WORLD WAR II 1939-1945
... EFFECTS U.S. and the Soviet Union compete to influence and rebuild Europe Cold War- period of conflict between U.S. and the Soviet Union 1949-1991 ...
... EFFECTS U.S. and the Soviet Union compete to influence and rebuild Europe Cold War- period of conflict between U.S. and the Soviet Union 1949-1991 ...
WWII as pdfs in 3 parts
... – Along with France, no more German territorial demands would be tolerated ...
... – Along with France, no more German territorial demands would be tolerated ...
Beginning of second world war in 1939
... September 1939 to Poland. The United Kingdom and France proclaimed two days later war to Germany. The declared war on Germany the Soviet Union, which with signed Germany the pact about non-aggression, occupied East part of Poland. Territory of Poland was splitted Germany and SSSR. In April 1940 into ...
... September 1939 to Poland. The United Kingdom and France proclaimed two days later war to Germany. The declared war on Germany the Soviet Union, which with signed Germany the pact about non-aggression, occupied East part of Poland. Territory of Poland was splitted Germany and SSSR. In April 1940 into ...
1. When speaking about the "Holocaust,"
... 1. When speaking about the "Holocaust," what time period are we referring to? The "Holocaust" refers to the period from January 30, 1933, when Hitler became Chancellor of Germany, to May 8, 1945 (V-E Day), the end of the war in Europe. 2. How many Jews were murdered during the Holocaust? Six mil ...
... 1. When speaking about the "Holocaust," what time period are we referring to? The "Holocaust" refers to the period from January 30, 1933, when Hitler became Chancellor of Germany, to May 8, 1945 (V-E Day), the end of the war in Europe. 2. How many Jews were murdered during the Holocaust? Six mil ...
The Rise of Dictators
... power constitutionally rather than by force of arms. He spoke to scores of mass audiences, calling for the German people to create a new empire which would rule the world for 1,000 years. In 1932, Hitler ran for President and won 30% of the vote. A political deal was made to make Hitler chancellor i ...
... power constitutionally rather than by force of arms. He spoke to scores of mass audiences, calling for the German people to create a new empire which would rule the world for 1,000 years. In 1932, Hitler ran for President and won 30% of the vote. A political deal was made to make Hitler chancellor i ...
Unit: World War II Topic: The Tide Turns
... B. Early on December 7, 1941, the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, killing over 2400 Americans. ...
... B. Early on December 7, 1941, the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, killing over 2400 Americans. ...
2nd World War The Second World War was the largest and richest
... Nazi Germany had developed a rocket program, launching explosive missiles against civilian targets in Britain. At war’s end, the US and USSR raced against each other to round up as many of the German scientists as they could to develop their own programs. This resulted not only in intercontinental b ...
... Nazi Germany had developed a rocket program, launching explosive missiles against civilian targets in Britain. At war’s end, the US and USSR raced against each other to round up as many of the German scientists as they could to develop their own programs. This resulted not only in intercontinental b ...
CPUSH (Unit , # )
... a. Totalitarian leaders came to power by promising _________________ and promoting ______________________________ b. Dictators controlled all aspects of the nation by eliminating __________________, denying ____________________________, using censorship, secret ______________________ 2. Joseph Stali ...
... a. Totalitarian leaders came to power by promising _________________ and promoting ______________________________ b. Dictators controlled all aspects of the nation by eliminating __________________, denying ____________________________, using censorship, secret ______________________ 2. Joseph Stali ...
UNIT 14 – Great Depression and World War II 1929 – 1945 1st
... a. citizens well informed, do their part b. women to factories, __________________________, buying bonds… 4. ___________________________ movements in Europe B. Japanese Internment ...
... a. citizens well informed, do their part b. women to factories, __________________________, buying bonds… 4. ___________________________ movements in Europe B. Japanese Internment ...
Fascist Dictatorships in Italy and Germany
... systematic suppression and extermination of millions of Jews and other so-called “impure” population groups in Nazi-occupied countries ...
... systematic suppression and extermination of millions of Jews and other so-called “impure” population groups in Nazi-occupied countries ...
Overview: The War in Europe In 1918, the Central Powers and Allies
... giving him the Sudetenland, a part of Czechoslovakia (which itself was a nation created as a result of the Versailles Treaty). Later, he simply seized the rest of Czechoslovakia. Again, the Allies merely watched. Standard 10.8 Introduction ...
... giving him the Sudetenland, a part of Czechoslovakia (which itself was a nation created as a result of the Versailles Treaty). Later, he simply seized the rest of Czechoslovakia. Again, the Allies merely watched. Standard 10.8 Introduction ...
World War II
... • Limited immigration of Jews by U.S. & other Western countries • War Refugee Board 1944 – Too little too late? – Lacked money & authority ...
... • Limited immigration of Jews by U.S. & other Western countries • War Refugee Board 1944 – Too little too late? – Lacked money & authority ...
World War II
... • Limited immigration of Jews by U.S. & other Western countries • War Refugee Board 1944 – Too little too late? – Lacked money & authority ...
