ppt - Study the Past -- Jeffrey L. Littlejohn
... during WWI -- was dissatisfied with small territorial gains. C. Germany: excluded from negotiations, forced to accept $33 billion debt, reduction of military, loss of territory, & war guilt. D. Japan felt it had fought heroically and received little; it wanted China and hegemony in East Asia. E. In ...
... during WWI -- was dissatisfied with small territorial gains. C. Germany: excluded from negotiations, forced to accept $33 billion debt, reduction of military, loss of territory, & war guilt. D. Japan felt it had fought heroically and received little; it wanted China and hegemony in East Asia. E. In ...
Chapter 23 – World War II Erupts The Main Idea
... After Germany invaded Poland, Congress passed FDR’s cash-andcarry program. It allowed countries at war to buy American goods if they paid cash and collected the goods in U.S. ports. Roosevelt hoped this would help the Allies. By the end of 1940, however, German victories led the government to pass t ...
... After Germany invaded Poland, Congress passed FDR’s cash-andcarry program. It allowed countries at war to buy American goods if they paid cash and collected the goods in U.S. ports. Roosevelt hoped this would help the Allies. By the end of 1940, however, German victories led the government to pass t ...
Treaty of Versallies – end of WWI
... WWI killed a lot of workers and customers After years of humiliation and starvation, Germans looked for a strong leader. ...
... WWI killed a lot of workers and customers After years of humiliation and starvation, Germans looked for a strong leader. ...
WW2 Europe
... • Oil refineries, rail yards, factories, U-boat bases • British pilots used “saturation bombing” – Large # of bombs over wide area at night • Often hit cities to destroy civilian morale • August 1944, US planes dropped 1,000+ bombs on oil-production facility in Poland – Five miles away stood Aushwit ...
... • Oil refineries, rail yards, factories, U-boat bases • British pilots used “saturation bombing” – Large # of bombs over wide area at night • Often hit cities to destroy civilian morale • August 1944, US planes dropped 1,000+ bombs on oil-production facility in Poland – Five miles away stood Aushwit ...
World War II Begins B. What was Hitler`s motivation for German
... In 1935, Mussolini invaded . Mussolini became invasion and welcomed Hitler’s . In 1936, both sent troops to aid the This alliance became known as the ...
... In 1935, Mussolini invaded . Mussolini became invasion and welcomed Hitler’s . In 1936, both sent troops to aid the This alliance became known as the ...
Cold War in Europe - Spring Branch ISD
... • The League of Nations was proven to act slowly, unable to make quick decisions o The Council of the League of Nations only met four times a year and decisions had to be agreed by all nations o When countries called for the League to intervene, the League had to set up an emergency meeting, hold di ...
... • The League of Nations was proven to act slowly, unable to make quick decisions o The Council of the League of Nations only met four times a year and decisions had to be agreed by all nations o When countries called for the League to intervene, the League had to set up an emergency meeting, hold di ...
World War II and Its Aftermath
... The first pact was an economic agreement, which Ribbentrop and Molotov signed on August 19, 1939. The economic agreement committed the Soviet Union to provide food products as well as raw materials to Germany in exchange for furnished products such as machinery from Germany. During the first years o ...
... The first pact was an economic agreement, which Ribbentrop and Molotov signed on August 19, 1939. The economic agreement committed the Soviet Union to provide food products as well as raw materials to Germany in exchange for furnished products such as machinery from Germany. During the first years o ...
EH Chapter 27 WWII Timeline
... Hitler violates the Treaty of Versailles by sending German troops to occupy the Rhineland. Great Britain and France do nothing in response. ...
... Hitler violates the Treaty of Versailles by sending German troops to occupy the Rhineland. Great Britain and France do nothing in response. ...
The Pacific Theater
... Wehrmacht rolled over virtually all opposition. The latter war years proved more challenging for Germany. When Hitler failed to bomb Britain into submission in 1940 (the celebrated “Battle of Britain”), he made the same fatal error that Napoleon Bonaparte had made a century and a quarter earlier: in ...
... Wehrmacht rolled over virtually all opposition. The latter war years proved more challenging for Germany. When Hitler failed to bomb Britain into submission in 1940 (the celebrated “Battle of Britain”), he made the same fatal error that Napoleon Bonaparte had made a century and a quarter earlier: in ...
Chapter 16/17
... The Entire World Was Dealing With the Depression – Not Just the United States London Conference ...
... The Entire World Was Dealing With the Depression – Not Just the United States London Conference ...
Chapter 17 - WWII
... 42. suicide mission in which young Japanese pilots flew their planes into U.S. fighting ships at sea 43. policy that sought peace and stability by satisfying reasonable demands of dissatisfied powers 44. process of preparing troops and supplies for war 45. period of political tension between the Uni ...
... 42. suicide mission in which young Japanese pilots flew their planes into U.S. fighting ships at sea 43. policy that sought peace and stability by satisfying reasonable demands of dissatisfied powers 44. process of preparing troops and supplies for war 45. period of political tension between the Uni ...
Hitler`s Aims - mrblacksclasses
... Strong NAZI party in Austria Opposition from Mussolini who had signed an agreement with Austria guaranteeing her independence…Hitler’s solution? ...
... Strong NAZI party in Austria Opposition from Mussolini who had signed an agreement with Austria guaranteeing her independence…Hitler’s solution? ...
