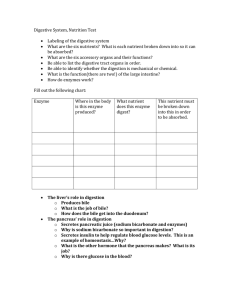
ESTABLISHING A SUGGESTED OPTIMAL NUTRIENT
... This study attempted to find a truly “ideal” daily consumption of nutrients, carbohydrates, protein and fat, on the logical hypothesis that relatively symptom-less and sign-less groups provides the basis for determining what should be the “ideal” daily nutrient level. This approach consistently rev ...
... This study attempted to find a truly “ideal” daily consumption of nutrients, carbohydrates, protein and fat, on the logical hypothesis that relatively symptom-less and sign-less groups provides the basis for determining what should be the “ideal” daily nutrient level. This approach consistently rev ...
Vitamins
... Bacteria used to ferment soy products such as tempeh may provide some vitamin B12, but much of the vitamin B12 may be an inactive form. ...
... Bacteria used to ferment soy products such as tempeh may provide some vitamin B12, but much of the vitamin B12 may be an inactive form. ...
Children
... dark green leafy vegetables, pulses, dried fruit, nuts, wholegrains and fortified breakfast cereals. Iron is essential for healthy blood and it also helps fight infections. Studies have shown that some children in the UK have low intakes of iron. Vitamin C – Fruits, especially citrus fruits and berr ...
... dark green leafy vegetables, pulses, dried fruit, nuts, wholegrains and fortified breakfast cereals. Iron is essential for healthy blood and it also helps fight infections. Studies have shown that some children in the UK have low intakes of iron. Vitamin C – Fruits, especially citrus fruits and berr ...
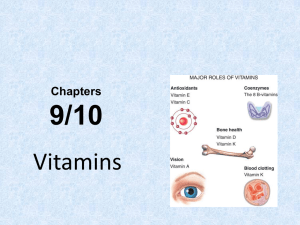
Chapter 9: Vitamins: Vital Keys to Health
... Vitamin A: Not Just For Eyes • A recent study conducted in Nepal showed that women who took vitamin A supplements during pregnancy had a much lower risk of maternal mortality than those who took a placebo. • The researchers concluded that regular and adequate intake of vitamin A or beta-carotene ca ...
... Vitamin A: Not Just For Eyes • A recent study conducted in Nepal showed that women who took vitamin A supplements during pregnancy had a much lower risk of maternal mortality than those who took a placebo. • The researchers concluded that regular and adequate intake of vitamin A or beta-carotene ca ...
【金屬鍵】
... A high intake of which of these fatty acids might be a contributory factor in heart disease? (1 mark) ...
... A high intake of which of these fatty acids might be a contributory factor in heart disease? (1 mark) ...
Slide 1
... . . . and justice for all The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, gender, religion, age, disability, political beliefs, sexual orientation, and marital or family status. (Not all prohibited b ...
... . . . and justice for all The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, gender, religion, age, disability, political beliefs, sexual orientation, and marital or family status. (Not all prohibited b ...
Nutritional Education in the USIn a 1991 survey, only 23%
... the 25(OH)D concentration and vitamin D dose are known, all involve intake of > or = 1000 microg (40000 IU)/d. • Because vitamin D is potentially toxic, intake of >25 microg (1000 IU)/d has been avoided even though the weight of evidence shows that the currently accepted, “no observed adverse effect ...
... the 25(OH)D concentration and vitamin D dose are known, all involve intake of > or = 1000 microg (40000 IU)/d. • Because vitamin D is potentially toxic, intake of >25 microg (1000 IU)/d has been avoided even though the weight of evidence shows that the currently accepted, “no observed adverse effect ...
Nutrition 1
... Throughout your life, the body replaces damaged and worn out cells by making new ones from proteins. Proteins also supply the body with energy, although it is not the body’s main source of energy. ...
... Throughout your life, the body replaces damaged and worn out cells by making new ones from proteins. Proteins also supply the body with energy, although it is not the body’s main source of energy. ...
nutrition - World of Teaching
... because you must obtain them from the foods you eat since your body cannot make them. ...
