ADHD information
... Whilst the fundamental diagnostic criteria for ADHD have not changed in the DSM5TM compared with the previous version, the DSM-5TM has been updated to more accurately characterize the experience of adolescents and adults with ADHD. This has been achieved with the inclusion of additional examples to ...
... Whilst the fundamental diagnostic criteria for ADHD have not changed in the DSM5TM compared with the previous version, the DSM-5TM has been updated to more accurately characterize the experience of adolescents and adults with ADHD. This has been achieved with the inclusion of additional examples to ...
View Presentation
... Abnormal Behavior versus Psychological Disorders • Abnormal behavior is defined by culture. • Psychological disorders are defined by psychologists and psychiatrists (in Western culture). ...
... Abnormal Behavior versus Psychological Disorders • Abnormal behavior is defined by culture. • Psychological disorders are defined by psychologists and psychiatrists (in Western culture). ...
Mental Health for Law Enforcement
... - Severity of Psychosocial Stressors (Axis IV) Events such as death, job, employment that can impact a conditions. (Psst…this is where you pay attention) ...
... - Severity of Psychosocial Stressors (Axis IV) Events such as death, job, employment that can impact a conditions. (Psst…this is where you pay attention) ...
Psychological Disorders
... Behavior patterns or mental processes that cause personal suffering or interfere with daily life ...
... Behavior patterns or mental processes that cause personal suffering or interfere with daily life ...
The neuropharmacology of impulsive behaviour
... Impulsivity is not defined in a separate diagnostic category in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders version IV (DSM-IV) [6], but is a key characteristic of several psychiatric disorders. Treating impulsivity therefore might represent a novel intervention strategy. Here, we will ...
... Impulsivity is not defined in a separate diagnostic category in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders version IV (DSM-IV) [6], but is a key characteristic of several psychiatric disorders. Treating impulsivity therefore might represent a novel intervention strategy. Here, we will ...
Personality Disorders Continued
... reinforcement in one’s life. Ambivalent individuals = conflicted over whether they should follow what others want them to do or follow their own needs and wishes. “Anxious – fearful” cluster with anxiety & tension prominent symptoms. OCPD: extreme rigidity, preoccupation with details & perfect ...
... reinforcement in one’s life. Ambivalent individuals = conflicted over whether they should follow what others want them to do or follow their own needs and wishes. “Anxious – fearful” cluster with anxiety & tension prominent symptoms. OCPD: extreme rigidity, preoccupation with details & perfect ...
Friday, October 29
... Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Differences in rates of depression between men & women Explaining depressive disorders (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
... Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Differences in rates of depression between men & women Explaining depressive disorders (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
Chapter 14- Psychological disorders
... anxiety disorders Cognitive: people who suffer from anxiety disorders may chronically overestimate the severity of a perceived threat ...
... anxiety disorders Cognitive: people who suffer from anxiety disorders may chronically overestimate the severity of a perceived threat ...
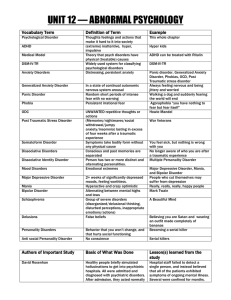
unit 12 — abnormal psychology
... fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience Symptoms take bodily form without any physical cause Conscious and past memories are sep ...
... fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience Symptoms take bodily form without any physical cause Conscious and past memories are sep ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Identity Disorder – (multiple personality disorder) – Eve (22), Sybil (16) – 2 or more separate and distinct identities – May or may not be aware of each other – Common cause is severe abuse at a young age ...
... Identity Disorder – (multiple personality disorder) – Eve (22), Sybil (16) – 2 or more separate and distinct identities – May or may not be aware of each other – Common cause is severe abuse at a young age ...
DM-ID-2: Growing Pains in Our Understanding of Psychiatric
... Accommodation with the basic issues related to borderline/mild v. severe/profound IDD- not taking into account qualitative differences, nor consideration of a novel approach to diagnosis Not specifically adapted for the special problems posed by ASD- will we need a new set of criteria or assessment ...
... Accommodation with the basic issues related to borderline/mild v. severe/profound IDD- not taking into account qualitative differences, nor consideration of a novel approach to diagnosis Not specifically adapted for the special problems posed by ASD- will we need a new set of criteria or assessment ...
Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders
... BUT no physiological basis can be found Emotions Physical Symptoms ...
... BUT no physiological basis can be found Emotions Physical Symptoms ...
Module 36 Chapter 110 Essentials of Understanding
... Bipolar Disorders (Manic-Depressive Disorder) ...
... Bipolar Disorders (Manic-Depressive Disorder) ...
What Causes Mental Illness?
... – Having two or more distinct personalities, which can show different physical conditions and are often the exact opposite of each other ...
... – Having two or more distinct personalities, which can show different physical conditions and are often the exact opposite of each other ...
Changing Brains Changes the Game: Clinical Relevance of Habit
... possibly have in common with the one suffering from alcoholism or BED. Studies that examine the brains of patients with eating disorders provide that deeper look. A recent study published in Nature Neuroscience highlights the role of altered brain circuitry underlying compulsive food choices (low ca ...
... possibly have in common with the one suffering from alcoholism or BED. Studies that examine the brains of patients with eating disorders provide that deeper look. A recent study published in Nature Neuroscience highlights the role of altered brain circuitry underlying compulsive food choices (low ca ...
Disruptive, Impulse Control, and Conduct Disorders
... control, and conduct disorders is new to DSM-5. It combines disorders that were previously included among disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence (that is, oppositional defiant disorder; conduct disorder; other specified and unspecified disruptive, impulse-control, an ...
... control, and conduct disorders is new to DSM-5. It combines disorders that were previously included among disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence (that is, oppositional defiant disorder; conduct disorder; other specified and unspecified disruptive, impulse-control, an ...
Abnormal Psychology
... What is the DSM-IV? How is the DSM-IV used by psychologists? Why the DSM-IV only bases diagnoses on observable patterns of behavior? self-fulfilling prophecies What is the difference between neurotic disorders and psychotic disorders? The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship betwee ...
... What is the DSM-IV? How is the DSM-IV used by psychologists? Why the DSM-IV only bases diagnoses on observable patterns of behavior? self-fulfilling prophecies What is the difference between neurotic disorders and psychotic disorders? The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship betwee ...
Psychological Disorders
... These are disorders in which individuals have symptoms typically associated with physical diseases or conditions, but in which no known organic or physiological basis for the symptoms can be found. ...
... These are disorders in which individuals have symptoms typically associated with physical diseases or conditions, but in which no known organic or physiological basis for the symptoms can be found. ...
Slide 1 - Barrington 220
... when combined with a sharp intellect the result may be a con artist ...
... when combined with a sharp intellect the result may be a con artist ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Possible Origins and Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder The cause of Borderline Personality disorder is still unclear. Research shows that chemical imbalances in the brain and other biological factors may be involved, such as heredity. Childhood trauma, such as abuse and neglect, have also be ...
... Possible Origins and Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder The cause of Borderline Personality disorder is still unclear. Research shows that chemical imbalances in the brain and other biological factors may be involved, such as heredity. Childhood trauma, such as abuse and neglect, have also be ...
Unit XII: Abnormal Behavior
... The goal of the Operation Beautiful website is to end negative self-talk or “Fat Talk.” ...
... The goal of the Operation Beautiful website is to end negative self-talk or “Fat Talk.” ...
Impulsivity
Impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a multifactorial construct that involves a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically ""poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences,"" which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. ""When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality"" Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least the two independent components of, first: acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and, second: choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.Impulsivity is both a facet of personality as well as a major component of various disorders, including ADHD, substance use disorders, bipolar disorder, antisocial personality disorder, and borderline personality disorder. Impulsiveness may also be a factor in procrastination. Abnormal patterns of impulsivity have also been noted instances of acquired brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiological findings suggest that there are specific brain regions involved in impulsive behavior, although different brain networks may contribute to different manifestations of impulsivity, and that genetics may play a role.Many actions contain both impulsive and compulsive features, but impulsivity and compulsivity are functionally distinct. Impulsivity and compulsivity are interrelated in that each exhibits a tendency to act prematurely or without considered thought and often include negative outcomes. Compulsivity may be on a continuum with compulsivity on one end and impulsivity on the other, but research has been contradictory on this point. Compulsivity occurs in response to a perceived risk or threat, impulsivity occurs in response to a perceived immediate gain or benefit, and, whereas compulsivity involves repetitive actions, impulsivity involves unplanned reactions.