Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... 16. What are the respective concentrations (M) of Na+ and SO42- produced by dissolving 0.500 mol Na2SO4 in water and diluting to 1.33 L? (a). 0.665 and 0.665 (b). 0.665 and 1.33 (c). 0.752 and 0.376 (d) 0.376 and 0.752 Explanation: Calculate the molarity of the solution and then the molarities of in ...
... 16. What are the respective concentrations (M) of Na+ and SO42- produced by dissolving 0.500 mol Na2SO4 in water and diluting to 1.33 L? (a). 0.665 and 0.665 (b). 0.665 and 1.33 (c). 0.752 and 0.376 (d) 0.376 and 0.752 Explanation: Calculate the molarity of the solution and then the molarities of in ...
workbook Chem (WP)
... a. copper (I) oxide b. nickel (III) sulfide c. manganese (IV) oxide d. yttrium (III) chloride e. titanium (III) nitride 4. Name the following: a. FeO(s) b. CoF2(s) c. V3N5(s) d. Cr3P2(s) e. MgS(s) Complex Ions 1. groups of atoms that remain together in a chemical reaction and contain a charge 2. nam ...
... a. copper (I) oxide b. nickel (III) sulfide c. manganese (IV) oxide d. yttrium (III) chloride e. titanium (III) nitride 4. Name the following: a. FeO(s) b. CoF2(s) c. V3N5(s) d. Cr3P2(s) e. MgS(s) Complex Ions 1. groups of atoms that remain together in a chemical reaction and contain a charge 2. nam ...
uplift luna ap chemistry
... CnH2n+1OH; Do not be fooled—this looks like a hydroxide ion, but is not! It does not make this hydrocarbon an alkaline or basic compound. Do not name these as a hydroxide! C2H6 is ethane while C2H5OH is ethanol. NAMING BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS How do I know it is ionic? The chemical formula will begin ...
... CnH2n+1OH; Do not be fooled—this looks like a hydroxide ion, but is not! It does not make this hydrocarbon an alkaline or basic compound. Do not name these as a hydroxide! C2H6 is ethane while C2H5OH is ethanol. NAMING BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS How do I know it is ionic? The chemical formula will begin ...
Technical Data Sheet (E
... E-Phos 660 is a calcium-modified formula which produces fine-grained crystalline coatings on iron and steel with a medium coating weight of 600 mg/ft2. The zinc phosphate coating remains fine-grained regardless of the cleaning method used prior to application. It can be applied by either immersion o ...
... E-Phos 660 is a calcium-modified formula which produces fine-grained crystalline coatings on iron and steel with a medium coating weight of 600 mg/ft2. The zinc phosphate coating remains fine-grained regardless of the cleaning method used prior to application. It can be applied by either immersion o ...
CH 4: Chemical Reactions
... reached. This point is when you have equal moles of titrant and analyte, from the volume of the titrant and analyte used and the molarity of the titrant, you can find the molarity of the analyte – Endpoint- based on an indicator – Indicator- a substance that changes color in a specific pH ...
... reached. This point is when you have equal moles of titrant and analyte, from the volume of the titrant and analyte used and the molarity of the titrant, you can find the molarity of the analyte – Endpoint- based on an indicator – Indicator- a substance that changes color in a specific pH ...
File
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
F Practice Test #2 Solutions
... C) A system that is disturbed from an equilibrium condition responds in such a way as to restore equilibrium. D) Equilibrium in molecular systems is dynamic, with two opposing processes balancing one another. E) A system moves spontaneously toward a state of equilibrium. 11. Which of the following i ...
... C) A system that is disturbed from an equilibrium condition responds in such a way as to restore equilibrium. D) Equilibrium in molecular systems is dynamic, with two opposing processes balancing one another. E) A system moves spontaneously toward a state of equilibrium. 11. Which of the following i ...
File - chemistryattweed
... Sodium and magnesium oxides are bases. Aluminium oxide is amphoteric, (it shows both acidic and basic characteristics). The oxides of silicon, phosphorus, sulfur and chlorine are all acidic but vary in strength. Silicon dioxide is weakly acidic while sulfur and perchloric acids are strongly acidic. ...
... Sodium and magnesium oxides are bases. Aluminium oxide is amphoteric, (it shows both acidic and basic characteristics). The oxides of silicon, phosphorus, sulfur and chlorine are all acidic but vary in strength. Silicon dioxide is weakly acidic while sulfur and perchloric acids are strongly acidic. ...
! !! ! n nn N P =
... 2. Normal rain is usually a bit acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide dissolving in water makes the solution slightly acidic: CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ...
... 2. Normal rain is usually a bit acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide dissolving in water makes the solution slightly acidic: CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ...
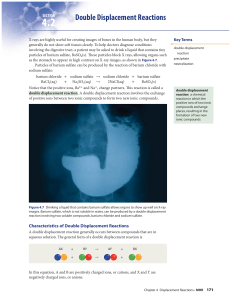
Double Displacement Reactions
... Reactions between acids and bases are also important for optimizing soil conditions. For example, lettuce and celery grow better in neutral to basic soil, but strawberries and tomatoes grow better in acidic soil. Figure 4.11 shows soil being tested to determine whether it is acidic, neutral, or basi ...
... Reactions between acids and bases are also important for optimizing soil conditions. For example, lettuce and celery grow better in neutral to basic soil, but strawberries and tomatoes grow better in acidic soil. Figure 4.11 shows soil being tested to determine whether it is acidic, neutral, or basi ...
3.10 Neutralization
... • Net ionic equations for reactions between strong acids and bases HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+ + Cl- + K+ + OH- → K+ + Cl- + H2O(l) ⇒H+ + OH- → H2O(l) – H+ is present in the form of H3O+ ...