... because you must obtain them from the foods you eat since your body cannot make them. ...
Nutrition - Cloudfront.net
... because you must obtain them from the foods you eat since your body cannot make them. ...
... because you must obtain them from the foods you eat since your body cannot make them. ...
FINAL B VITAMIN SHOW[1]
... • Critical in the metabolism and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats • Needed to form coenzyme-A (CoA); this is a way to transport carbon atoms within the cell. The transfer of carbon atoms by coenzyme A is important in cellular respiration • Secretion of hormones that assist metabolism, ...
... • Critical in the metabolism and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats • Needed to form coenzyme-A (CoA); this is a way to transport carbon atoms within the cell. The transfer of carbon atoms by coenzyme A is important in cellular respiration • Secretion of hormones that assist metabolism, ...
Basic Principles of Nutriton
... Fats and free radicals • Since saturated fats (from animal foods and the tropical oils) and monounsaturated oils (from olive oil and cold-pressed nut oils) are more chemically stable, they are much less susceptible to oxidation and rancidity than their polyunsaturated cousins, which are mostly foun ...
... Fats and free radicals • Since saturated fats (from animal foods and the tropical oils) and monounsaturated oils (from olive oil and cold-pressed nut oils) are more chemically stable, they are much less susceptible to oxidation and rancidity than their polyunsaturated cousins, which are mostly foun ...
SCF Class 10
... in which they are fried are often reused. These omega 6 fats contribute to inflammation in the blood, heart and lymph systems. Along with sugar foods, this inflammation increases acne breakouts. Friends often influence our food choices. This can be for better or for worse. Some day we will have impr ...
... in which they are fried are often reused. These omega 6 fats contribute to inflammation in the blood, heart and lymph systems. Along with sugar foods, this inflammation increases acne breakouts. Friends often influence our food choices. This can be for better or for worse. Some day we will have impr ...
Vitamin D and Calcium for patients with Epilepsy
... may come from shell sources, usually oyster. Shell sources are often described on the label as a "natural" source. Calcium carbonate from oyster shells is not "refined" and can contain variable amounts of lead. • Chelated calcium, which refers to a special way in which calcium is chemically combin ...
... may come from shell sources, usually oyster. Shell sources are often described on the label as a "natural" source. Calcium carbonate from oyster shells is not "refined" and can contain variable amounts of lead. • Chelated calcium, which refers to a special way in which calcium is chemically combin ...
Hygiene of feeding
... found in vegetables, fruits, cereal, etc. It is hard to digest and has no nutritive value. However, cellulose acts as "roughage" and prevents constipation. ...
... found in vegetables, fruits, cereal, etc. It is hard to digest and has no nutritive value. However, cellulose acts as "roughage" and prevents constipation. ...
A GUIDE TO PLANT-BASED DINING AT TUFTS
... contain some protein, but the best sources are legumes and nuts. Soybeans are the only legume that contains complete protein and are the basis of tofu, tempeh, miso, and soy milk. In addition to high protein content, soy foods are rich in minerals and have no cholesterol. Soy products are available ...
... contain some protein, but the best sources are legumes and nuts. Soybeans are the only legume that contains complete protein and are the basis of tofu, tempeh, miso, and soy milk. In addition to high protein content, soy foods are rich in minerals and have no cholesterol. Soy products are available ...
chapter overview
... 2. Alcohol and certain intestinal diseases can also lead to deficiency states (cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease) F. Preservation of Vitamins in Food 1. Water soluble vitamins, especially thiamin, vitamin C, and folate, can be destroyed with improper storage and excessive cooking 2. H ...
... 2. Alcohol and certain intestinal diseases can also lead to deficiency states (cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease) F. Preservation of Vitamins in Food 1. Water soluble vitamins, especially thiamin, vitamin C, and folate, can be destroyed with improper storage and excessive cooking 2. H ...
