Energy and Work - Stanley Teacher Prep
... created or destroyed, only changes state – As you move back and forth, energy is converted from kinetic to potential back to kinetic energy continuously – So why does the swing eventually stop? ...
... created or destroyed, only changes state – As you move back and forth, energy is converted from kinetic to potential back to kinetic energy continuously – So why does the swing eventually stop? ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Problems
... 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcase. The height of each shelf is 1.0 meters, 1.5 meters, and 2.0 meters. 4) If you had a book that had a mass of 2.7 kg and it is sitting on a desk that is 2 meters off the ground, what is th ...
... 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcase. The height of each shelf is 1.0 meters, 1.5 meters, and 2.0 meters. 4) If you had a book that had a mass of 2.7 kg and it is sitting on a desk that is 2 meters off the ground, what is th ...
ITB - In the Beginning
... The Hot Big Bang (the standard model) Developed in the late 1940’s by Gamow– named by Hoyle as an “insult” – it is the current basic model. Out of “nothingness”; the universe has a tiny, hot, beginning – then expands. As the energy-universe expands, it cools enough for matter to form (E=mc2), then ...
... The Hot Big Bang (the standard model) Developed in the late 1940’s by Gamow– named by Hoyle as an “insult” – it is the current basic model. Out of “nothingness”; the universe has a tiny, hot, beginning – then expands. As the energy-universe expands, it cools enough for matter to form (E=mc2), then ...
Work and Energy PPT - Aurora City Schools
... This is the energy that an object possesses due to its position of being stretched or deformed FOR A SPRING (or similar)… EPE= ½ k x2 x = amount of stretch k = the spring constant (a characteristic of the object being stretched) ...
... This is the energy that an object possesses due to its position of being stretched or deformed FOR A SPRING (or similar)… EPE= ½ k x2 x = amount of stretch k = the spring constant (a characteristic of the object being stretched) ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • Indication that the Universe is expanding, and it has been ever since it was created in the Big Bang about 13 billion years ago • Understanding how the expansion rate changes with time tells us about the inherent mass and energy which makes up the Universe, a more precise values for its age, and w ...
... • Indication that the Universe is expanding, and it has been ever since it was created in the Big Bang about 13 billion years ago • Understanding how the expansion rate changes with time tells us about the inherent mass and energy which makes up the Universe, a more precise values for its age, and w ...
Unit8TheUniverse
... A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. ...
... A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. ...
PPT - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... This dark matter is believed to surround most galaxies, and the massto-light ratio for certain galaxies can exceed 300 times that of the sun. ...
... This dark matter is believed to surround most galaxies, and the massto-light ratio for certain galaxies can exceed 300 times that of the sun. ...
Energy and energy resources
... Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually be silent) Light- the ...
... Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually be silent) Light- the ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned into kinetic energy when you start running around or into potential energy when you climb up to the top of the slide and wait before sliding down. Energy cannot be created or d ...
... batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned into kinetic energy when you start running around or into potential energy when you climb up to the top of the slide and wait before sliding down. Energy cannot be created or d ...
Earth Science
... 9. Describe the Inflationary Model and draw the graph. 18. As the Earth orbits the Sun, what happens to the orientation of the Earth’s axis? 10. Match the following terms with their definitions. ___ Big Bang theory ___ steady-state theory ___ cosmic background radiation ___ inflationary universe A. ...
... 9. Describe the Inflationary Model and draw the graph. 18. As the Earth orbits the Sun, what happens to the orientation of the Earth’s axis? 10. Match the following terms with their definitions. ___ Big Bang theory ___ steady-state theory ___ cosmic background radiation ___ inflationary universe A. ...
Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS) Observation
... • Coordinate the space by means of static reference points in the sky. • Four such (quasi) static points are the equinoxes and solstices. • We use the Spring Solstice as the zero point of one coordinate. • CAUTION! The solstice actually ...
... • Coordinate the space by means of static reference points in the sky. • Four such (quasi) static points are the equinoxes and solstices. • We use the Spring Solstice as the zero point of one coordinate. • CAUTION! The solstice actually ...
Bang To Sol - Transcript
... particles to form. Today, quarks only exist in tightly bound groups, but back then, space was so small and quarks were squeezed so close together that they were not bound to other specific quarks. The colors of these quarks just represent a property that attracts them to one another. There are two k ...
... particles to form. Today, quarks only exist in tightly bound groups, but back then, space was so small and quarks were squeezed so close together that they were not bound to other specific quarks. The colors of these quarks just represent a property that attracts them to one another. There are two k ...
Chapter 12
... is closed and that there is enough matter in the universe to slow (because of gravity) and eventually stop the expansion of the universe. According to this theory, all matter will meet again in a Big Crunch. 5. Cosmic background radiation is the radiation left over from the Big Bang expansion. ...
... is closed and that there is enough matter in the universe to slow (because of gravity) and eventually stop the expansion of the universe. According to this theory, all matter will meet again in a Big Crunch. 5. Cosmic background radiation is the radiation left over from the Big Bang expansion. ...
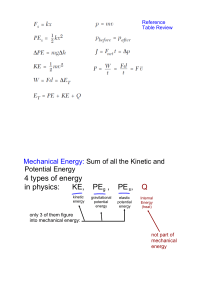
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
The Prelude - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to form low energy gammaray photons that can not reverse the process •As a result, matter and anti-matter content decreased, and radiation content increased •From 1 second to 380,000 years, the universe is ...
... •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to form low energy gammaray photons that can not reverse the process •As a result, matter and anti-matter content decreased, and radiation content increased •From 1 second to 380,000 years, the universe is ...
Dark energy

In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy which is hypothesized to permeate all of space, tending to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted hypothesis to explain the observations since the 1990s indicating that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. Assuming that the standard model of cosmology is correct, the best current measurements indicate that dark energy contributes 68.3% of the total energy in the present-day observable universe. The mass–energy of dark matter and ordinary matter contribute 26.8% and 4.9%, respectively, and other components such as neutrinos and photons contribute a very small amount. Again on a mass–energy equivalence basis, the density of dark energy (6.91 × 10−27 kg/m3) is very low, much less than the density of ordinary matter or dark matter within galaxies. However, it comes to dominate the mass–energy of the universe because it is uniform across space.Two proposed forms for dark energy are the cosmological constant, a constant energy density filling space homogeneously, and scalar fields such as quintessence or moduli, dynamic quantities whose energy density can vary in time and space. Contributions from scalar fields that are constant in space are usually also included in the cosmological constant. The cosmological constant can be formulated to be equivalent to vacuum energy. Scalar fields that do change in space can be difficult to distinguish from a cosmological constant because the change may be extremely slow.High-precision measurements of the expansion of the universe are required to understand how the expansion rate changes over time and space. In general relativity, the evolution of the expansion rate is parameterized by the cosmological equation of state (the relationship between temperature, pressure, and combined matter, energy, and vacuum energy density for any region of space). Measuring the equation of state for dark energy is one of the biggest efforts in observational cosmology today.Adding the cosmological constant to cosmology's standard FLRW metric leads to the Lambda-CDM model, which has been referred to as the ""standard model of cosmology"" because of its precise agreement with observations. Dark energy has been used as a crucial ingredient in a recent attempt to formulate a cyclic model for the universe.