worksheet #1 - chemistryrocks.net
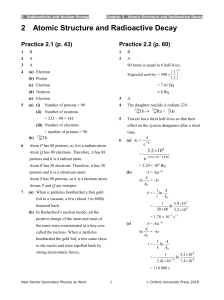
... tables are “weighted averages” of the weights of the different naturally occurring isotopes of the element. Let’s look at an example. Approximately 75% of the chlorine atoms found in nature have a mass of 35. The other 25% have a mass of 37. What should we report as the atomic weight for chlorine? W ...
... tables are “weighted averages” of the weights of the different naturally occurring isotopes of the element. Let’s look at an example. Approximately 75% of the chlorine atoms found in nature have a mass of 35. The other 25% have a mass of 37. What should we report as the atomic weight for chlorine? W ...
Name: Period: _____ Date
... 8. _____ average mass of all the isotopes of an element 9. _____ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons 10. _____ s, p, d, f…sublevels of the electron cloud 11. _____ any element that tends to take electrons and get a negative charge 12. _____ part of an atom with a negative ...
... 8. _____ average mass of all the isotopes of an element 9. _____ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons 10. _____ s, p, d, f…sublevels of the electron cloud 11. _____ any element that tends to take electrons and get a negative charge 12. _____ part of an atom with a negative ...
Unit 3 Notes only
... 1) Explain how the following terms are related – Atomic number and proton – the atomic number tells you how many protons there are in an element – Isotope and neutron – isotopes are based on different number of neutrons – Electrons and energy levels – electrons are found in energy levels. Energy l ...
... 1) Explain how the following terms are related – Atomic number and proton – the atomic number tells you how many protons there are in an element – Isotope and neutron – isotopes are based on different number of neutrons – Electrons and energy levels – electrons are found in energy levels. Energy l ...
Ch-03 Notes
... One atomic mass unit (amu) is exactly 1/12 of the mass of one C-12 atom. (1.660540 ×10-27 kg) ...
... One atomic mass unit (amu) is exactly 1/12 of the mass of one C-12 atom. (1.660540 ×10-27 kg) ...
Review Outline for Atomic Structure Test
... a. What determines the location of an electron in the electron cloud? How many energy levels are present. Electrons fill the energy levels in order (2-8-8-18) b. How many electrons can be found in the first energy level of an atom? 2 c. How many electrons can be found in the second energy level of a ...
... a. What determines the location of an electron in the electron cloud? How many energy levels are present. Electrons fill the energy levels in order (2-8-8-18) b. How many electrons can be found in the first energy level of an atom? 2 c. How many electrons can be found in the second energy level of a ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the
... Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the smallest units of matter. An atom is too small to see directly through a microscope. The smallest speck that can be seen under an ordinary microscope contains more than ten billion atoms. An atom is more that a million times smaller than ...
... Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the smallest units of matter. An atom is too small to see directly through a microscope. The smallest speck that can be seen under an ordinary microscope contains more than ten billion atoms. An atom is more that a million times smaller than ...
Atomic Theory PPT
... atomic number) with different atomic masses (different # of neutrons). C-14 and ...
... atomic number) with different atomic masses (different # of neutrons). C-14 and ...
Atom/Elements Study Guide
... 3. The atom is composed mostly of empty space. 4. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? In the nucleus 5. How many electrons can exist in the first shell? The second? 2, 8, 8,18 6. Which two subatomic particles have approximately the same mass? Neutrons and protons 7. Atoms with the same nu ...
... 3. The atom is composed mostly of empty space. 4. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? In the nucleus 5. How many electrons can exist in the first shell? The second? 2, 8, 8,18 6. Which two subatomic particles have approximately the same mass? Neutrons and protons 7. Atoms with the same nu ...
Radioactivity
... Some isotopes of atoms can be unstable. They may have: a) Too much energy or b) The wrong number of particles in the nucleus. We call these radioisotopes. To make themselves more stable, they throw out particles and/or energy from the nucleus. We call this process ‘radioactive decay’. The atom is al ...
... Some isotopes of atoms can be unstable. They may have: a) Too much energy or b) The wrong number of particles in the nucleus. We call these radioisotopes. To make themselves more stable, they throw out particles and/or energy from the nucleus. We call this process ‘radioactive decay’. The atom is al ...
Thinking about Atomic Mass and Density sheet
... Thinking About Atomic Mass and Density Every element has a different number of protons. Scientists have given each element a number based on the number of protons in an atom of that element. This number is called an atomic number. Each element’s atomic number is unique. The higher the atomic number, ...
