Hereditary Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets, (HVDRR)
... The underlying cause for hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets is a defect in the vitamin D receptor that prevents vitamin D from reaching its target tissues. HVDRR is characterised by low calcium levels leading to secondary hyperparathyroidism. Vitamin D enhances bone mineraliza ...
... The underlying cause for hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets is a defect in the vitamin D receptor that prevents vitamin D from reaching its target tissues. HVDRR is characterised by low calcium levels leading to secondary hyperparathyroidism. Vitamin D enhances bone mineraliza ...
Chapter 05
... – Metabolic rate is the relationship of calories consumed to the calories energized – Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the energy used when a person is at rest ...
... – Metabolic rate is the relationship of calories consumed to the calories energized – Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the energy used when a person is at rest ...
Nutritional Diseases Powerpoint 3A
... What is it? Who is at risk? Marasmus is severe undernourishment causing an infant’s or child’s weight to be significantly low for their age. It consists of the chronic wasting away of fat, muscle,a and other tissues in the body. Marasmus is most common in children in developing regions, such as Afr ...
... What is it? Who is at risk? Marasmus is severe undernourishment causing an infant’s or child’s weight to be significantly low for their age. It consists of the chronic wasting away of fat, muscle,a and other tissues in the body. Marasmus is most common in children in developing regions, such as Afr ...
News-Product launch KSED
... 100% natural drops from seaweed, found naturally in France, extracted by Miro Vitamins Ltd. based in Paris, France. Keva Solar Energy Drops is the one of the most challenging product that accomplices the sufficiency of Vitamin D3 in human body & hence a precautionary measure for treating dreadful di ...
... 100% natural drops from seaweed, found naturally in France, extracted by Miro Vitamins Ltd. based in Paris, France. Keva Solar Energy Drops is the one of the most challenging product that accomplices the sufficiency of Vitamin D3 in human body & hence a precautionary measure for treating dreadful di ...
GI Sustain
... ounces of chilled water or juice twice daily or as directed by your healthcare practitioner. For highly sensitive individuals, consider reducing consumption to 1/2 to 1 scoop with 4 to 5 ounces of chilled water or juice twice daily during the first 3 to 4 days before starting a full daily dose. Form ...
... ounces of chilled water or juice twice daily or as directed by your healthcare practitioner. For highly sensitive individuals, consider reducing consumption to 1/2 to 1 scoop with 4 to 5 ounces of chilled water or juice twice daily during the first 3 to 4 days before starting a full daily dose. Form ...
Chemistry 1010 The Chemistry of Food: Vitamins and Minerals
... cooking vegetables in water removes these ...
... cooking vegetables in water removes these ...
vitamins-one word answers
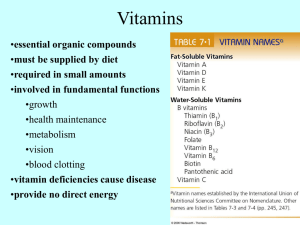
... Vitamins are regulators necessary for the normal metabolic activities. Deficiency of vitamins (Hypovitaminosis) causes Deficiency diseases. Vitamins are classified into Fat soluble (Vit. A, D, E and K) vitamins and Water soluble (Vit. B complex and Vit. C) Vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins Vitamin A is ...
... Vitamins are regulators necessary for the normal metabolic activities. Deficiency of vitamins (Hypovitaminosis) causes Deficiency diseases. Vitamins are classified into Fat soluble (Vit. A, D, E and K) vitamins and Water soluble (Vit. B complex and Vit. C) Vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins Vitamin A is ...
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
... VITAMIN C Synthesized by most animals (not by humans) Decrease absorption with high intakes ...
... VITAMIN C Synthesized by most animals (not by humans) Decrease absorption with high intakes ...
Canada`s food Guide Key Nutrients
... Vitamin C Helps the body absorb iron Helps build teeth and bones Helps keep blood vessels healthy Provided O2 to cells Prevents scurvy Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, green vegetables ...
... Vitamin C Helps the body absorb iron Helps build teeth and bones Helps keep blood vessels healthy Provided O2 to cells Prevents scurvy Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, green vegetables ...
Vitamin C
... Why vitamin C? Vitamin C, also called ascorbic acid, is a factor in: • Healing cuts and wounds • Synthesizing carnitine, which is needed by the body to burn fat • Producing collagen: a protein in skin, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels • Keeping gums, teeth and bones healthy • Countering damage to y ...
