No Slide Title
... in the water is caused when the bacteria consuming the dead algae is pulled from the water, leading to the suffocation of aquatic life like fish. ...
... in the water is caused when the bacteria consuming the dead algae is pulled from the water, leading to the suffocation of aquatic life like fish. ...
1 Types of Chemical Reactions
... Chemical Changes are represented by word equations and chemical equations. When propane gas burns in air it produces carbon dioxide and water. The word equation for this reaction is: Reactants Products propane + oxygen => carbon dioxide + water are consumed are produced The chemical equation is: C3 ...
... Chemical Changes are represented by word equations and chemical equations. When propane gas burns in air it produces carbon dioxide and water. The word equation for this reaction is: Reactants Products propane + oxygen => carbon dioxide + water are consumed are produced The chemical equation is: C3 ...
AP® Biology Scoring Guidelines Question 7 The diagram above
... Increase in plant stratification (increased layering of plants; e.g., canopy, understory). More niches/habitats formed (plants, animals, decomposers). Pioneer plant species dominants (more shade-tolerant plants emerge). Increase in producer diversity brings about increase in consumer diversity. ...
... Increase in plant stratification (increased layering of plants; e.g., canopy, understory). More niches/habitats formed (plants, animals, decomposers). Pioneer plant species dominants (more shade-tolerant plants emerge). Increase in producer diversity brings about increase in consumer diversity. ...
`Angyo Star` Fatshedera > Fact Sheet
... x Fatshedera lizei ‘Angyo Star’ Hybrid between Fatsia japonica and English ivy, these plants have the best of both parents. Giant ivy leaves provide color in darker locations, but will not root into stucco or spread where it is not wanted. Stems will need to be staked or supported. Can be used indoo ...
... x Fatshedera lizei ‘Angyo Star’ Hybrid between Fatsia japonica and English ivy, these plants have the best of both parents. Giant ivy leaves provide color in darker locations, but will not root into stucco or spread where it is not wanted. Stems will need to be staked or supported. Can be used indoo ...
1 The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle of Forest Ecosystems
... however, it assimilates inorganic N and releases organic N in form of litter. Depending on conditions, the N cycle shows a number of nested cycles during decomposition. Mycorrhizae are capable of breaking down proteins (Abuzinadah and Read 1986) and most likely contribute to the capacity of plants t ...
... however, it assimilates inorganic N and releases organic N in form of litter. Depending on conditions, the N cycle shows a number of nested cycles during decomposition. Mycorrhizae are capable of breaking down proteins (Abuzinadah and Read 1986) and most likely contribute to the capacity of plants t ...
1 The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle of Forest Ecosystems
... however, it assimilates inorganic N and releases organic N in form of litter. Depending on conditions, the N cycle shows a number of nested cycles during decomposition. Mycorrhizae are capable of breaking down proteins (Abuzinadah and Read 1986) and most likely contribute to the capacity of plants t ...
... however, it assimilates inorganic N and releases organic N in form of litter. Depending on conditions, the N cycle shows a number of nested cycles during decomposition. Mycorrhizae are capable of breaking down proteins (Abuzinadah and Read 1986) and most likely contribute to the capacity of plants t ...
Ecology-Weathering-Erosion-and-Changes-in-the
... Groundwater will keep going lower in elevation until it reaches a layer of impermeable rock below the aquifer. This rock acts like a barrier and the water can't move down any deeper. As groundwater and carbon dioxide mix they form carbonic acid and cause erosion in cracks enlarging in the limest ...
... Groundwater will keep going lower in elevation until it reaches a layer of impermeable rock below the aquifer. This rock acts like a barrier and the water can't move down any deeper. As groundwater and carbon dioxide mix they form carbonic acid and cause erosion in cracks enlarging in the limest ...
Geology
... through a vent or fissure (also released are gases carbon dioxide, water vapor, hydrogen sulfide, ash, and other ejecta Mt. St. Helens – worst US volcano disaster ...
... through a vent or fissure (also released are gases carbon dioxide, water vapor, hydrogen sulfide, ash, and other ejecta Mt. St. Helens – worst US volcano disaster ...
