Early Atomic Theorists
... All nuclear reactions are: transmutation reactions o Some transmutation reactions are induced o All transuranium elements (atomic #93 and greater) have been produced through induced transmutation. ...
... All nuclear reactions are: transmutation reactions o Some transmutation reactions are induced o All transuranium elements (atomic #93 and greater) have been produced through induced transmutation. ...
File
... Found in each elements’ box on the periodic table and indicates how many protons that element contains (also tells ...
... Found in each elements’ box on the periodic table and indicates how many protons that element contains (also tells ...
and View
... c. Alpha particle—consists of protons and neutrons from nucleus d. Beta particle—high-energy electron that comes from the nucleus not from the electron cloud. i. Neutron becomes unstable and splits into an electron and proton—electron is then spit out—proton stays in nucleus. ii. Beta decay—atomic n ...
... c. Alpha particle—consists of protons and neutrons from nucleus d. Beta particle—high-energy electron that comes from the nucleus not from the electron cloud. i. Neutron becomes unstable and splits into an electron and proton—electron is then spit out—proton stays in nucleus. ii. Beta decay—atomic n ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... 2. What is the structure of an atom? 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth ...
... 2. What is the structure of an atom? 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth ...
Test Review: Unit 1 - Ms. Hill`s Pre
... normal chemical and physical changes (Dalton didn’t describe/clarify normal circumstances, matter can be created and destroyed in nuclear reactions) b. Law of Definite Proportions: the fact that a chemical compound contain exactly the same elements in exactly the same proportions in exactly the same ...
... normal chemical and physical changes (Dalton didn’t describe/clarify normal circumstances, matter can be created and destroyed in nuclear reactions) b. Law of Definite Proportions: the fact that a chemical compound contain exactly the same elements in exactly the same proportions in exactly the same ...
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
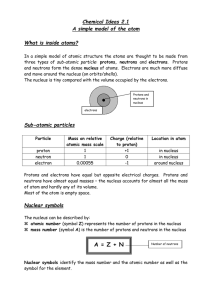
... Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # Neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number ISOTOPES o Isotop ...
... Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # Neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number ISOTOPES o Isotop ...
Document
... Chemical Ideas 2.2 Nuclear reactions Emissions from radioactive substances Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be trig ...
... Chemical Ideas 2.2 Nuclear reactions Emissions from radioactive substances Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be trig ...
Atomic Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Use the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule to write the electron configurations and orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element u ...
... Use the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule to write the electron configurations and orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element u ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary crossword puzzle
... Use the clues below to complete the crossword on the next page. Across 2. Set of elements that exhibit similar electron configurations in highest occupied energy level 4. Class of elements possessing the property of being ductile 5. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are comple ...
... Use the clues below to complete the crossword on the next page. Across 2. Set of elements that exhibit similar electron configurations in highest occupied energy level 4. Class of elements possessing the property of being ductile 5. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are comple ...
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
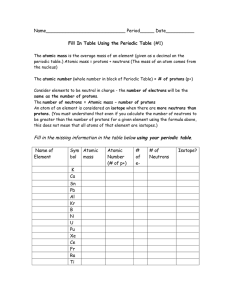
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 13. Explain the difference between a group and a period on the periodic table of elements. Groups = columns (there are 18 total) and Periods = Rows (there are 7). Also, a group shares similar properties. 14. Why are neither the alkali metals nor the alkaline-earth metals found uncombined in nature? ...
... 13. Explain the difference between a group and a period on the periodic table of elements. Groups = columns (there are 18 total) and Periods = Rows (there are 7). Also, a group shares similar properties. 14. Why are neither the alkali metals nor the alkaline-earth metals found uncombined in nature? ...
Chemistry Overview
... – Begin with 1 capital letter – Some based on Latin names • Ex/ gold = Au for Aurum iron = Fe for Ferros ...
... – Begin with 1 capital letter – Some based on Latin names • Ex/ gold = Au for Aurum iron = Fe for Ferros ...
Chapter 2
... (earth,air,fire,water) • “atomos” – later became atom – small, indivisible particles • Dalton’s Atomic Theory – • Each element made up of atoms • Atoms of same element same; different element different • Compounds form from combinations of elements in definite proportions. • Chemical reactions invol ...
... (earth,air,fire,water) • “atomos” – later became atom – small, indivisible particles • Dalton’s Atomic Theory – • Each element made up of atoms • Atoms of same element same; different element different • Compounds form from combinations of elements in definite proportions. • Chemical reactions invol ...
Present - Images
... Nuclear Reactions Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bom ...
... Nuclear Reactions Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bom ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.