... Thinking About Atomic Mass and Density Every element has a different number of protons. Scientists have given each element a number based on the number of protons in an atom of that element. This number is called an atomic number. Each element’s atomic number is unique. The higher the atomic number, ...
Atom Reading Passage and Questions File
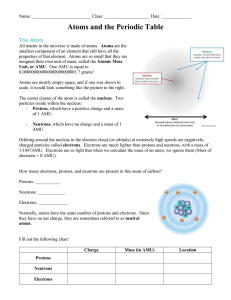
... The center of the atom is called the nucleus. Neutrons and protons are located in the atomic nucleus. Electrons are very small particles located outside the nucleus. They orbit the nucleus at fantasist speeds, like the Earth orbits the sun. Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical ...
... The center of the atom is called the nucleus. Neutrons and protons are located in the atomic nucleus. Electrons are very small particles located outside the nucleus. They orbit the nucleus at fantasist speeds, like the Earth orbits the sun. Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... His ideas agreed with later scientific theory, but didn’t explain chemical behavior - was not based on scientific methods – only philosophy ...
... His ideas agreed with later scientific theory, but didn’t explain chemical behavior - was not based on scientific methods – only philosophy ...
Atom - WCHS Physical Science
... • SPS1 Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of • proton, electron, and neutron locations. • atomic mass and atomic number. • atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). • explain the relationship of the proton number ...
... • SPS1 Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of • proton, electron, and neutron locations. • atomic mass and atomic number. • atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). • explain the relationship of the proton number ...
Atoms, the Periodic Table and Moles - Ars
... A theory (or model) of the way matter works goes back to the ancient Greeks. Two competing theories at that time were the idea that matter is continuous and that matter is composed of indivisible particles called atoms. The first states that however finely matter is divided it is the same. The secon ...
... A theory (or model) of the way matter works goes back to the ancient Greeks. Two competing theories at that time were the idea that matter is continuous and that matter is composed of indivisible particles called atoms. The first states that however finely matter is divided it is the same. The secon ...
Section 6.2 Notes - oologah.k12.ok.us
... There were four things that were known to be true about atoms atoms have no net electric charge electric charges are carried by particles of matter electric charges always exist in whole-numbered ratios when a given number of negatively charged particles combine with the same number of pos ...
... There were four things that were known to be true about atoms atoms have no net electric charge electric charges are carried by particles of matter electric charges always exist in whole-numbered ratios when a given number of negatively charged particles combine with the same number of pos ...
1. Structure and Properties of the Atom
... When a shell is filled a new electron shell is started for the remaining electrons. There is a rule, however, which does not allow the outermost shell (valence shell) of an atom of an element to hold more than 8 electrons. For example, as the third (M) shell has a capacity of 18 electrons you would ...
... When a shell is filled a new electron shell is started for the remaining electrons. There is a rule, however, which does not allow the outermost shell (valence shell) of an atom of an element to hold more than 8 electrons. For example, as the third (M) shell has a capacity of 18 electrons you would ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
Isotopes File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... gland is to produce a substance that helps the body regulate some of its activities. Molecules of this substance contain natural iodine atoms (iodine-127) that are normally absorbed by the body from foods. Put another way, iodine supplied by nutrients becomes concentrated in the thyroid gland and it ...
... gland is to produce a substance that helps the body regulate some of its activities. Molecules of this substance contain natural iodine atoms (iodine-127) that are normally absorbed by the body from foods. Put another way, iodine supplied by nutrients becomes concentrated in the thyroid gland and it ...
1 An atom is the smallest particle of any element that still retains the
... nucleus is unchanged, but the atomic number increases by one unit. c) Gamma Radiation. γ. It is high-energy photons . This emission results from an energy change within the atomic nucleus. This radiation changes neither the atomic number nor the atomic mass. ...
... nucleus is unchanged, but the atomic number increases by one unit. c) Gamma Radiation. γ. It is high-energy photons . This emission results from an energy change within the atomic nucleus. This radiation changes neither the atomic number nor the atomic mass. ...
Document
... Atoms gain electrons (negatives) and become more negative. Atoms with 2-3 valence electrons will LOSE electrons and become more positive. Who will lose and who will gain an electron? ...
... Atoms gain electrons (negatives) and become more negative. Atoms with 2-3 valence electrons will LOSE electrons and become more positive. Who will lose and who will gain an electron? ...
Inside an Atom
... same number of protons, but can have different number of neutrons Ex. Carbon has 6 protons, but can ...
... same number of protons, but can have different number of neutrons Ex. Carbon has 6 protons, but can ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.