... Why vitamin C? Vitamin C, also called ascorbic acid, is a factor in: • Healing cuts and wounds • Synthesizing carnitine, which is needed by the body to burn fat • Producing collagen: a protein in skin, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels • Keeping gums, teeth and bones healthy • Countering damage to y ...
vitamin C
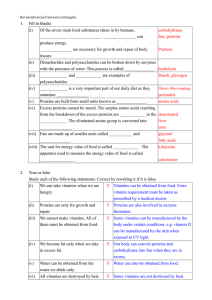
... Study each of the following statements. Correct by rewriting it if it is false. (i) ...
... Study each of the following statements. Correct by rewriting it if it is false. (i) ...
Though Val Thinks His Meth
... which releases niacin from the grain and prevented pellagra. Vitamin B12 or cobalamin does not occur in plant-derived foods. It must come from meat, dairy products and eggs in the diet. Vegans must take dietary supplements. The most common symptoms of deficiency are weakness, fatigue, palpitations, ...
... which releases niacin from the grain and prevented pellagra. Vitamin B12 or cobalamin does not occur in plant-derived foods. It must come from meat, dairy products and eggs in the diet. Vegans must take dietary supplements. The most common symptoms of deficiency are weakness, fatigue, palpitations, ...
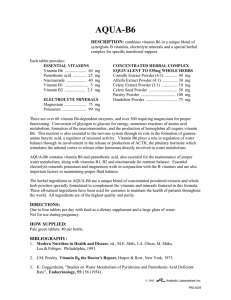
AQUA-B6 - Anabolic Laboratories
... electrolyte minerals potassium and magnesium work in conjunction with the B vitamins and are also important factors in maintaining proper fluid balance. The herbal ingredients in AQUA-B6 are a unique blend of concentrated powdered extracts and whole herb powders specially formulated to complement th ...
... electrolyte minerals potassium and magnesium work in conjunction with the B vitamins and are also important factors in maintaining proper fluid balance. The herbal ingredients in AQUA-B6 are a unique blend of concentrated powdered extracts and whole herb powders specially formulated to complement th ...
Diseases related to Hunger or Over-Nutrition - Mrs. Standish
... • Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. • Scurvy is one of the accompanying diseases of malnutrition (other such micronutrient deficiencies are beriberi or pellagra) and thus is still widespread in areas of the world ...
... • Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. • Scurvy is one of the accompanying diseases of malnutrition (other such micronutrient deficiencies are beriberi or pellagra) and thus is still widespread in areas of the world ...
Liposomal Vitamin C - American Wellness and Rehab Clinic
... • Lipo-Spheric Vitamin C is encapsulated in liposomes. • It is digested as a fat instead of an acid. ...
... • Lipo-Spheric Vitamin C is encapsulated in liposomes. • It is digested as a fat instead of an acid. ...
Clinical Proof We Don`t Get What We Need From Our Food
... and fractures; and low levels of the antioxidant vitamins (vitamins A, E, and C) may increase risk for several chronic diseases. Most Social people do not consume an optimal amount of all vitamins by Bookmarking diet alone. Pending strong evidence of effectiveness from randomized trials, it appears ...
... and fractures; and low levels of the antioxidant vitamins (vitamins A, E, and C) may increase risk for several chronic diseases. Most Social people do not consume an optimal amount of all vitamins by Bookmarking diet alone. Pending strong evidence of effectiveness from randomized trials, it appears ...
Vitamin C (Ascorbate) - SpectraCell Laboratories
... Since excess vitamin C can actually increase free radical production, it is important to balance it with other antioxidants in order to not induce a pro-oxidant effect. Large doses may result in diarrhea. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level has been established at 2000 mg per day. Although vitamin C is ...
... Since excess vitamin C can actually increase free radical production, it is important to balance it with other antioxidants in order to not induce a pro-oxidant effect. Large doses may result in diarrhea. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level has been established at 2000 mg per day. Although vitamin C is ...
Vitamin B2 - Nutri
... low socio-economic backgrounds, elderly people with poor diets, chronic dieters, and people who exclude milk products from their diet (vegans). Symptoms of riboflavin deficiency include fatigue, slowed growth, digestive problems, cracks and sores around the corners of the mouth, swollen magenta tong ...
... low socio-economic backgrounds, elderly people with poor diets, chronic dieters, and people who exclude milk products from their diet (vegans). Symptoms of riboflavin deficiency include fatigue, slowed growth, digestive problems, cracks and sores around the corners of the mouth, swollen magenta tong ...
Vitamin_E_121809 - The Bronx High School of Science
... Intakes by Individuals have found that the diets of most Americans provide less than the RDA levels of vitamin E. • Because the digestive tract requires fat to absorb vitamin E, people with fatmalabsorption disorders are more likely to become ...
