Nuclear Particles p. 706
... Some elements decay to a stable nucleus in less than 1 second. Others may require millions of years. Carbon-14 (isotope of carbon with neutrons) It is found in all living things. It is absorbed in CO2. The half-life is 5730 years. By measuring the percentage of C-14 in a fossil or skeleton, scientis ...
... Some elements decay to a stable nucleus in less than 1 second. Others may require millions of years. Carbon-14 (isotope of carbon with neutrons) It is found in all living things. It is absorbed in CO2. The half-life is 5730 years. By measuring the percentage of C-14 in a fossil or skeleton, scientis ...
File
... compound: a substance made up of atoms of two ore more different elements joined by chemical bonds. atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. (The atomic number is the same for all atoms of an element.) chemical symbol: a one, two, or three-letter abbreviation of the name of an ...
... compound: a substance made up of atoms of two ore more different elements joined by chemical bonds. atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. (The atomic number is the same for all atoms of an element.) chemical symbol: a one, two, or three-letter abbreviation of the name of an ...
Chapter 6 Review“The Periodic Table”
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... particle, the atom's mass will not change (since there is no change in the total number of nuclear particles), however the atomic number will increase by one (because the neutron transmutated into an additional proton). An example of this is the decay of the isotope of carbon named carbon-14 into th ...
... particle, the atom's mass will not change (since there is no change in the total number of nuclear particles), however the atomic number will increase by one (because the neutron transmutated into an additional proton). An example of this is the decay of the isotope of carbon named carbon-14 into th ...
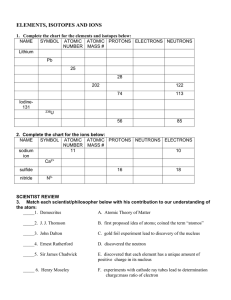
ELEMENTS, ISOTOPES AND IONS
... SYMBOL ATOMIC ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER MASS # sodium ...
... SYMBOL ATOMIC ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER MASS # sodium ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... 13. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements? 14. Know characteristics regarding the nucleus of an atom. 15. Describe the model of the atom as a result of Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus. 16. The smallest particle of an element that retains the pr ...
... 13. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements? 14. Know characteristics regarding the nucleus of an atom. 15. Describe the model of the atom as a result of Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus. 16. The smallest particle of an element that retains the pr ...
In a nuclear reaction
... absorption of energy from an out side source. 2- Elements with atomic # greater then Bi 83 are unstable and are radioactive. 3- Isotopes that are unstable have an unstable ratio of protons and neutrons greater then 1:1 3- TRANSMUTATION- changes to the nucleus of an ...
... absorption of energy from an out side source. 2- Elements with atomic # greater then Bi 83 are unstable and are radioactive. 3- Isotopes that are unstable have an unstable ratio of protons and neutrons greater then 1:1 3- TRANSMUTATION- changes to the nucleus of an ...
Salesian High School Elements and atoms Chemistry quiz The
... 7) Which of the following is one of the statements that make up Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All atoms contain electrons. b) All atoms of a given element are identical. c) Atoms are divisible. d) Atoms gain and lose electrons in chemical reactions ...
... 7) Which of the following is one of the statements that make up Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All atoms contain electrons. b) All atoms of a given element are identical. c) Atoms are divisible. d) Atoms gain and lose electrons in chemical reactions ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... isotope is predictable. That is, we cannot predict when a specific atom will decay, but after one half-life half of the atoms will have decayed into a daughter nuclide. ...
... isotope is predictable. That is, we cannot predict when a specific atom will decay, but after one half-life half of the atoms will have decayed into a daughter nuclide. ...
Intro to Atoms Clicker Questions 1. "atomos" means? 2. Atoms of one
... 5. In Rutherford's Atomic model, the protons - positively charged particles are located where? 6. Rutherford's proof of the proton's location in the atom came from an experiment with _______ 7. In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons are arranged how? 8. A neutron has (a) _____ charge 9. (T/F) The ...
... 5. In Rutherford's Atomic model, the protons - positively charged particles are located where? 6. Rutherford's proof of the proton's location in the atom came from an experiment with _______ 7. In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons are arranged how? 8. A neutron has (a) _____ charge 9. (T/F) The ...
Homework Geochem Test Review
... 2. What is smallest part of an element that has all the properties of that element? ...
... 2. What is smallest part of an element that has all the properties of that element? ...
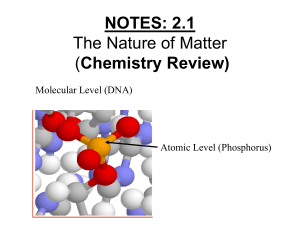
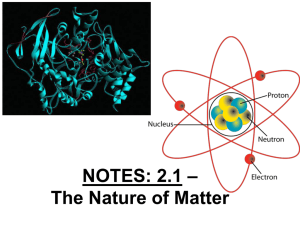
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element ...
... Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element ...
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... 107.868 = 106.9041 (X) + 108.9047 (1.000 - X) -1.0367 = -2.0006 X X = 0.51819 ...
... 107.868 = 106.9041 (X) + 108.9047 (1.000 - X) -1.0367 = -2.0006 X X = 0.51819 ...
Unit 2 Overview
... periodic table possesses. In part two, we will relate the number of neutrons to the formation of isotopes which are linked to radioactive behavior allowing us to study many applications of radioactivity in everyday life. In part three, we will seek to understand how the electron is inextricably link ...
... periodic table possesses. In part two, we will relate the number of neutrons to the formation of isotopes which are linked to radioactive behavior allowing us to study many applications of radioactivity in everyday life. In part three, we will seek to understand how the electron is inextricably link ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... 15._____ His oil-drop experiment enabled scientists to measure the charge on the electron. 16._____ He concluded that the atom had a small, compact, positively-charged nucleus surrounded by electrons based on his gold-foil experiment. 17._____ He invented the mass spectrograph, an instrument that is ...
... 15._____ His oil-drop experiment enabled scientists to measure the charge on the electron. 16._____ He concluded that the atom had a small, compact, positively-charged nucleus surrounded by electrons based on his gold-foil experiment. 17._____ He invented the mass spectrograph, an instrument that is ...
Atomic Crossword Name: Period: ____
... 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (usually with heavy elements) 17. British scientist who formulated our modern atomic theory 22. The mergin ...
... 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (usually with heavy elements) 17. British scientist who formulated our modern atomic theory 22. The mergin ...
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... explain the relationship of the proton number to the element’s identity. SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half- ...
... explain the relationship of the proton number to the element’s identity. SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half- ...
Radioisotopes
... having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have different mass numbers, which give the total number of nucleons, the number of protons plus neutron ...
... having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have different mass numbers, which give the total number of nucleons, the number of protons plus neutron ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.