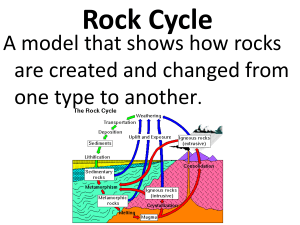
Rock Cycle
... The breaking down of rocks, soil, and minerals by exposing them to water, oxygen, wind, ice, and other outside forces. ...
... The breaking down of rocks, soil, and minerals by exposing them to water, oxygen, wind, ice, and other outside forces. ...
Hormonal Control of Flowering
... Essential elements • Necessary for plant growth • In the absence plant displayed characteristic abnormalities of growth, or deficiency symptoms, reproduction • In 1880 established that at least 10 essential • Essential elements/minerals (inorganic nutrients)- Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, potassium, ca ...
... Essential elements • Necessary for plant growth • In the absence plant displayed characteristic abnormalities of growth, or deficiency symptoms, reproduction • In 1880 established that at least 10 essential • Essential elements/minerals (inorganic nutrients)- Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, potassium, ca ...
File
... G. Tyler Miller’s Living in the Environment 13th Edition Chapter 10 Dr. Richard Clements Chattanooga State Technical Community College ...
... G. Tyler Miller’s Living in the Environment 13th Edition Chapter 10 Dr. Richard Clements Chattanooga State Technical Community College ...
See Q. “Sampler” on packet, pages 12
... o All planets circle sun in same direction and their orbits lie on the ecliptic plane o Earth’s formation: ! Planetesimal (chunks of matter) accretion by coalescence ! Internal melting due to • Gravitational compression • Impact heating • Radioactive decay ! Differentiation into layers • Light mater ...
... o All planets circle sun in same direction and their orbits lie on the ecliptic plane o Earth’s formation: ! Planetesimal (chunks of matter) accretion by coalescence ! Internal melting due to • Gravitational compression • Impact heating • Radioactive decay ! Differentiation into layers • Light mater ...
GEOMORPHOlOGICAl AND PEDOlOGICAl
... work deals with the morphologlcal, chemical, physical and mineralogical characteristics of the soil cover that has developed upon these intrusive rocks. According to CAVALCANTE et ai. (1979), the "metabasics· of the area are represented by ophitic epimetamorphic gabbros consisting of labradorite in ...
... work deals with the morphologlcal, chemical, physical and mineralogical characteristics of the soil cover that has developed upon these intrusive rocks. According to CAVALCANTE et ai. (1979), the "metabasics· of the area are represented by ophitic epimetamorphic gabbros consisting of labradorite in ...
Heuchera Peach Flambe
... Great addition to any garden, as a hedge, in a rockery or in a hanging basket. Prefers a shaded area but can tolerate sun in cooler climates. Thrives in moist well drained soil. o o Temperature Range 5 to 37 ...
... Great addition to any garden, as a hedge, in a rockery or in a hanging basket. Prefers a shaded area but can tolerate sun in cooler climates. Thrives in moist well drained soil. o o Temperature Range 5 to 37 ...
Sodicity - Speedweb
... which measures how much sodium is in the soil, compared to other cations like calcium and magnesium • Soils are considered sodic once the ESP is above 6% ...
... which measures how much sodium is in the soil, compared to other cations like calcium and magnesium • Soils are considered sodic once the ESP is above 6% ...
Plant uptake of inorganic waste constituents
... REF-VER/Copy [Hyperaccumulators: Chaney et al.] REVIEW. Summarizes information on metal uptake and tolerance by plants in relation to soil metals concentrations and other soil properties such as pH and OC. Reviewed metal hyperaccumulator crops, as reported by Brooks et al. in 1977. First published ...
... REF-VER/Copy [Hyperaccumulators: Chaney et al.] REVIEW. Summarizes information on metal uptake and tolerance by plants in relation to soil metals concentrations and other soil properties such as pH and OC. Reviewed metal hyperaccumulator crops, as reported by Brooks et al. in 1977. First published ...
mokasa joint examination
... Leaves behind a barren rock creating aderelict topraphy that cannot support vegetation 5.(a) This is water that exist below the surface for the earth in the soil, sub soils and underlying rocks above the impermeable layers (b) I) SIPPAGE ROM LAKE OR SEA WATER ii) Magmatic water trapped in the rocks ...
... Leaves behind a barren rock creating aderelict topraphy that cannot support vegetation 5.(a) This is water that exist below the surface for the earth in the soil, sub soils and underlying rocks above the impermeable layers (b) I) SIPPAGE ROM LAKE OR SEA WATER ii) Magmatic water trapped in the rocks ...
Chapter 37 Plant Nutrition
... The agriculture benefits of symbiotic nitrogen fixation are the basis for crop rotation In this practice a non-legume such as maize is planted one year, and the following year a legume is planted to restore the concentration of nitrogen in the soil ...
... The agriculture benefits of symbiotic nitrogen fixation are the basis for crop rotation In this practice a non-legume such as maize is planted one year, and the following year a legume is planted to restore the concentration of nitrogen in the soil ...
The way rocks are broken down into smaller bits and soil, either by
... • The top layer of soil. It is made of the smallest grains and has the most humus. This makes it the richest layer of soil, and good for growing plants. Social Studies 3G Ch 3f ...
... • The top layer of soil. It is made of the smallest grains and has the most humus. This makes it the richest layer of soil, and good for growing plants. Social Studies 3G Ch 3f ...
