Molarity = M (Concentration of Solutions)
... loose two protons to yield two Hydronium ions, and one sulfate ion. What is the molarity of the sulfate and Hydronium ions in a solution prepared by dissolving 155g of concentrate sulfuric acid into sufficient water to produce 2.30 Liters of acid solution? Plan: Determine the number of moles of sulf ...
... loose two protons to yield two Hydronium ions, and one sulfate ion. What is the molarity of the sulfate and Hydronium ions in a solution prepared by dissolving 155g of concentrate sulfuric acid into sufficient water to produce 2.30 Liters of acid solution? Plan: Determine the number of moles of sulf ...
chapter4-bur.2917051..
... “insoluble” compounds will dissolve to a slight extent. For “soluble” compounds there will be a limit as to the amount of compound that will dissolve in a given amount of water. We can also discuss solubility in other solvents. ...
... “insoluble” compounds will dissolve to a slight extent. For “soluble” compounds there will be a limit as to the amount of compound that will dissolve in a given amount of water. We can also discuss solubility in other solvents. ...
AP Chem – Unit 1 Part 2 AP Chemistry 2016-‐2017 Unit 1
... Example Problem 19: Solid lithium hydroxide is used in space vehicles to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the living environment by forming solid lithium carbonate and liquid water. What mass of gaseous ...
... Example Problem 19: Solid lithium hydroxide is used in space vehicles to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the living environment by forming solid lithium carbonate and liquid water. What mass of gaseous ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Final Exam Review 1. Write the name for
... □Know how to interpret a Solubility Graph and determine if a solution is supersaturated, unsaturated, or saturated. □Define and describe the differences between a saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated solution. □Know how to speed up the dissolving of a solute. □Know what it means to dilute a so ...
... □Know how to interpret a Solubility Graph and determine if a solution is supersaturated, unsaturated, or saturated. □Define and describe the differences between a saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated solution. □Know how to speed up the dissolving of a solute. □Know what it means to dilute a so ...
No Slide Title
... “insoluble” compounds will dissolve to a slight extent. For “soluble” compounds there will be a limit as to the amount of compound that will dissolve in a given amount of water. We can also discuss solubility in other solvents. ...
... “insoluble” compounds will dissolve to a slight extent. For “soluble” compounds there will be a limit as to the amount of compound that will dissolve in a given amount of water. We can also discuss solubility in other solvents. ...
Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
... of reactants and/or products involved in a chemical reaction. • However, the coefficient ratio can only be used to compare amounts of chemicals. • For example, in the formation of carbon dioxide gas, C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) it would be correct to say that 1 mol of carbon reacts with 1 mol of oxygen, b ...
... of reactants and/or products involved in a chemical reaction. • However, the coefficient ratio can only be used to compare amounts of chemicals. • For example, in the formation of carbon dioxide gas, C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) it would be correct to say that 1 mol of carbon reacts with 1 mol of oxygen, b ...
Net ionic equation
... “insoluble” compounds will dissolve to a slight extent. For “soluble” compounds there will be a limit as to the amount of compound that will dissolve in a given amount of water. We can also discuss solubility in other solvents. ...
... “insoluble” compounds will dissolve to a slight extent. For “soluble” compounds there will be a limit as to the amount of compound that will dissolve in a given amount of water. We can also discuss solubility in other solvents. ...
Solution
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
Acids ,Bases and Salts
... This dissociation/ionization makes aqueous ammonia to: (i)turn litmus paper/solution blue. (ii)have pH 8/9/10/11 (iii)be a good electrical conductor (iv)react with acids to form ammonium salt and water only. NH4OH(aq) + HCl(aq) -> NH4Cl(aq) + H2O(l) (d)Ammonia gas dissolves in methylbenzene/benzene ...
... This dissociation/ionization makes aqueous ammonia to: (i)turn litmus paper/solution blue. (ii)have pH 8/9/10/11 (iii)be a good electrical conductor (iv)react with acids to form ammonium salt and water only. NH4OH(aq) + HCl(aq) -> NH4Cl(aq) + H2O(l) (d)Ammonia gas dissolves in methylbenzene/benzene ...
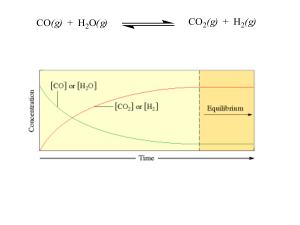
BONUS: Which line in the above graph represents G for the reaction
... A sample of 25.0 mL of vinegar (acetic acid) is titrated with standard sodium hydroxide solution, which is 0.500 M. If 30.0 mL of the NaOH solution are required for exact neutralization (phenolphthalein as indicator), the vinegar is HAc + OH- Ac- + H2O (A) ...
... A sample of 25.0 mL of vinegar (acetic acid) is titrated with standard sodium hydroxide solution, which is 0.500 M. If 30.0 mL of the NaOH solution are required for exact neutralization (phenolphthalein as indicator), the vinegar is HAc + OH- Ac- + H2O (A) ...
Chemistry II Aqueous Reactions and Solution Chemistry Chapter 4
... are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to form hydrogen ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. Because hydrogen ions are just a proton, acids are known as proton ...
