The earliest datable observation of the aurora borealis
... The most common colour in the high-latitude aurora is green. However, the relatively rare aurorae that are seen at low latitudes are most commonly red and consequently are known as great red aurorae. Such aurorae are observed most frequently in a general northerly direction from a particular site, b ...
... The most common colour in the high-latitude aurora is green. However, the relatively rare aurorae that are seen at low latitudes are most commonly red and consequently are known as great red aurorae. Such aurorae are observed most frequently in a general northerly direction from a particular site, b ...
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
Apr 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... The planetary spotlight shines brightest on Jupiter this month. Jupiter reaches opposition on the 7th, the position in it’s orbit when it is directly opposite the Sun from the Earth. At opposition, it will be just 414 million miles from Earth. This opposition, however, occurs close to Jupiter being ...
... The planetary spotlight shines brightest on Jupiter this month. Jupiter reaches opposition on the 7th, the position in it’s orbit when it is directly opposite the Sun from the Earth. At opposition, it will be just 414 million miles from Earth. This opposition, however, occurs close to Jupiter being ...
The Planetarium Fleischmann Planetarium
... light up in ultraviolet because they are filled with hot, newborn stars, objects that pack most of their light into ultraviolet wavelengths. Older galaxies have less star-forming activity and thus give off less ultraviolet light. Both young and old stars radiate visible light, so young and old galax ...
... light up in ultraviolet because they are filled with hot, newborn stars, objects that pack most of their light into ultraviolet wavelengths. Older galaxies have less star-forming activity and thus give off less ultraviolet light. Both young and old stars radiate visible light, so young and old galax ...
VNOS/VOSI-ASTR
... “birth” of stars in various nebulae as well as conducted study of our own star, the Sun. Astronomers used specific evidence of what stars look like from viewing them with the naked eye and then through telescopes. At first they just drew records of what they saw but as technology developed, they wer ...
... “birth” of stars in various nebulae as well as conducted study of our own star, the Sun. Astronomers used specific evidence of what stars look like from viewing them with the naked eye and then through telescopes. At first they just drew records of what they saw but as technology developed, they wer ...
Binary Star - Armagh Observatory
... float off into the atmosphere along with all of the other matter on Earth. ...
... float off into the atmosphere along with all of the other matter on Earth. ...
astro 001 - courses.psu.edu
... does not change its distance above the horizon, as depicted above maintains its altitude above the horizon, as depicted above, but gradually drifts eastward, so that eventually it appears directly above the east point on the horion e) By the time we get to Florida, Polaris certainly will have disapp ...
... does not change its distance above the horizon, as depicted above maintains its altitude above the horizon, as depicted above, but gradually drifts eastward, so that eventually it appears directly above the east point on the horion e) By the time we get to Florida, Polaris certainly will have disapp ...
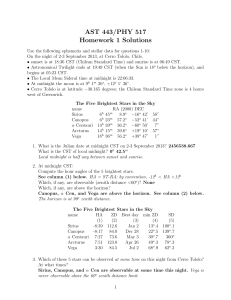
review1
... Q1.35 A person with good vision can see details that subtend an angle of as small as 1 arcminute. If two dark lines on an eye chart are 2 millimeters apart, how far can such a person be from the chart and still be able to tell that there are two distinct lines? Give your answer in meters. ...
... Q1.35 A person with good vision can see details that subtend an angle of as small as 1 arcminute. If two dark lines on an eye chart are 2 millimeters apart, how far can such a person be from the chart and still be able to tell that there are two distinct lines? Give your answer in meters. ...
Visualization of eclipses and planetary conjunction events. The
... different distances from the spectator in the center. The near (metereological) sphere contains a cloudtexture, the far sphere consist of a texture for fixed stars on the firmament. Both spheres are moving with different speeds, no further animation is required. However, sun and moon are moving inde ...
... different distances from the spectator in the center. The near (metereological) sphere contains a cloudtexture, the far sphere consist of a texture for fixed stars on the firmament. Both spheres are moving with different speeds, no further animation is required. However, sun and moon are moving inde ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... Another reason why you obtain lower temperatures is that the Interstellar space is not a perfect vacuum. The interstellar medium (ISM) comprises cold neutral gas (H I at ≈ 70 K), warm neutral gas (H I at 6,000 K) and hot ionised plasma (H II at 10 6 K) primarily located in the plane of the galaxy in ...