Table 1: Greenhouse area by Crop in Macedonia
... In the rest of the area, growers do not apply any sterilization method, but they use various plant protection products such as fungicides, nematicides, insecticides and herbicides. These are used either to prevent, according to the history of soil, or to suppress the pest when there is evidence to d ...
... In the rest of the area, growers do not apply any sterilization method, but they use various plant protection products such as fungicides, nematicides, insecticides and herbicides. These are used either to prevent, according to the history of soil, or to suppress the pest when there is evidence to d ...
J Gruv - Nutrientspart1
... Most growers believe that high rates of nutrients are needed to produce high yields of high quality vegetables ...
... Most growers believe that high rates of nutrients are needed to produce high yields of high quality vegetables ...
1st Semester Post Test Study Guide 2010 – 2011 KEY 1. Define
... 34.Explain the two types of weathering. Give examples of each. chemical and mechanical processes that break down the surface Mechanical weathering is the type of weathering in which rock is physically broken into smaller pieces. Ex. ice wedging, abrasion, plants, animals, release of pressure Chemica ...
... 34.Explain the two types of weathering. Give examples of each. chemical and mechanical processes that break down the surface Mechanical weathering is the type of weathering in which rock is physically broken into smaller pieces. Ex. ice wedging, abrasion, plants, animals, release of pressure Chemica ...
CTS Earth Processes
... A. Changes are always sudden B. Earth never changes. It’s old? C. Process of soil, forms clay, forms rock D. Distinguishing rocks and minerals, confused about minerals E. Metamorphic changes in animals F. Rocks with layers sedimentary G. All mountains are volcanoes H. Limited concept of rocks I. ...
... A. Changes are always sudden B. Earth never changes. It’s old? C. Process of soil, forms clay, forms rock D. Distinguishing rocks and minerals, confused about minerals E. Metamorphic changes in animals F. Rocks with layers sedimentary G. All mountains are volcanoes H. Limited concept of rocks I. ...
SLSN, 11-14-08,CTS Notes (Earth Processes)
... b. Imagining geologic time will be difficult c. Improve understanding of continental movement by multiplying small increments by large numbers of years d. Be careful not to sacrifice science for advocacy e. With little direct contact with phenomena, instruction in tectonic theory should be reserved ...
... b. Imagining geologic time will be difficult c. Improve understanding of continental movement by multiplying small increments by large numbers of years d. Be careful not to sacrifice science for advocacy e. With little direct contact with phenomena, instruction in tectonic theory should be reserved ...
wisconsin construction specification - NRCS
... Additional comments such as: presence of roots or root holes, presence of mica, gypsum, etc., surface coatings on coarse-grained particles, caving or sloughing of auger hole or pit sides, difficulty in augering or excavating, etc. should be noted. The depth to standing water in the soil boring or te ...
... Additional comments such as: presence of roots or root holes, presence of mica, gypsum, etc., surface coatings on coarse-grained particles, caving or sloughing of auger hole or pit sides, difficulty in augering or excavating, etc. should be noted. The depth to standing water in the soil boring or te ...
soil formation by ecological factors: critical review
... tobacco, has acidic leaves. As this plant litter decays and percolates through the soil with precipitation, an acidic environment is created in which little vegetation can exist. These conditions naturally occur in pine forests, creating spodosols or ultisols. Humans can stimulate podzolization by p ...
... tobacco, has acidic leaves. As this plant litter decays and percolates through the soil with precipitation, an acidic environment is created in which little vegetation can exist. These conditions naturally occur in pine forests, creating spodosols or ultisols. Humans can stimulate podzolization by p ...
The best plants for 30 tough sites - University of Minnesota Extension
... 1) Have your soil tested for initial pH level. Sending a sample to the University of Minnesota Soil Testing Laboratory soiltest.coafes.umn.edu 2) If your soil pH is less than 5.5 the only amendment suggested before planting is to mix in sphagnum peat moss into your soil at the rate of 1 to 2 cubic f ...
