Chapter 12: Chemical Periodicity
... - low densities and melting points - good electrical conductivity - the most reactive metals - react with oxygen and moisture in the air - they will react violently with water and are stored under oil or kerosene - due to their reactivity, they are not found uncombined in nature ...
... - low densities and melting points - good electrical conductivity - the most reactive metals - react with oxygen and moisture in the air - they will react violently with water and are stored under oil or kerosene - due to their reactivity, they are not found uncombined in nature ...
UNIT 6: PERIODICITY THE FOREST: Repeating (periodic) patterns
... Describe the locations in the periodic table and the general properties of the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals, the halogens, and the noble gases. Use the periodic table to predict the electron configurations of elements. Give examples of the relationship between an element’s electron confi ...
... Describe the locations in the periodic table and the general properties of the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals, the halogens, and the noble gases. Use the periodic table to predict the electron configurations of elements. Give examples of the relationship between an element’s electron confi ...
PPT_Topic1d_Higher
... Trends in Elements To keep oxygen away from the titanium when it was extracted it was important to convert the titanium oxide into another compound that did not contain any oxygen which could then have pure titanium extracted from it. In order to achieve this chemists needed to find another non met ...
... Trends in Elements To keep oxygen away from the titanium when it was extracted it was important to convert the titanium oxide into another compound that did not contain any oxygen which could then have pure titanium extracted from it. In order to achieve this chemists needed to find another non met ...
S8P1-a-and-f-study-guide
... particles that carry a positive charge. Neutrons are particles that carry no electric charge. The nucleus is the center of the atom that is made up of both protons and neutrons. Electrons are particles that carry a negative charge and surround the nucleus in what is know as the electron cloud on ene ...
... particles that carry a positive charge. Neutrons are particles that carry no electric charge. The nucleus is the center of the atom that is made up of both protons and neutrons. Electrons are particles that carry a negative charge and surround the nucleus in what is know as the electron cloud on ene ...
Uint one - pisscience
... 2-He had to put more than one element in one cell in his table because he could not deal with isotops which are forms of elements are different in their atomic weights. Rutherford He discovered that the nucleus of the atom contains positively charged protons. Moseley's Periodic Table: *He discovered ...
... 2-He had to put more than one element in one cell in his table because he could not deal with isotops which are forms of elements are different in their atomic weights. Rutherford He discovered that the nucleus of the atom contains positively charged protons. Moseley's Periodic Table: *He discovered ...
AKS Review
... Groups(families)- vertical column on periodic table. Elements in the same family have similar properties because they have the same valence electron configuration Periodic law- “Properties of elements are a Periodic Function of the atomic number.” When elements are arranged by increasing atomic numb ...
... Groups(families)- vertical column on periodic table. Elements in the same family have similar properties because they have the same valence electron configuration Periodic law- “Properties of elements are a Periodic Function of the atomic number.” When elements are arranged by increasing atomic numb ...
Chapter 6
... • appeared to be a repetition of properties every eighth element • arranged elements into groups of 7 • Law of Octaves – same properties repeat every 8th element • (but it didn’t account for Noble gases and transition metals) ...
... • appeared to be a repetition of properties every eighth element • arranged elements into groups of 7 • Law of Octaves – same properties repeat every 8th element • (but it didn’t account for Noble gases and transition metals) ...
Chemistry test Review
... of an atom or its parts? Is this the same general unit we use for everything else? Why/why not? • Amu – Atomic mass unit • It is not the same as a gram – Because atoms and their particles are way too small to use the normal mass measurement system so scientists had to come up with a new way to measu ...
... of an atom or its parts? Is this the same general unit we use for everything else? Why/why not? • Amu – Atomic mass unit • It is not the same as a gram – Because atoms and their particles are way too small to use the normal mass measurement system so scientists had to come up with a new way to measu ...
Chapter 4 – Atomic Structure (Sec 4.2 pages 108
... Transition Metals • Some transition elements have more properties in common than elements in other groups. – Elements in the lanthanide and actinide series – These elements are so similar that chemists in the 1800s had difficulty separating them when they were found mixed together in nature. ...
... Transition Metals • Some transition elements have more properties in common than elements in other groups. – Elements in the lanthanide and actinide series – These elements are so similar that chemists in the 1800s had difficulty separating them when they were found mixed together in nature. ...
Our modern Periodic Table
... Atomic Number - number of protons Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
... Atomic Number - number of protons Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
Holt Modern Chemistry -
... o transition element -- one of the metals that can use the inner shell before using the outer shell to bond o main-group element -- an element in the s-block or p-block of the periodic table o halogen -- one of the elements of Group 17 (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine); halogens co ...
... o transition element -- one of the metals that can use the inner shell before using the outer shell to bond o main-group element -- an element in the s-block or p-block of the periodic table o halogen -- one of the elements of Group 17 (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine); halogens co ...
Periodicity Periodic Table Periodic Properties
... 7.10 The History of the Periodic Table 7.11 The Aufbau Principles and the Periodic Table 7.12 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties 7.13 The Properties of a Group: The Alkali Metals ...
... 7.10 The History of the Periodic Table 7.11 The Aufbau Principles and the Periodic Table 7.12 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties 7.13 The Properties of a Group: The Alkali Metals ...
