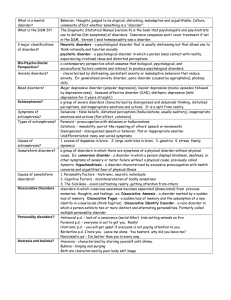
Psychological Disorders notes
... Major depressive disorder (unipolar depression), bipolar depression (mainic episodes followed by depressive ones), Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), disthymic depression (mild depression for 2 years straight.) a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, distur ...
... Major depressive disorder (unipolar depression), bipolar depression (mainic episodes followed by depressive ones), Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), disthymic depression (mild depression for 2 years straight.) a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, distur ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
Abnormal Psychology - AP Psychology Community
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
Psy 258 Behaviorism
... Responsive to cues to punishment, frustration, uncertainty, and motivates ceasing, inhibiting, or avoidance behavior Active BIS produces anxiety, active BAS produces impulsivity ...
... Responsive to cues to punishment, frustration, uncertainty, and motivates ceasing, inhibiting, or avoidance behavior Active BIS produces anxiety, active BAS produces impulsivity ...
A mental or emotional condition that makes it difficult for
... Mental Disorders – A mental or emotional condition that makes it difficult for a person to live in a normal way ...
... Mental Disorders – A mental or emotional condition that makes it difficult for a person to live in a normal way ...
2. Personality Disorders
... would clear up in a few days. Laura is concerned because she is sure the ear infection is the sign of something much more serious, such as a brain tumor, and she has made appointments with three different specialists to ...
... would clear up in a few days. Laura is concerned because she is sure the ear infection is the sign of something much more serious, such as a brain tumor, and she has made appointments with three different specialists to ...
CHAPTER 18
... B. Explaining Mood Disorders 1. Psychological View - psychoanalysts: because they suffered real or imagined loss of an object or person in childhood. Behaviorists: learned helplessness causes depression. Cognitive: some people are prone to depression because of their habitual style of a negative int ...
... B. Explaining Mood Disorders 1. Psychological View - psychoanalysts: because they suffered real or imagined loss of an object or person in childhood. Behaviorists: learned helplessness causes depression. Cognitive: some people are prone to depression because of their habitual style of a negative int ...
Psychological Disorders
... Classifying Psychological Disorders • What is the DSM-IV? Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: the book to classify mental disorders • In 2012- updated version = DSM V ...
... Classifying Psychological Disorders • What is the DSM-IV? Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: the book to classify mental disorders • In 2012- updated version = DSM V ...
Power point
... • This person may then mis-interpret how others respond to her and begin believing these things ...
... • This person may then mis-interpret how others respond to her and begin believing these things ...
File
... Symptom substitution- happens in other types of therapy when the underlying problem is not addressed; person will have a new psychological ...
... Symptom substitution- happens in other types of therapy when the underlying problem is not addressed; person will have a new psychological ...
Personality Disorders
... limited. Emotions are usually a key aspect of treatment of this disorder. Patients often have had little or no significant emotionally-rewarding relationships in their lives. The therapeutic relationship, therefore, can be one of the first ones. This can be very scary for the client, initially ...
... limited. Emotions are usually a key aspect of treatment of this disorder. Patients often have had little or no significant emotionally-rewarding relationships in their lives. The therapeutic relationship, therefore, can be one of the first ones. This can be very scary for the client, initially ...
Mental Illness 101 - Chagrin Falls Schools
... There will be legitimate physical problems but no physical cause…often related to stressors ...
... There will be legitimate physical problems but no physical cause…often related to stressors ...
Psychological Disorders
... Know the 5 types and delusional disorders and their characteristics (erotomanic, grandiose, etc) List the characteristics of schizophrenia Know the 4 types of schizophrenia Define Mood Disorder Define Depressive and bipolar disorders Define moderate mood disorder What are the symptoms of dysthymic d ...
... Know the 5 types and delusional disorders and their characteristics (erotomanic, grandiose, etc) List the characteristics of schizophrenia Know the 4 types of schizophrenia Define Mood Disorder Define Depressive and bipolar disorders Define moderate mood disorder What are the symptoms of dysthymic d ...
Chapter 10
... Chapter 10. Personality Disorders Personality disorders -Diagnosed on the Axis II, along with MR in the DSM-V, but no more in the current DSM-IV. -Definitions: An enduring pattern of cognition, affectivity, interpersonal functioning, and/or impulse control that deviates form the expectations of the ...
... Chapter 10. Personality Disorders Personality disorders -Diagnosed on the Axis II, along with MR in the DSM-V, but no more in the current DSM-IV. -Definitions: An enduring pattern of cognition, affectivity, interpersonal functioning, and/or impulse control that deviates form the expectations of the ...
Personality Disorders - Identification & Treatment
... General Information • Data from 2001-2002 National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions suggest that 15% of U.S adults have at least one personality disorder. • People frequently have more than one cooccurring personality disorder • It is extremely common for people with other p ...
... General Information • Data from 2001-2002 National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions suggest that 15% of U.S adults have at least one personality disorder. • People frequently have more than one cooccurring personality disorder • It is extremely common for people with other p ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
Abnormal Psychology - West Essex High School
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
el-Guebaly - University of Calgary
... Restless or irritable when cutting down/ stop Unsuccessful efforts to control, stop… Preoccupied with gambling ...
... Restless or irritable when cutting down/ stop Unsuccessful efforts to control, stop… Preoccupied with gambling ...
Child and Adolescent Psychopathology
... processing could contribute to poor reinforcement learning, poor executive functioning, and even poor motor coordination. ...
... processing could contribute to poor reinforcement learning, poor executive functioning, and even poor motor coordination. ...
Impulsivity
Impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a multifactorial construct that involves a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically ""poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences,"" which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. ""When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality"" Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least the two independent components of, first: acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and, second: choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.Impulsivity is both a facet of personality as well as a major component of various disorders, including ADHD, substance use disorders, bipolar disorder, antisocial personality disorder, and borderline personality disorder. Impulsiveness may also be a factor in procrastination. Abnormal patterns of impulsivity have also been noted instances of acquired brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiological findings suggest that there are specific brain regions involved in impulsive behavior, although different brain networks may contribute to different manifestations of impulsivity, and that genetics may play a role.Many actions contain both impulsive and compulsive features, but impulsivity and compulsivity are functionally distinct. Impulsivity and compulsivity are interrelated in that each exhibits a tendency to act prematurely or without considered thought and often include negative outcomes. Compulsivity may be on a continuum with compulsivity on one end and impulsivity on the other, but research has been contradictory on this point. Compulsivity occurs in response to a perceived risk or threat, impulsivity occurs in response to a perceived immediate gain or benefit, and, whereas compulsivity involves repetitive actions, impulsivity involves unplanned reactions.























