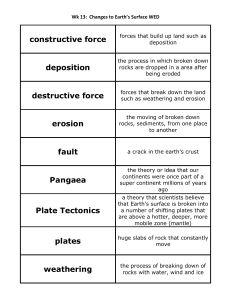
The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
External Forces Shaping the Earth
... As water flows in a stream or river, the motion picks up loose material and moves downstream & the force will also break landform. Most streams erode both vertically & horizontally– it will cut a stream as it get deeper & wider, forming a V—shaped valley. ...
... As water flows in a stream or river, the motion picks up loose material and moves downstream & the force will also break landform. Most streams erode both vertically & horizontally– it will cut a stream as it get deeper & wider, forming a V—shaped valley. ...
tx_ecoregions2013_weatheringerosion_and_deposition
... • an area defined by its environmental conditions, esp. climate, landforms, and soil characteristics. ...
... • an area defined by its environmental conditions, esp. climate, landforms, and soil characteristics. ...
Texas Ecoregions - Gorzycki Middle School
... • an area defined by its environmental conditions, esp. climate, landforms, and soil characteristics. ...
... • an area defined by its environmental conditions, esp. climate, landforms, and soil characteristics. ...
What is Erosion?
... practices are still ignored when using large machinery because many practices are more difficult to do on a large scale. Besides farming, highway construction, building construction, overgrazing and some logging activities all increase the rate of erosion ...
... practices are still ignored when using large machinery because many practices are more difficult to do on a large scale. Besides farming, highway construction, building construction, overgrazing and some logging activities all increase the rate of erosion ...
Agricultural Soil and Water Conservation Stewardship
... processes 4) Identify various types of soil erosion while utilizing different methods of to estimate soil erosion to assess land use impacts* 5)Explain why land-use planning is necessary for our ecosystems and the economy to achieve sustainable agriculture ...
... processes 4) Identify various types of soil erosion while utilizing different methods of to estimate soil erosion to assess land use impacts* 5)Explain why land-use planning is necessary for our ecosystems and the economy to achieve sustainable agriculture ...
Erosion - Weebly
... Soil Erosion: Degradation and Conservation ■ The ideal soil for agriculture is a loamy mixture with a pH close to neutral that is also workable and capable of holding nutrients. ■ Soil is naturally far from this ideal, especially with increased soil degradation due to human impact. ...
... Soil Erosion: Degradation and Conservation ■ The ideal soil for agriculture is a loamy mixture with a pH close to neutral that is also workable and capable of holding nutrients. ■ Soil is naturally far from this ideal, especially with increased soil degradation due to human impact. ...
Data/hora: 10/03/2017 22:04:43 Provedor de dados: 177 País
... of Southeast Asia, one of the most bio-geochemically active regions of the world. Investigations were performed on a typical hillslope of Northern Laos subjected to slash and burn agriculture practiced as shifting cultivation. Situations with different periods of the shifting cultivation cycle (seco ...
... of Southeast Asia, one of the most bio-geochemically active regions of the world. Investigations were performed on a typical hillslope of Northern Laos subjected to slash and burn agriculture practiced as shifting cultivation. Situations with different periods of the shifting cultivation cycle (seco ...
Fortune Teller
... 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the boundary of plates (faults). 2. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks chemically and physically. 3. Erosion causes weathered rocks and soil to be washed away. 4. Sedimentary – layers of sediment cemented together Igneous – melting and ...
... 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the boundary of plates (faults). 2. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks chemically and physically. 3. Erosion causes weathered rocks and soil to be washed away. 4. Sedimentary – layers of sediment cemented together Igneous – melting and ...
Weathering, Erosion, Soil, Mass Movement
... Weathering, Erosion and Deposition 1. Compare and contrast the following terms: a) Weathering and Erosion: ...
... Weathering, Erosion and Deposition 1. Compare and contrast the following terms: a) Weathering and Erosion: ...
Constructive and Destructive study guide
... manage the destructive force of water erosion. 3. Levees help to contain the flow of water. Rivers naturally create their own levees through the process of deposition. During flooding periods man-made levees may be added. They help to control the destructive force of water erosion. 4. Storm-Drainage ...
... manage the destructive force of water erosion. 3. Levees help to contain the flow of water. Rivers naturally create their own levees through the process of deposition. During flooding periods man-made levees may be added. They help to control the destructive force of water erosion. 4. Storm-Drainage ...