... Another reason why you obtain lower temperatures is that the Interstellar space is not a perfect vacuum. The interstellar medium (ISM) comprises cold neutral gas (H I at ≈ 70 K), warm neutral gas (H I at 6,000 K) and hot ionised plasma (H II at 10 6 K) primarily located in the plane of the galaxy in ...
The Sun - GeoScience
... Click on “Advanced” at the top of the page 1. Where is our Sun located in our solar system? Click on “Interior” from the list on the left 2. a. Name the inner most layer of the sun. b. What occurs in this layer? Click on “Surface of the Sun” in the text 3. What is the name of the ‘surface of the sun ...
... Click on “Advanced” at the top of the page 1. Where is our Sun located in our solar system? Click on “Interior” from the list on the left 2. a. Name the inner most layer of the sun. b. What occurs in this layer? Click on “Surface of the Sun” in the text 3. What is the name of the ‘surface of the sun ...
02-02Stars_Part_One
... The idea here is that the total power is spread out over the area of an sphere whose surface is where you are, with the center on the star. ...
... The idea here is that the total power is spread out over the area of an sphere whose surface is where you are, with the center on the star. ...
The Sun and other Stars
... When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
... When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
Origin of stars
... cloud collapses gravitationally into a star … is still a challenging theoretical problem… Astronomers have yet to find an interstellar cloud in the actual process of collapse.” ...
... cloud collapses gravitationally into a star … is still a challenging theoretical problem… Astronomers have yet to find an interstellar cloud in the actual process of collapse.” ...
The Italic School in Astronomy: From Pythagoras to Archimedes
... apparent motion of the sun, therefore, is composed by its daily motion, the circle route from east to west, due to the rotation of the heaven of the fixed stars, and by a contemporary slow moving eastward along the ecliptic. This also appears to be inclined with respect to the celestial equator of 2 ...
... apparent motion of the sun, therefore, is composed by its daily motion, the circle route from east to west, due to the rotation of the heaven of the fixed stars, and by a contemporary slow moving eastward along the ecliptic. This also appears to be inclined with respect to the celestial equator of 2 ...
Some Basic Principles from Astronomy
... object defines a lower limit on the radius, r, of the observable Universe. We will return to this. ...
... object defines a lower limit on the radius, r, of the observable Universe. We will return to this. ...
the copernican revolution - University of Florida Astronomy
... 2. Explain how the observed motions of the planets led to our modern view of a Sun-centered solar system. 3. Describe the major contributions of Galileo and Kepler to our understanding of the solar system. 4. State Kepler's laws of planetary motion. 5. Explain how astronomers have measured the true ...
... 2. Explain how the observed motions of the planets led to our modern view of a Sun-centered solar system. 3. Describe the major contributions of Galileo and Kepler to our understanding of the solar system. 4. State Kepler's laws of planetary motion. 5. Explain how astronomers have measured the true ...
5th
... the constellation of Perseus, which is a northern constellation, named after the Greek hero who slew the monster Medusa. However, they can be spotted all around the sky. Because of the positioning of Swift-Tuttle’s orbit, Perseids are mostly visible on the northern hemisphere. ...
... the constellation of Perseus, which is a northern constellation, named after the Greek hero who slew the monster Medusa. However, they can be spotted all around the sky. Because of the positioning of Swift-Tuttle’s orbit, Perseids are mostly visible on the northern hemisphere. ...
Branches of Earth Science Tools Used to Study Stars Constellations
... o Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light the star actually gives off ...
... o Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light the star actually gives off ...
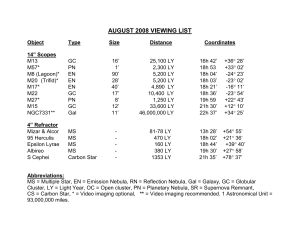
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... July–August–September Objects The following information may help you understand why these objects are on the Night Sky Checklists. Constellations and asterisms (Astronomers recognize 88 official constellations, but asterisms are unofficial and made from parts of one or more constellation. All are im ...
... July–August–September Objects The following information may help you understand why these objects are on the Night Sky Checklists. Constellations and asterisms (Astronomers recognize 88 official constellations, but asterisms are unofficial and made from parts of one or more constellation. All are im ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.