How to Size a Trench Shield
... • Cohesive/non-cohesive soils with unconfined compressive strength of 0.5 tsf or less • Granular soils including gravel, sand, and loamy sand • Submerged soil or soil from which water is freely seeping • Submerged rock that is not stable • Sloped, layered system which slopes into an excavation ...
... • Cohesive/non-cohesive soils with unconfined compressive strength of 0.5 tsf or less • Granular soils including gravel, sand, and loamy sand • Submerged soil or soil from which water is freely seeping • Submerged rock that is not stable • Sloped, layered system which slopes into an excavation ...
3rd Grade Science - Rocks, Minerals, Fossils Checkpoint
... 3rd Grade Rocks/Fossils/Minerals Checkpoint 2nd Nine Weeks ...
... 3rd Grade Rocks/Fossils/Minerals Checkpoint 2nd Nine Weeks ...
THE ROLES OF VARIOUS FUNCTIONAL GROUPS OF
... simulate the nitrogen mineralization on a tens of m2 scale over the entire growing season, i.e. on one level of scale beyond. If the objective would have been to explain the decomposition or mineralization process on the scale of the individual plant, we should have sampled the microsites below the ...
... simulate the nitrogen mineralization on a tens of m2 scale over the entire growing season, i.e. on one level of scale beyond. If the objective would have been to explain the decomposition or mineralization process on the scale of the individual plant, we should have sampled the microsites below the ...
Rocks - SupaScience
... A well-balanced soil that contains lots of nutrients. It is the best soil for most plants. Loam contains some sand, some clay and some humus. It stays moist but still allows water to drain away. ...
... A well-balanced soil that contains lots of nutrients. It is the best soil for most plants. Loam contains some sand, some clay and some humus. It stays moist but still allows water to drain away. ...
Name
... Chemical weathering – occurs when _____________ break up rocks, often in _____________, by dissolving parts of them. This can be compared to a ___________ that holds pieces together. There are ________ layers of soil. The very bottom layer of the soil is known as ____________________ and is mostly s ...
... Chemical weathering – occurs when _____________ break up rocks, often in _____________, by dissolving parts of them. This can be compared to a ___________ that holds pieces together. There are ________ layers of soil. The very bottom layer of the soil is known as ____________________ and is mostly s ...
Soil Security 1.1. Overview The world`s soils are critical to the well
... positioned along environmental gradients of management, soil conditions, and climate. We are exploring mutual interests with NSF, where joint funding could extend a portion of the funding for a joint UK-US study that uses broader environmental gradients delivered via their Critical Zone Observatory ...
... positioned along environmental gradients of management, soil conditions, and climate. We are exploring mutual interests with NSF, where joint funding could extend a portion of the funding for a joint UK-US study that uses broader environmental gradients delivered via their Critical Zone Observatory ...
Please the Rapporteurs` Report for this session here.
... Global soil and land related initiatives and agreements are crucial to catalyze actions for the sustainable management and governance of these resources. Examples of these initiatives are the current process to set universal Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) where soils and land will play a cross ...
... Global soil and land related initiatives and agreements are crucial to catalyze actions for the sustainable management and governance of these resources. Examples of these initiatives are the current process to set universal Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) where soils and land will play a cross ...
Soil Survey
... Web Soil Survey is unavailable nightly between 1:00 AM and 5:00 AM Eastern time for soil survey data updates. Web Soil Survey may be unavailable on Tuesdays and Thursdays between 8:00 PM and 10:30 PM Eastern time for scheduled maintenance and software updates. Web Soil Survey may also be unavailable ...
... Web Soil Survey is unavailable nightly between 1:00 AM and 5:00 AM Eastern time for soil survey data updates. Web Soil Survey may be unavailable on Tuesdays and Thursdays between 8:00 PM and 10:30 PM Eastern time for scheduled maintenance and software updates. Web Soil Survey may also be unavailable ...
Native Forestry on Unsuitable Cropping Land
... sandy and stony it is freely draining internally, but has a low (50 mm/m) water holding capacity. It is equivalent to the Murray soil of the Mackay Sugarcane soil study. The analytical data in the table below shows that the topsoil is acidic with very low levels of soluble salts and has good fertili ...
... sandy and stony it is freely draining internally, but has a low (50 mm/m) water holding capacity. It is equivalent to the Murray soil of the Mackay Sugarcane soil study. The analytical data in the table below shows that the topsoil is acidic with very low levels of soluble salts and has good fertili ...
How should farmers respond? - Agricultural Policy Analysis Center
... soil. Ground that is regularly plowed never has the chance to build up a significant amount of humus. Nitrous oxide is released as the result of the application of nitrogen fertilizers, particularly their improper and excessive application. Methane is released from the gut of ruminant animals as wel ...
... soil. Ground that is regularly plowed never has the chance to build up a significant amount of humus. Nitrous oxide is released as the result of the application of nitrogen fertilizers, particularly their improper and excessive application. Methane is released from the gut of ruminant animals as wel ...
No Slide Title
... in the water is caused when the bacteria consuming the dead algae is pulled from the water, leading to the suffocation of aquatic life like fish. ...
... in the water is caused when the bacteria consuming the dead algae is pulled from the water, leading to the suffocation of aquatic life like fish. ...