Name: Group: Date: ______ 4-ESS2-1. Evidence of Weathering and
... List the five weathering agents Physical Changes ...
... List the five weathering agents Physical Changes ...
Texas Ecoregions
... • This is a small, thin region running North to South on either side of the prairies and plains. • The soil is not as prone to flooding because it allows water to infiltrate very easily. • The region is described as rough, hilly terrain. ...
... • This is a small, thin region running North to South on either side of the prairies and plains. • The soil is not as prone to flooding because it allows water to infiltrate very easily. • The region is described as rough, hilly terrain. ...
Agents of Erosion Notes
... & sediment are transported from one location to another. The running water of the Colorado River cut down into the rock and formed the Grand Canyon over millions of years. ...
... & sediment are transported from one location to another. The running water of the Colorado River cut down into the rock and formed the Grand Canyon over millions of years. ...
File - Mr. Coach Risinger 7Y Science
... primarily sand-based. 2. If there isn’t enough vegetation to keep the soil in place, rainfall received can cause severe erosion. 3. Catastrophic events such as hurricanes can increase wave erosion and deposition. ...
... primarily sand-based. 2. If there isn’t enough vegetation to keep the soil in place, rainfall received can cause severe erosion. 3. Catastrophic events such as hurricanes can increase wave erosion and deposition. ...
Landforms from Erosion and Deposition by Gravity Quiz
... 5) A talus slope is formed… a) at the base of a cliff due to falling rocks. b) in valleys as a result of mudflows. c) where lava flows enter the ocean. d) none of the above 6) Rainfall greatly ...
... 5) A talus slope is formed… a) at the base of a cliff due to falling rocks. b) in valleys as a result of mudflows. c) where lava flows enter the ocean. d) none of the above 6) Rainfall greatly ...
File - Mr Raynes Geography
... taking small soil particles and stones with them. When the needles collapse during the day, the dislodged particles will roll downhill, resulting in mass movement on a small scale • Illustrate: ...
... taking small soil particles and stones with them. When the needles collapse during the day, the dislodged particles will roll downhill, resulting in mass movement on a small scale • Illustrate: ...
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition: Effects on the Texas
... colors of igneous rocks show oxidation, oxygen reacting with iron forming rust ...
... colors of igneous rocks show oxidation, oxygen reacting with iron forming rust ...
Erosion and Weathering ppt
... • a. For the Ring of Fire, the location is due to being where the crust of the earth is very thin. This is the primary factor, plate tectonics, not climate. • b. For the Great Plains, climate & type of soil are the primary factors in the location of this region. • c. The climate of the Great Plains ...
... • a. For the Ring of Fire, the location is due to being where the crust of the earth is very thin. This is the primary factor, plate tectonics, not climate. • b. For the Great Plains, climate & type of soil are the primary factors in the location of this region. • c. The climate of the Great Plains ...
Review Page for Earth Processes Final Test
... Magma-molten rock called lava when it reaches surface & hardens to form new crust P waves-compression waves, arrive first, travel quickly primary go through liquids& solids S waves-Transverse of shear waves, arrive second, travel slower only go through solid Focus- the point inside the earth where t ...
... Magma-molten rock called lava when it reaches surface & hardens to form new crust P waves-compression waves, arrive first, travel quickly primary go through liquids& solids S waves-Transverse of shear waves, arrive second, travel slower only go through solid Focus- the point inside the earth where t ...
Erosion

In geomorphology and geology, erosion is the action of exogenicprocesses (such as water flow or wind) which remove soil and rock from one location on the Earth's crust, then transport it to another location where it is deposited. Eroded sediment may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.While erosion is a natural process, human activities have increased by 10-40 times the rate at which erosion is occurring globally. Excessive (or accelerated) erosion causes both ""on-site"" and ""off-site"" problems. On-site impacts include decreases in agricultural productivity and (on natural landscapes) ecological collapse, both because of loss of the nutrient-rich upper soil layers. In some cases, the eventual end result is desertification. Off-site effects include sedimentation of waterways and eutrophication of water bodies, as well as sediment-related damage to roads and houses. Water and wind erosion are the two primary causes of land degradation; combined, they are responsible for about 84% of the global extent of degraded land, making excessive erosion one of the most significant environmental problems world-wide.Intensive agriculture, deforestation, roads, anthropogenic climate change and urban sprawl are amongst the most significant human activities in regard to their effect on stimulating erosion. However, there are many prevention and remediation practices that can curtail or limit erosion of vulnerable soils.