World War II
... 4. The North African Front A. Erwin Rommel (“Desert Fox”)– secure N. Africa for AXIS Powers B. “Beat Hitler first” strategy – defeat AXIS Powers in Europe first ...
... 4. The North African Front A. Erwin Rommel (“Desert Fox”)– secure N. Africa for AXIS Powers B. “Beat Hitler first” strategy – defeat AXIS Powers in Europe first ...
Action This Day Vol.1 No.3
... the City of Light, the symbol of France, was liberated by the Allied Armies. all of paris was ecstatic; parisiens embraced their liberators and danced in the streets. the German occupation had been terrible, from the draconian rules enforced by the Germans to the shortages of food and consumer goods ...
... the City of Light, the symbol of France, was liberated by the Allied Armies. all of paris was ecstatic; parisiens embraced their liberators and danced in the streets. the German occupation had been terrible, from the draconian rules enforced by the Germans to the shortages of food and consumer goods ...
Chapter 29-Totalitarianism Powerpoint
... • extremely fascist , nationalistic and totalitarian • based on beliefs of the National Socialist German Workers Party • belief in the racial superiority of the Aryan, the “master race” • belief that all Germans should have “lebensraum” or living space in Europe •Violent hatred towards Jews and blam ...
... • extremely fascist , nationalistic and totalitarian • based on beliefs of the National Socialist German Workers Party • belief in the racial superiority of the Aryan, the “master race” • belief that all Germans should have “lebensraum” or living space in Europe •Violent hatred towards Jews and blam ...
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit V Reading
... Hitler’s Nazi initiative had given direction, hope, and stability to a people who had either lost or forfeited much of their culture after the Great War. By 1936, the swastika hung in Berlin next to the Olympic flag. Hitler’s and His Allies In 1933, Hitler had taken the role of Chancellor. He had su ...
... Hitler’s Nazi initiative had given direction, hope, and stability to a people who had either lost or forfeited much of their culture after the Great War. By 1936, the swastika hung in Berlin next to the Olympic flag. Hitler’s and His Allies In 1933, Hitler had taken the role of Chancellor. He had su ...
Scavenger Hunt
... On August 8, 1938, just a few weeks after the Nazi occupation of Austria, prisoners from the Dachau, concentration camp near Munich, were transferred to the Austrian town of Mauthausen, near Linz. They were brought to the rock quarry there, known as the "Wiener Graben", where they began to build the ...
... On August 8, 1938, just a few weeks after the Nazi occupation of Austria, prisoners from the Dachau, concentration camp near Munich, were transferred to the Austrian town of Mauthausen, near Linz. They were brought to the rock quarry there, known as the "Wiener Graben", where they began to build the ...
U.S. History Notes ~ 1933 – 1941 ~
... themselves in the Rome-Berlin Axis. 3. Japan slowly began gaining strength, refusing to cooperate with the world and quickly arming itself by ending the Washington Naval Treaty ( 5:5:3) in 1934 and walking out of the London Conference. 4. In 1935, Mussolini attacked Ethiopia, conquering it, but the ...
... themselves in the Rome-Berlin Axis. 3. Japan slowly began gaining strength, refusing to cooperate with the world and quickly arming itself by ending the Washington Naval Treaty ( 5:5:3) in 1934 and walking out of the London Conference. 4. In 1935, Mussolini attacked Ethiopia, conquering it, but the ...
File
... The Allies developed a “Europe First” plan to defeat Hitler. Victories at Stalingrad and Midway proved to be key turning points. Allied dominance in North Africa, the invasion of Italy, and bombing raids in Germany increased pressure on the Axis. ...
... The Allies developed a “Europe First” plan to defeat Hitler. Victories at Stalingrad and Midway proved to be key turning points. Allied dominance in North Africa, the invasion of Italy, and bombing raids in Germany increased pressure on the Axis. ...
Chapter 28 Study Guide
... Chiang Kai-Shek Neville Chamberlain appeasement Munich Agreement Polish Corridor Pact of Steel Non-aggression Pact “Winter War” “The Phony War” Questions 1. What had Hitler promised in his book Mein Kampf? What was the population of the Third Reich after Germany annexed Austria in 1938? 2. Why were ...