... Intakes by Individuals have found that the diets of most Americans provide less than the RDA levels of vitamin E. • Because the digestive tract requires fat to absorb vitamin E, people with fatmalabsorption disorders are more likely to become ...
Reaching out to Mothers Public Health and Child Welfare
... ‘ONE-A-DAY’ tablets unless you take them regularly.” ...
... ‘ONE-A-DAY’ tablets unless you take them regularly.” ...
Nutrients that Help Relieve Depression, and Support Mental Health:
... and Support Mental Health: Folate: Folate may increase the effectiveness of other treatments for depression. The recommended intake is 400 mcg folate per day. Good food sources of folate include: fortified cereals, liver, cooked dried beans, orange juice, and green vegetables such as okra, spinach a ...
... and Support Mental Health: Folate: Folate may increase the effectiveness of other treatments for depression. The recommended intake is 400 mcg folate per day. Good food sources of folate include: fortified cereals, liver, cooked dried beans, orange juice, and green vegetables such as okra, spinach a ...
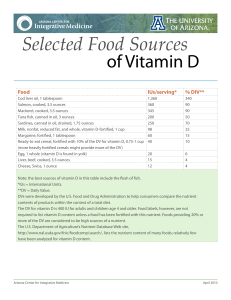
Selected Food Sources - Arizona Center for Integrative Medicine
... Liver, beef, cooked, 3.5 ounces Cheese, Swiss, 1 ounce ...
... Liver, beef, cooked, 3.5 ounces Cheese, Swiss, 1 ounce ...
Scurvy

Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C. Scurvy often presents initially with fatigue, followed by formation of spots on the skin, spongy gums, and bleeding from the mucous membranes. Spots are most abundant on the thighs and legs, and a person may look pale, feel depressed, and be partially immobilized. As scurvy advances, there can be open, suppurating wounds, loss of teeth, yellow skin, fever, neuropathy and finally death from bleeding.While today scurvy is known to be caused by a nutritional deficiency, until the isolation of vitamin C and direct evidence of its link to scurvy in 1932, numerous theories and treatments were proposed, often on little or no experimental data. This inconsistency is attributed to the lack of vitamin C as a distinct concept, and an inability to reliably link different foods (notably present in fresh citrus, watercress, and organ meat) to scurvy. An additional concept required to understand scurvy was the degradation of vitamin C by exposure to air and copper and other transition metal salts such as those of iron, thus changing the links of foods to scurvy over time. Vitamin C is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic (""of, characterized by or having to do with scurvy"").Treatment by fresh food, particularly citrus fruit, was periodically implemented, as it had been since antiquity. However until the 1930s, treatment was inconsistent, with many ineffective treatments used into the 20th century. It was a Scottish surgeon in the Royal Navy, James Lind, who first proved it could be treated with citrus fruit in experiments he described in his 1753 book A Treatise of the Scurvy, though following a failed trial with extracted lime juice, it would be 40 years before effective prevention based on fresh produce became widespread.Scurvy was at one time common among sailors, pirates and others aboard ships at sea longer than perishable fruits and vegetables could be stored (subsisting instead only on cured and salted meats and dried grains) and by soldiers similarly deprived of these foods for extended periods. It was described by Hippocrates (c. 460 BC–c. 380 BC), and herbal cures for scurvy have been known in many native cultures since prehistory. Scurvy was one of the limiting factors of marine travel, often killing large numbers of the passengers and crew on long-distance voyages. This became a significant issue in Europe from the beginning of the modern era in the Age of Discovery in the 15th century, continuing to play a significant role through World War I in the early 20th century. In infants, scurvy is sometimes referred to as Barlow's disease, named after Sir Thomas Barlow, a British physician who described it in 1883. However, Barlow's disease may also refer to mitral valve prolapse. Other eponyms for scurvy include Moeller's disease and Cheadle's disease.Scurvy does not occur in most animals as they can synthesize their own vitamin C. However, humans and other higher primates (the simians—monkeys and apes—and tarsiers), guinea pigs, most or all bats, and some species of birds and fish lack an enzyme (L-gulonolactone oxidase) necessary for such synthesis and must obtain vitamin C through their diet. Vitamin C is widespread in plant tissues, with particularly high concentrations occurring in cruciferous vegetables, capsicum fruit including chili and all colours of bell peppers, citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits), and almost all fruits including botanical fruits that are culinary vegetables, like tomatoes. The fruit with the highest concentration of vitamin C is the Kakadu Plum with nearly 3000 mg per 100g. Cooking significantly reduces the concentration of vitamin C.