General Structure of the Periodic Table
... In the sixty-seven years from Dalton's formulation of atomic weight to Mendeleyev's periodic table many scientists had tried to create a working organizational structure for the elements. Mendeleyev succeeded where others failed because he realized that there existed a number of as yet unknown eleme ...
... In the sixty-seven years from Dalton's formulation of atomic weight to Mendeleyev's periodic table many scientists had tried to create a working organizational structure for the elements. Mendeleyev succeeded where others failed because he realized that there existed a number of as yet unknown eleme ...
Unit 2 Outline
... number of unpaired electrons results (Hund’s Rule). Energy levels are designated 1–7. Orbitals are designated s, p, d, and f according to their shapes s, p, d, f orbitals relate to the regions of the Periodic Table. Loss of electrons from neutral atoms results in the formation of an ion with a ...
... number of unpaired electrons results (Hund’s Rule). Energy levels are designated 1–7. Orbitals are designated s, p, d, and f according to their shapes s, p, d, f orbitals relate to the regions of the Periodic Table. Loss of electrons from neutral atoms results in the formation of an ion with a ...
The Periodic Table
... In the periodic table, elements have something in common if they are in the same row. All of the elements in a period have the same number of atomic shells/orbitals. ...
... In the periodic table, elements have something in common if they are in the same row. All of the elements in a period have the same number of atomic shells/orbitals. ...
A Level Chemistry B (Salters) Lesson Element Teachers` Instructions
... 17. Which of these has the higher first ionisation enthalpy? Radium or barium? (6) 20. Which of these has the higher boiling point? Magnesium or aluminium? (9) 21. All the elements in the s-block are these. (8,6) 22. This measures how strongly an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond. (17) ...
... 17. Which of these has the higher first ionisation enthalpy? Radium or barium? (6) 20. Which of these has the higher boiling point? Magnesium or aluminium? (9) 21. All the elements in the s-block are these. (8,6) 22. This measures how strongly an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond. (17) ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE The Periodic Table lists all known
... than the one before. There are a few reasons for this. Firstly, it is always harder to remove an electron from a positively-charged ion (a cation) than from a neutral atom. The higher the charge on the cation, the more difficult it is to ionise. Secondly, an ionisation energy depends on the electron ...
... than the one before. There are a few reasons for this. Firstly, it is always harder to remove an electron from a positively-charged ion (a cation) than from a neutral atom. The higher the charge on the cation, the more difficult it is to ionise. Secondly, an ionisation energy depends on the electron ...
The placement of an element on the periodic table gives clues about
... The repeating pattern across the periods of the periodic table is the filling of each energy level with electrons. For example, since hydrogen and helium are in period 1, they only have electrons in the 1st energy level. Since potassium, calcium, and bromine are in the 4th row or period, their outer ...
... The repeating pattern across the periods of the periodic table is the filling of each energy level with electrons. For example, since hydrogen and helium are in period 1, they only have electrons in the 1st energy level. Since potassium, calcium, and bromine are in the 4th row or period, their outer ...
The Periodic Table
... element is called an ATOM. • An element is a PURE substance, containing only one kind of ATOM. • The PERIODIC TABLE is a list of all the elements that have been discovered and named, with each element listed in its own element square. • Elements are represented on the Periodic Table by a one or two ...
... element is called an ATOM. • An element is a PURE substance, containing only one kind of ATOM. • The PERIODIC TABLE is a list of all the elements that have been discovered and named, with each element listed in its own element square. • Elements are represented on the Periodic Table by a one or two ...
Document
... The energy needed to remove one electron from every atom in 1 mole of a gaseous element X(g) X+(g) +eThis is the number of vibrations per second. The units are Hertz (Hz). E=h. h is the Planck constant and is 6.6.3 x 10-34 J Hz-1.. E is energy in joules (J). The joining together of 2 small nuclei ...
... The energy needed to remove one electron from every atom in 1 mole of a gaseous element X(g) X+(g) +eThis is the number of vibrations per second. The units are Hertz (Hz). E=h. h is the Planck constant and is 6.6.3 x 10-34 J Hz-1.. E is energy in joules (J). The joining together of 2 small nuclei ...
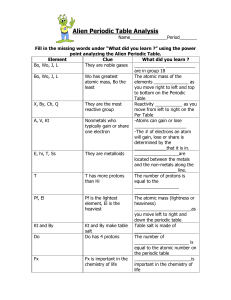
Alien Periodic Table Analysis
... They are the most Reactivity ___________ as you reactive group move from left to right on the Per Table A, V, Kt Nonmetals who -Atoms can gain or lose typically gain or share _____________________ one electron -The # of electrons an atom will gain, lose or share is determined by the _____________tha ...
... They are the most Reactivity ___________ as you reactive group move from left to right on the Per Table A, V, Kt Nonmetals who -Atoms can gain or lose typically gain or share _____________________ one electron -The # of electrons an atom will gain, lose or share is determined by the _____________tha ...
Periodic Table
... Each horizontal row across the table is called a ___________________________. A period contains a ________________________________________________of elements from ___________________________________, just as a week on a calendar has a series of different days. Unlike the elements in a ______________ ...
... Each horizontal row across the table is called a ___________________________. A period contains a ________________________________________________of elements from ___________________________________, just as a week on a calendar has a series of different days. Unlike the elements in a ______________ ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.