... Chiang Kai-Shek Neville Chamberlain appeasement Munich Agreement Polish Corridor Pact of Steel Non-aggression Pact “Winter War” “The Phony War” Questions 1. What had Hitler promised in his book Mein Kampf? What was the population of the Third Reich after Germany annexed Austria in 1938? 2. Why were ...
Chapter 35 - Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Shadow of War I. The
... o Blitzing without mercy, he then struck a paralyzing blow toward France, which was forced to surrender by late June of that year. o The fall of France was shocking, because now, all that stood between Hitler and the world was Britain: if the English lost, Hitler would have all of Europe in which to ...
... o Blitzing without mercy, he then struck a paralyzing blow toward France, which was forced to surrender by late June of that year. o The fall of France was shocking, because now, all that stood between Hitler and the world was Britain: if the English lost, Hitler would have all of Europe in which to ...
sample
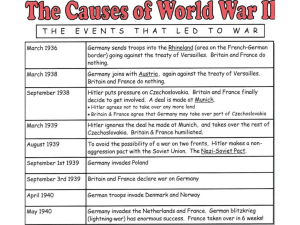
... Hitler challenged the Versailles settlement step by step. He rapidly set about rebuilding Germany’s armed forces, including its air force. Rearmament was already well under way by the time it was officially announced in 1935. The following year, German troops marched into the demilitarized Rhineland ...
... Hitler challenged the Versailles settlement step by step. He rapidly set about rebuilding Germany’s armed forces, including its air force. Rearmament was already well under way by the time it was officially announced in 1935. The following year, German troops marched into the demilitarized Rhineland ...
Causes of WWII - ECI Summer School 2014
... • In 1935, the League received its second test: Italy. • Italy was disappointed with the terms of the Treaty of Versailles. Italy had expected more land as a reward for changing sides during the war (to the Allies). Italy was also experiencing a depressed economy following the war, with high unemplo ...
... • In 1935, the League received its second test: Italy. • Italy was disappointed with the terms of the Treaty of Versailles. Italy had expected more land as a reward for changing sides during the war (to the Allies). Italy was also experiencing a depressed economy following the war, with high unemplo ...
Nazi Fourth Reich - Friends of the Sabbath
... Commissioner for Germany, issued an amnesty for industrialists convicted of war crimes. The two most powerful Nazi industrialists, Alfried Krupp of Krupp Industries and Friedrich Flick, whose Flick Group eventually owned a 40 per cent stake in Daimler-Benz, were released from prison after serving ba ...
... Commissioner for Germany, issued an amnesty for industrialists convicted of war crimes. The two most powerful Nazi industrialists, Alfried Krupp of Krupp Industries and Friedrich Flick, whose Flick Group eventually owned a 40 per cent stake in Daimler-Benz, were released from prison after serving ba ...
Hitler`s Operation Barbarossa - Mr. Longacre`s US History Website
... 3) The failed battle of Britain led a frustrated Hitler to turn on his former ally, and the Nazi war machine opened the “Eastern Front” by invading the Soviet Union in June 1941. Despite the NonAgression Pact, many had already concluded that the German invasion of the Soviet Union was an inevitibili ...
... 3) The failed battle of Britain led a frustrated Hitler to turn on his former ally, and the Nazi war machine opened the “Eastern Front” by invading the Soviet Union in June 1941. Despite the NonAgression Pact, many had already concluded that the German invasion of the Soviet Union was an inevitibili ...
The World at War (again)
... – Many point to General Tojo as the true leader of Japan – When he spoke to Surrender at the end of WWII, it was the first time ordinary citizens had ever heard his voice ...
... – Many point to General Tojo as the true leader of Japan – When he spoke to Surrender at the end of WWII, it was the first time ordinary citizens had ever heard his voice ...
Chapter 26 – 60 million people died
... Interventionist alarmed by 1936 Germany and Italy agreed to cooperate as Axis Power + Japan. Germany left League 1938. Hitler annexed Austria as part of Third Reich and wanted to take Sudetenland – Checz. May FDR increased navy past treaty. Outbreak of War in Europe – France and Britain and Munich ...