Take Serving Sizes to Heart
... Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calor ie diet. Your daily values may be higher or low er depending on your calorie needs: Total Fat Sat Fat Cholesterol Sodium Total Carbohydrate3 Dietary Fiber2 ...
... Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calor ie diet. Your daily values may be higher or low er depending on your calorie needs: Total Fat Sat Fat Cholesterol Sodium Total Carbohydrate3 Dietary Fiber2 ...
Lecture Materials/Unit 1
... to vitamin E supplementation; involved in immunity; injection or feed ...
... to vitamin E supplementation; involved in immunity; injection or feed ...
EAT FORTIFIED FOOD TO STAY STRONG AND HEALTHY DRAFT
... restores micronutrients to the white and brown bread flour and maize meal that may be lost during the manufacturing process, as well as adding additional vitamins and minerals. It Samp, grits, maize rice, maize flour, cake flour, selfraising flour and semolina (or goods baked with these products) ar ...
... restores micronutrients to the white and brown bread flour and maize meal that may be lost during the manufacturing process, as well as adding additional vitamins and minerals. It Samp, grits, maize rice, maize flour, cake flour, selfraising flour and semolina (or goods baked with these products) ar ...
Vitamin

A vitamin (US /ˈvaɪtəmɪn/ and UK /ˈvɪtəmɪn/) is an organic compound and a vital nutrient that an organism requires in limited amounts. An organic chemical compound (or related set of compounds) is called a vitamin when the organism cannot synthesize the compound in sufficient quantities, and it must be obtained through the diet; thus, the term ""vitamin"" is conditional upon the circumstances and the particular organism. For example, ascorbic acid (one form of vitamin C) is a vitamin for humans, but not for most other animal organisms. Supplementation is important for the treatment of certain health problems, but there is little evidence of nutritional benefit when used by otherwise healthy people.By convention, the term vitamin includes neither other essential nutrients, such as dietary minerals, essential fatty acids, or essential amino acids (which are needed in greater amounts than vitamins) nor the great number of other nutrients that promote health, and are required less often to maintain the health of the organism. Thirteen vitamins are universally recognized at present. Vitamins are classified by their biological and chemical activity, not their structure. Thus, each ""vitamin"" refers to a number of vitamer compounds that all show the biological activity associated with a particular vitamin. Such a set of chemicals is grouped under an alphabetized vitamin ""generic descriptor"" title, such as ""vitamin A"", which includes the compounds retinal, retinol, and four known carotenoids. Vitamers by definition are convertible to the active form of the vitamin in the body, and are sometimes inter-convertible to one another, as well.Vitamins have diverse biochemical functions. Some, such as vitamin D, have hormone-like functions as regulators of mineral metabolism, or regulators of cell and tissue growth and differentiation (such as some forms of vitamin A). Others function as antioxidants (e.g., vitamin E and sometimes vitamin C). The largest number of vitamins, the B complex vitamins, function as precursors for enzyme cofactors, that help enzymes in their work as catalysts in metabolism. In this role, vitamins may be tightly bound to enzymes as part of prosthetic groups: For example, biotin is part of enzymes involved in making fatty acids. They may also be less tightly bound to enzyme catalysts as coenzymes, detachable molecules that function to carry chemical groups or electrons between molecules. For example, folic acid may carry methyl, formyl, and methylene groups in the cell. Although these roles in assisting enzyme-substrate reactions are vitamins' best-known function, the other vitamin functions are equally important.Until the mid-1930s, when the first commercial yeast-extract vitamin B complex and semi-synthetic vitamin C supplement tablets were sold, vitamins were obtained solely through food intake, and changes in diet (which, for example, could occur during a particular growing season) usually greatly altered the types and amounts of vitamins ingested. However, vitamins have been produced as commodity chemicals and made widely available as inexpensive semisynthetic and synthetic-source multivitamin dietary and food supplements and additives, since the middle of the 20th century. Study of structural activity, function and their role in maintaining health is called as vitaminology.











![FINAL B VITAMIN SHOW[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008774373_1-f0814fbf384f7a06f9bab3474db9d76d-300x300.png)