Chapter 17-2 Questions ppt
... Ocean before the United States was even in the war? World War II began when Germany invaded ...
... Ocean before the United States was even in the war? World War II began when Germany invaded ...
World War II 1939-1945: 16-1 Hitler’s Lightening War
... Sept 15—Jews stripped of rights by Nuremburg Race Laws •Deprived German Jews of their rights of citizenship, giving them the status of "subjects" in Hitler's Reich. •The laws also made it forbidden for Jews to marry or have sexual relations with Aryans or to employ young Aryan women as household hel ...
... Sept 15—Jews stripped of rights by Nuremburg Race Laws •Deprived German Jews of their rights of citizenship, giving them the status of "subjects" in Hitler's Reich. •The laws also made it forbidden for Jews to marry or have sexual relations with Aryans or to employ young Aryan women as household hel ...
WWII PowerPoint - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
... • Why do you think the League of Nations, among other western European nations (i.e., Great Britain, France) did NOTHING? ANSWER: because they would do ANYTHING to keep peace and not start another war. ...
... • Why do you think the League of Nations, among other western European nations (i.e., Great Britain, France) did NOTHING? ANSWER: because they would do ANYTHING to keep peace and not start another war. ...
Social Studies 11- World War Two Document Based Analysis
... keeping peace depends on holding back the aggressor. After Hitler’s seizure of Austria in March, I appealed to the government. I asked that Britain, together with France and other powers, guarantee the security of Czechoslovakia. If that course had been followed, events would not have fallen into th ...
... keeping peace depends on holding back the aggressor. After Hitler’s seizure of Austria in March, I appealed to the government. I asked that Britain, together with France and other powers, guarantee the security of Czechoslovakia. If that course had been followed, events would not have fallen into th ...
Unit 7 - Section 1
... in Munich to discuss Germany’s aggressiveness in the Sudetenland (Czechoslovakia) and Austria Agreement that Germany could keep these possessions but should stop aggressive nature ...
... in Munich to discuss Germany’s aggressiveness in the Sudetenland (Czechoslovakia) and Austria Agreement that Germany could keep these possessions but should stop aggressive nature ...
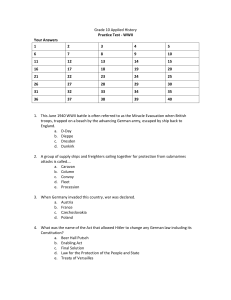
Grade 10 History
... c. Convoy d. Fleet e. Procession 3. When Germany invaded this country, war was declared. a. Austria b. France c. Czechoslovakia d. Poland 4. What was the name of the Act that allowed Hitler to change any German law including its Constitution? a. Beer Hall Putsch b. Enabling Act c. Final Solution d. ...
... c. Convoy d. Fleet e. Procession 3. When Germany invaded this country, war was declared. a. Austria b. France c. Czechoslovakia d. Poland 4. What was the name of the Act that allowed Hitler to change any German law including its Constitution? a. Beer Hall Putsch b. Enabling Act c. Final Solution d. ...
WWII Review PowerPoint
... Great Britain.........................$31 billion Soviet Union..........................$11 billion ...
... Great Britain.........................$31 billion Soviet Union..........................$11 billion ...
Chapter 6 : Canada at War
... Germany. Once he became leader, all other political parties were outlawed and he became dictator or sole ruler of Germany. ...
... Germany. Once he became leader, all other political parties were outlawed and he became dictator or sole ruler of Germany. ...
Causes of World War 2
... Hitlers actions • 1934 - increased size of army, navy, and created an airforce. • 1936 - Ordered German troops to enter the Rhineland. As well in 1936 two important alliances were made, between Germany and Japan, and Germany and Italy. • 1938 - Hitler began taking back the land that had been taken ...
... Hitlers actions • 1934 - increased size of army, navy, and created an airforce. • 1936 - Ordered German troops to enter the Rhineland. As well in 1936 two important alliances were made, between Germany and Japan, and Germany and Italy. • 1938 - Hitler began taking back the land that had been taken ...
The World at War - Merrillville Community School
... 350 miles from Japan 100,000 Japanese pledged to fight to the death Japan had 2,000 kamikazes vs. Americans 1,300 warships and 180,000 troops American soldiers made Banzai charges- these are where they try to kill as many of the enemies as ...
... 350 miles from Japan 100,000 Japanese pledged to fight to the death Japan had 2,000 kamikazes vs. Americans 1,300 warships and 180,000 troops American soldiers made Banzai charges- these are where they try to kill as many of the enemies as ...
including draftees before Pearl Harbor 10110114 By Year
... 1933. He declares himself dictator. He banned ALL other political parties. He began jailing and killing those who disagreed with him. Hitler’s goal was to wipe out all Jews. ...
... 1933. He declares himself dictator. He banned ALL other political parties. He began jailing and killing those who disagreed with him. Hitler’s goal was to wipe out all Jews. ...
The Road to WWII American Isolationism
... would engage in no further territorial aggression in Europe • British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain returned home declaring to the British public that “I believe it is peace for our time” (it wasn’t!) ...
... would engage in no further territorial aggression in Europe • British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain returned home declaring to the British public that “I believe it is peace for our time” (it wasn’t!) ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.