... Interventionist alarmed by 1936 Germany and Italy agreed to cooperate as Axis Power + Japan. Germany left League 1938. Hitler annexed Austria as part of Third Reich and wanted to take Sudetenland – Checz. May FDR increased navy past treaty. Outbreak of War in Europe – France and Britain and Munich ...
Vocabulary - FDR Library
... Secret Service was barred. Munich Agreement - Accord reached in September, 1938 at which Britain and France agreed to Hitler’s demand to annex Czechoslovakia’s Sudetenland. Nazi - German political party of the 1930s and ‘40s which promoted extreme nationalism, aggression, and racism. Nazi-Soviet Mut ...
... Secret Service was barred. Munich Agreement - Accord reached in September, 1938 at which Britain and France agreed to Hitler’s demand to annex Czechoslovakia’s Sudetenland. Nazi - German political party of the 1930s and ‘40s which promoted extreme nationalism, aggression, and racism. Nazi-Soviet Mut ...
Intro to World War Two Work Package 2015
... fig 2: - This is a picture of Italian Fascist leader Benito Mussolini after a march of his supporters on Rome. 1. What message does this image communicate to the viewer? 2. Based on your understanding of the authority of a dictator, how would an image like this reaffirm their position in government? ...
... fig 2: - This is a picture of Italian Fascist leader Benito Mussolini after a march of his supporters on Rome. 1. What message does this image communicate to the viewer? 2. Based on your understanding of the authority of a dictator, how would an image like this reaffirm their position in government? ...
World.WWII.4.29 - Steven-J
... 1. What started WWII? 2. How did the US get into WWII? 3. Why did Hitler invade the Soviet Union? 4. Who won the Battle of Stalingrad? ...
... 1. What started WWII? 2. How did the US get into WWII? 3. Why did Hitler invade the Soviet Union? 4. Who won the Battle of Stalingrad? ...
Chapter 37: Franklin D. Roosevelt And The Shadow of War
... i. Blitzing without stop or mercy, he then forced a paralyzing blow toward France, which was forced to surrender by late June of that year. ii. The fall of France was shocking, because now, all that stood between Hitler and the world was Britain: if the English lost, Hitler would have all of Europe ...
... i. Blitzing without stop or mercy, he then forced a paralyzing blow toward France, which was forced to surrender by late June of that year. ii. The fall of France was shocking, because now, all that stood between Hitler and the world was Britain: if the English lost, Hitler would have all of Europe ...
37_FDR_and_Shadow_of_War
... i. Blitzing without stop or mercy, he then forced a paralyzing blow toward France, which was forced to surrender by late June of that year. ii. The fall of France was shocking, because now, all that stood between Hitler and the world was Britain: if the English lost, Hitler would have all of Europe ...
... i. Blitzing without stop or mercy, he then forced a paralyzing blow toward France, which was forced to surrender by late June of that year. ii. The fall of France was shocking, because now, all that stood between Hitler and the world was Britain: if the English lost, Hitler would have all of Europe ...
WWII - Mr. Zittle`s Classroom
... • Mein Kampf—basic beliefs of Nazism, based on extreme nationalism • Wants to unite German-speaking people, enforce racial “purification” • 1932, 6 million unemployed; many men join Hitler’s private army • Nazis become strongest political party; Hitler named chancellor • Third Reich established ...
... • Mein Kampf—basic beliefs of Nazism, based on extreme nationalism • Wants to unite German-speaking people, enforce racial “purification” • 1932, 6 million unemployed; many men join Hitler’s private army • Nazis become strongest political party; Hitler named chancellor • Third Reich established ...
Unit 17 ~ World War II
... Munich • When they arrived, Hitler promised this would be his “last territorial demand” • They two leaders chose to believe him • On September 30, 1938 all three signed the Munich Agreement, which turned the Sudetenland over to Germany without a single shot being fired ...
... Munich • When they arrived, Hitler promised this would be his “last territorial demand” • They two leaders chose to believe him • On September 30, 1938 all three signed the Munich Agreement, which turned the Sudetenland over to Germany without a single shot being fired ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.