... • Net ionic equations for reactions between strong acids and bases HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+ + Cl- + K+ + OH- → K+ + Cl- + H2O(l) ⇒H+ + OH- → H2O(l) – H+ is present in the form of H3O+ ...
Lab 13
... 2. Which of the following rankings correctly shows the order of increasing acidity for benzoic acid, benzensulfonic acid, ethanol and phenol? __A. phenol < ethanol < benzoic acid < benzenesulfonic acid __B. ethanol < phenol < benzenesulfonic acid < benzoic acid __C. ethanol < phenol < benzoic acid < ...
... 2. Which of the following rankings correctly shows the order of increasing acidity for benzoic acid, benzensulfonic acid, ethanol and phenol? __A. phenol < ethanol < benzoic acid < benzenesulfonic acid __B. ethanol < phenol < benzenesulfonic acid < benzoic acid __C. ethanol < phenol < benzoic acid < ...
Qualitative Analysis of Anions
... Test for Carbonate CO3 Place a small (pea sized) amount of the solid to be tested into a small test tube. Dip a Nichrome wire loop into Ba(OH)2 solution so that some of the Ba(OH)2 solution adheres to the wire. Place the wire with the suspended Ba(OH)2 just down into the test tube containing the sam ...
... Test for Carbonate CO3 Place a small (pea sized) amount of the solid to be tested into a small test tube. Dip a Nichrome wire loop into Ba(OH)2 solution so that some of the Ba(OH)2 solution adheres to the wire. Place the wire with the suspended Ba(OH)2 just down into the test tube containing the sam ...
Chapter 7. CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... When solutions are involved in a reaction, only some of the ions present are usually involved. Other ions may be present, but they are still in the solution at the end of the reaction, unchanged by the chemical process. These ions are called spectator ions and are best left out of the balanced equat ...
... When solutions are involved in a reaction, only some of the ions present are usually involved. Other ions may be present, but they are still in the solution at the end of the reaction, unchanged by the chemical process. These ions are called spectator ions and are best left out of the balanced equat ...
Formulation - Good Hope School
... Scandinavia. The problem was due to sulphur dioxide produced, form acid rain, which contains sulphuric acid. The problem became so great that in many lakes all the fish died. In North Wales, the water company treated the acidic lakes with thousands of tones of powdered limestone (mainly calcium carb ...
... Scandinavia. The problem was due to sulphur dioxide produced, form acid rain, which contains sulphuric acid. The problem became so great that in many lakes all the fish died. In North Wales, the water company treated the acidic lakes with thousands of tones of powdered limestone (mainly calcium carb ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 04 - Kinetics, Equilibria
... l You must answer the questions in the spaces provided. Do not write outside the box around each page or on blank pages. ...
... l You must answer the questions in the spaces provided. Do not write outside the box around each page or on blank pages. ...
Chapter 4 Notes: Types of Reactions & Solution
... •For instance, hydrogen chloride molecules, which are polar, give up their hydrogens to water, •forming chloride ions (Cl-) •and hydronium ions (H3O+). ...
... •For instance, hydrogen chloride molecules, which are polar, give up their hydrogens to water, •forming chloride ions (Cl-) •and hydronium ions (H3O+). ...
File
... There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each corre ...
... There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each corre ...
Teacher`s Guide
... an allergen for some students. It can be used to demonstrate grain dust explosions. Chalk dust works equally well. Pepper can be used if it is ground to a fine powder. Circular flat trays that have a diameter of approximately 40 cm are required. Rigid trays reduce the movement of water affecting the ...
... an allergen for some students. It can be used to demonstrate grain dust explosions. Chalk dust works equally well. Pepper can be used if it is ground to a fine powder. Circular flat trays that have a diameter of approximately 40 cm are required. Rigid trays reduce the movement of water affecting the ...
+ Cl
... The interionic distance for NaCl crystal is 200 pm, while for 0.1 moldm-3 solution is 2000 pm. To draw Na+ and Cl apart from 200 nm to 2000 nm, the work is: W (/kJ) = 625 / r for melting: r =1, W = 625 kJ, m.p. = 801 oC。 for dissolution in water: r = 78.5, W = 8 kJ. Therefore, NaCl is difficult ...
... The interionic distance for NaCl crystal is 200 pm, while for 0.1 moldm-3 solution is 2000 pm. To draw Na+ and Cl apart from 200 nm to 2000 nm, the work is: W (/kJ) = 625 / r for melting: r =1, W = 625 kJ, m.p. = 801 oC。 for dissolution in water: r = 78.5, W = 8 kJ. Therefore, NaCl is difficult ...
Introduction to Qualitative Analysis
... Lewis acid and the Lewis base. Certain metal cations act as Lewis acids. This type of reaction can result in the formation of a complex ion, an ion formed by a central metal cation bonded to from two up to six lone pairs of electrons on surrounding Lewis base species. In a complex ion, the Lewis bas ...
... Lewis acid and the Lewis base. Certain metal cations act as Lewis acids. This type of reaction can result in the formation of a complex ion, an ion formed by a central metal cation bonded to from two up to six lone pairs of electrons on surrounding Lewis base species. In a complex ion, the Lewis bas ...
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. A hydroxide attached to a strongly electropositive center may itself ionize, liberating a hydrogen cation (H+), making the parent compound an acid.The corresponding electrically neutral compound •HO is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently-bound group -OH of atoms is the hydroxyl group.Hydroxide ion and hydroxyl group are nucleophiles and can act as a catalyst in organic chemistry.Many inorganic substances which bear the word ""hydroxide"" in their names are not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which contain hydroxyl groups.