... 1) Have your soil tested for initial pH level. Sending a sample to the University of Minnesota Soil Testing Laboratory soiltest.coafes.umn.edu 2) If your soil pH is less than 5.5 the only amendment suggested before planting is to mix in sphagnum peat moss into your soil at the rate of 1 to 2 cubic f ...
Comments on “Draft Final Remedial Action Confirmation Report
... landfills that are now leaking into the groundwater. This original decision in 1997 (as described in the present report), clearly does not account for the fact that the OU-2 landfills are now a problem and are leaking vapors and into groundwater. Areas that had soil lead levels in excess of 300 mg/k ...
... landfills that are now leaking into the groundwater. This original decision in 1997 (as described in the present report), clearly does not account for the fact that the OU-2 landfills are now a problem and are leaking vapors and into groundwater. Areas that had soil lead levels in excess of 300 mg/k ...
BIODRILLING BY FORAGE RADISHES – Research Update
... significant differences were found with the varying soil quality indicators, it may be a sign that the current practices of the pasture are working positively. Perhaps with a poorly managed soil, differing results may occur. However, ...
... significant differences were found with the varying soil quality indicators, it may be a sign that the current practices of the pasture are working positively. Perhaps with a poorly managed soil, differing results may occur. However, ...
Fundamentals of River Restoration and Salmonid Habitat (*)
... • Precipitation uses three pathways on Earth’s surface —Intercepted by vegetation and evaporated or transpired back to atmosphere —Move downslope on surface or through soil to stream system —Stored in snowpack, groundwater, ponds, or wetlands for a period of time ...
... • Precipitation uses three pathways on Earth’s surface —Intercepted by vegetation and evaporated or transpired back to atmosphere —Move downslope on surface or through soil to stream system —Stored in snowpack, groundwater, ponds, or wetlands for a period of time ...
Picture
... The unit test will count for 25% of your unit grade. Study Guide: To do well on the test, you must be able to answer the following questions: Standard 1, MS-ESS3-b: Soil Formation I will construct explanations for the formation of soil types and other natural resources that result from the weather ...
... The unit test will count for 25% of your unit grade. Study Guide: To do well on the test, you must be able to answer the following questions: Standard 1, MS-ESS3-b: Soil Formation I will construct explanations for the formation of soil types and other natural resources that result from the weather ...
Human Activities Study Guide
... Acid rain causes the pH of rivers, lakes, and streams on Earth to change. Based on the data table, which animal population will be the LAST to die out due to an increase in acid rain? 3. Excess carbon gases released into the atmosphere cause additional radiation to be retained and Earth's average te ...
... Acid rain causes the pH of rivers, lakes, and streams on Earth to change. Based on the data table, which animal population will be the LAST to die out due to an increase in acid rain? 3. Excess carbon gases released into the atmosphere cause additional radiation to be retained and Earth's average te ...
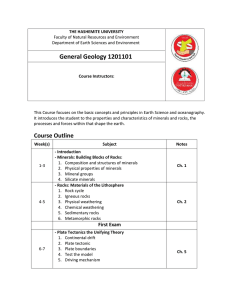
Outline General Geology 2011
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
Rock stars of soil science head for Vic
... December 5 such an important day to dig in and celebrate,” he said. The day recognised the importance of soils to global terrestrial ecosystems and to food and fibre production around the world. McDonald believed careful management of soils, backed up by research and development, was the bedrock of o ...
... December 5 such an important day to dig in and celebrate,” he said. The day recognised the importance of soils to global terrestrial ecosystems and to food and fibre production around the world. McDonald believed careful management of soils, backed up by research and development, was the bedrock of o ...
Earth Revealed #10: Geologic Time
... 7. What kind of conditions exist for the formation of gold, silver and copper (in other words, how do they form)? ...
... 7. What kind of conditions exist for the formation of gold, silver and copper (in other words, how do they form)? ...
Name…………………………………………………
... a) Name one are in Kenya which is not predominantly covered by derived vegetation. (1mk) b) Describe four characteristics of the Mediterranean type of vegetation. ...
... a) Name one are in Kenya which is not predominantly covered by derived vegetation. (1mk) b) Describe four characteristics of the Mediterranean type of vegetation. ...