the curvature of space. Flat universe has critical density, W0=1 . Closed or positive curvature universe has higher than critical density and Open or negative curvature universe has lower than critical density. The cosmic microwave background lets us measure the curvature. CMB has tin ...
... from measuring the curvature of space. Flat universe has critical density, W0=1 . Closed or positive curvature universe has higher than critical density and Open or negative curvature universe has lower than critical density. The cosmic microwave background lets us measure the curvature. CMB has tin ...
Perimeter Dark Matter Online Game Worksheet #2 1. Match the
... 3. Scientists observed the speeds of stars in galaxies were: a. Faster than theory predicted b. Slower than theory predicted c. In agreement with theory 4. The following graph is: ...
... 3. Scientists observed the speeds of stars in galaxies were: a. Faster than theory predicted b. Slower than theory predicted c. In agreement with theory 4. The following graph is: ...
Lecture 20, PPT version
... • if universe has been expanding at constant rate for all time, then all galaxies would have been on top of each other at time equal to 1/H0 Distance between any two galaxy clusters at the present day: distance = speed x time (the standard formula) speed = H0 x distance (Hubble’s Law, specifically) ...
... • if universe has been expanding at constant rate for all time, then all galaxies would have been on top of each other at time equal to 1/H0 Distance between any two galaxy clusters at the present day: distance = speed x time (the standard formula) speed = H0 x distance (Hubble’s Law, specifically) ...
Forms of Energy Quiz - RRMS 8th Grade Science
... C. Total energy of the particles that make up an object. Higher temperature, particles move faster. ...
... C. Total energy of the particles that make up an object. Higher temperature, particles move faster. ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... – Much greater and the Universe would already have collapsed in on itself – Much less and stars could not have formed ...
... – Much greater and the Universe would already have collapsed in on itself – Much less and stars could not have formed ...
Expansion of the Universe
... 1. Scattering of blue and green light - i.e. why the sky appears blue, and why some sunrises or sunsets may appear red. Dust, smoke from forest fires, or other intervening material between the source and the observer can scatter (remove) the higher frequency colors (blue, green, yellow, and orange) ...
... 1. Scattering of blue and green light - i.e. why the sky appears blue, and why some sunrises or sunsets may appear red. Dust, smoke from forest fires, or other intervening material between the source and the observer can scatter (remove) the higher frequency colors (blue, green, yellow, and orange) ...
Small angle equation:
... where 29.8 km s is the Earth’s orbital velocity, and r and a are the distance of the object from the Sun and the semi-major axis of its orbit, respectively, in Astronomical Units (A.U.). ...
... where 29.8 km s is the Earth’s orbital velocity, and r and a are the distance of the object from the Sun and the semi-major axis of its orbit, respectively, in Astronomical Units (A.U.). ...
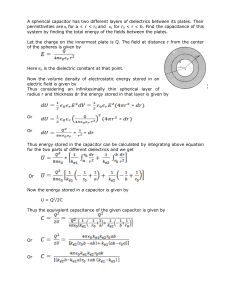
A spherical capacitor has two different layers of
... A spherical capacitor has two different layers of dielectrics between its plates. Their permittivities are ϵ1 for a < r < r0 and ϵ2 for r0 < r < b. Find the capacitance of this system by finding the total energy of the fields between the plates. Let the charge on the innermost plate is Q. The field ...
... A spherical capacitor has two different layers of dielectrics between its plates. Their permittivities are ϵ1 for a < r < r0 and ϵ2 for r0 < r < b. Find the capacitance of this system by finding the total energy of the fields between the plates. Let the charge on the innermost plate is Q. The field ...
The Components and Origin of the Universe
... think of raison bread dough…….you are sitting on a single raison and so it appears you are sitting still The ...
... think of raison bread dough…….you are sitting on a single raison and so it appears you are sitting still The ...
Origins Of The Universe
... concentrated into a single incredibly tiny point This began to enlarge rapidly in a hot explosion, and it is still expanding today – this Big Bang happened about 15 billion years ago ...
... concentrated into a single incredibly tiny point This began to enlarge rapidly in a hot explosion, and it is still expanding today – this Big Bang happened about 15 billion years ago ...
Dark energy

In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy which is hypothesized to permeate all of space, tending to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted hypothesis to explain the observations since the 1990s indicating that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. Assuming that the standard model of cosmology is correct, the best current measurements indicate that dark energy contributes 68.3% of the total energy in the present-day observable universe. The mass–energy of dark matter and ordinary matter contribute 26.8% and 4.9%, respectively, and other components such as neutrinos and photons contribute a very small amount. Again on a mass–energy equivalence basis, the density of dark energy (6.91 × 10−27 kg/m3) is very low, much less than the density of ordinary matter or dark matter within galaxies. However, it comes to dominate the mass–energy of the universe because it is uniform across space.Two proposed forms for dark energy are the cosmological constant, a constant energy density filling space homogeneously, and scalar fields such as quintessence or moduli, dynamic quantities whose energy density can vary in time and space. Contributions from scalar fields that are constant in space are usually also included in the cosmological constant. The cosmological constant can be formulated to be equivalent to vacuum energy. Scalar fields that do change in space can be difficult to distinguish from a cosmological constant because the change may be extremely slow.High-precision measurements of the expansion of the universe are required to understand how the expansion rate changes over time and space. In general relativity, the evolution of the expansion rate is parameterized by the cosmological equation of state (the relationship between temperature, pressure, and combined matter, energy, and vacuum energy density for any region of space). Measuring the equation of state for dark energy is one of the biggest efforts in observational cosmology today.Adding the cosmological constant to cosmology's standard FLRW metric leads to the Lambda-CDM model, which has been referred to as the ""standard model of cosmology"" because of its precise agreement with observations. Dark energy has been used as a crucial ingredient in a recent attempt to formulate a cyclic model for the universe.