... • Limited immigration of Jews by U.S. & other Western countries • War Refugee Board 1944 – Too little too late? – Lacked money & authority ...
WWII - WF - D
... • August, 1942, Germany begins its assault on the Russian city of Stalingrad. In a battle that will rage for six months, and take hundreds of thousands of German and Russian lives, the Red Army finally defeats invading Nazis. The long, bloody battle proves to be a turning point in the war, as German ...
... • August, 1942, Germany begins its assault on the Russian city of Stalingrad. In a battle that will rage for six months, and take hundreds of thousands of German and Russian lives, the Red Army finally defeats invading Nazis. The long, bloody battle proves to be a turning point in the war, as German ...
Totalitarian Regimes 2012-2013
... - Adolf Hitler and Nazism, a type of Fascism in Germany - Benito Mussolini and Fascism in Italy * Most of the new Republics of Europe were not meeting the economic and social needs of their people * Weimar Republic of Germany could not deal with inflation in the German economy * The Italian Social R ...
... - Adolf Hitler and Nazism, a type of Fascism in Germany - Benito Mussolini and Fascism in Italy * Most of the new Republics of Europe were not meeting the economic and social needs of their people * Weimar Republic of Germany could not deal with inflation in the German economy * The Italian Social R ...
The Largest, Costliest, and Deadliest Conflict WHAP/Napp “Hitler
... And by 1933, Hitler withdrew from the League of Nations In 1935, Hitler openly rebuilt German military, violating Treaty of Versailles In 1936, Hitler sent German troops into Rhineland, a demilitarized zone In 1937, Hitler signed the Anti-Comintern Pact with Italy and Japan Hitler made public desire ...
... And by 1933, Hitler withdrew from the League of Nations In 1935, Hitler openly rebuilt German military, violating Treaty of Versailles In 1936, Hitler sent German troops into Rhineland, a demilitarized zone In 1937, Hitler signed the Anti-Comintern Pact with Italy and Japan Hitler made public desire ...
How Did Hitler Happen Notes?
... -Hitler and the Nazis take over most of Europe -1941: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor and the U.S. enters the war (Turning Point) -1942-43: Battle of Stalingrad-Germany attacks the Soviet Union and looks like they may defeat the Soviets until the Russian winter stops the Germans at Stalingrad. The German ...
... -Hitler and the Nazis take over most of Europe -1941: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor and the U.S. enters the war (Turning Point) -1942-43: Battle of Stalingrad-Germany attacks the Soviet Union and looks like they may defeat the Soviets until the Russian winter stops the Germans at Stalingrad. The German ...
Holocaust Glossary and Timeline
... Immediately, Hitler stated, "The Reich Government has enacted the following law which is hereby promulgated. Section 1. The office of Reich President will be combined with that of Reich Chancellor. The existing authority of the Reich President will consequently be transferred to the Führer and Reich ...
... Immediately, Hitler stated, "The Reich Government has enacted the following law which is hereby promulgated. Section 1. The office of Reich President will be combined with that of Reich Chancellor. The existing authority of the Reich President will consequently be transferred to the Führer and Reich ...
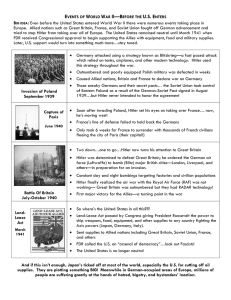
BIG IDEA: Even before the United States entered World War II there
... BIG IDEA: Even before the United States entered World War II there were numerous events taking place in Europe. Allied nations such as Great Britain, France, and Soviet Union fought off German advancement and tried to stop Hitler from taking over all of Europe. The United States remained neutral unt ...
... BIG IDEA: Even before the United States entered World War II there were numerous events taking place in Europe. Allied nations such as Great Britain, France, and Soviet Union fought off German advancement and tried to stop Hitler from taking over all of Europe. The United States remained neutral unt ...
Background - Colby College
... Decisive step: break of Munich Agreement through the invasion of Czechoslovakia, March 1939 ...
... Decisive step: break of Munich Agreement through the invasion of Czechoslovakia, March 1939 ...
PowerPoint 2
... Sitzkrieg: The sitting war May 1940: Hitler enters France by passing through Ardennes and begins to march towards Paris ...
... Sitzkrieg: The sitting war May 1940: Hitler enters France by passing through Ardennes and begins to march towards Paris ...
Between the Wars & World War II Study Guide
... to death camps where they were killed with poisonous gas and then their bodies were cremated. ...
... to death camps where they were killed with poisonous gas and then their bodies were cremated. ...
Ch 19 study guide - Spring Branch ISD
... Italy, a Fascist leader promised that a strong government would return the social order. ...
... Italy, a Fascist leader promised that a strong government would return the social order. ...
Blank 7 - Spring Branch ISD
... Italy, a Fascist leader promised that a strong government would return the social order. ...
... Italy, a Fascist leader promised that a strong government would return the social order. ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.