... are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to form hydrogen ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. Because hydrogen ions are just a proton, acids are known as proton ...
PowerPoint Lectures - Northwest ISD Moodle
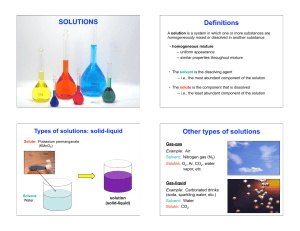
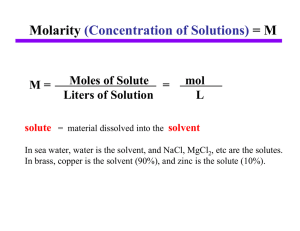
... Solutions • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • Aqueous solution – solution in which water is the dissolving medium • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes; they are dissolved in the solvent. – Example: NaCl diss ...
... Solutions • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • Aqueous solution – solution in which water is the dissolving medium • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes; they are dissolved in the solvent. – Example: NaCl diss ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... 7. Copper (I) sulfide reacts with oxygen to form copper (I) oxide and sulfur dioxide in the first step of the purification of copper ore. If the copper ore is 90.0 % copper (I) sulfide, how many grams of the ore would be needed to produce 500. g of copper (I) oxide? 8. Chemists sometimes obtain calc ...
... 7. Copper (I) sulfide reacts with oxygen to form copper (I) oxide and sulfur dioxide in the first step of the purification of copper ore. If the copper ore is 90.0 % copper (I) sulfide, how many grams of the ore would be needed to produce 500. g of copper (I) oxide? 8. Chemists sometimes obtain calc ...
Inorganic Chemistry 412 / 512
... Briefly describe the structure of black phosphorous (you do not need to sketch). [6 pts] Essentially this is the graphite structure, with non-planar sheets. P atoms form 6membered rings with chair-type conformations, each P has 3 single bonds within the sheet. There are no covalent interactions betw ...
... Briefly describe the structure of black phosphorous (you do not need to sketch). [6 pts] Essentially this is the graphite structure, with non-planar sheets. P atoms form 6membered rings with chair-type conformations, each P has 3 single bonds within the sheet. There are no covalent interactions betw ...
xy3-allyl Benzoic Acid, CsHa(COOH)1(OW)2(CsH6)3.---Thi
... The presence of agmantin which was found may have some bearing on the hay fever problem because of the possibility of a similarity which it may possess with 0-iminazolylethylamine. The latter is known t o produce asphyxia in guinea pigs with anaphylactic shock. This similarity is quite doubtful howe ...
... The presence of agmantin which was found may have some bearing on the hay fever problem because of the possibility of a similarity which it may possess with 0-iminazolylethylamine. The latter is known t o produce asphyxia in guinea pigs with anaphylactic shock. This similarity is quite doubtful howe ...
Name: Per: Date: Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter B. Periodic
... 37. Polyatomic Ions. A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that, as a group, carries an electrical charge. There are many negatively-charged polyatomic ions, but the only polyatomic ion with a positive charge is NH4+. When a polyatomic ion occurs two or more times in a formula, its formula is placed ...
... 37. Polyatomic Ions. A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that, as a group, carries an electrical charge. There are many negatively-charged polyatomic ions, but the only polyatomic ion with a positive charge is NH4+. When a polyatomic ion occurs two or more times in a formula, its formula is placed ...
Acid‒base reaction
... An alkali is a base, more precisely a base which contains a metal from column 1 or 2 of the periodic table (the alkali metals or the alkaline earth metals). Alkalis may be defined as soluble bases, which means they must be able to dissolve in water. Bases generally are defined as substances which co ...
... An alkali is a base, more precisely a base which contains a metal from column 1 or 2 of the periodic table (the alkali metals or the alkaline earth metals). Alkalis may be defined as soluble bases, which means they must be able to dissolve in water. Bases generally are defined as substances which co ...
CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 11-12 Mid
... B) there are equal numbers of molecules on each side of the reaction arrow. C) there are equal numbers of atoms on each side of the reaction arrow. D) the number of atoms depends present in a reaction can vary when the conditions change during the reaction. E) none of the above 4) The oxidation numb ...
... B) there are equal numbers of molecules on each side of the reaction arrow. C) there are equal numbers of atoms on each side of the reaction arrow. D) the number of atoms depends present in a reaction can vary when the conditions change during the reaction. E) none of the above 4) The oxidation numb ...
C3 Revision Question Booklet
... List A gives the names of four compounds in solution. List B gives tests and the result of the tests. Draw a straight line from each compound in List A to its test and test result in List B. The first one has been done for you. ...
... List A gives the names of four compounds in solution. List B gives tests and the result of the tests. Draw a straight line from each compound in List A to its test and test result in List B. The first one has been done for you. ...
Equations - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... In the exam, you will be asked to write, or complete, word equations and chemical equations (balanced symbol equations), and you might need to add state symbols to an equation. This unit will help you to write these types of equation and to get information from equations. ...
... In the exam, you will be asked to write, or complete, word equations and chemical equations (balanced symbol equations), and you might need to add state symbols to an equation. This unit will help you to write these types of equation and to get information from equations. ...
Lecture 25 Notes
... -- the chemical formula of a polyatomic acid begins with H -- the second part of the formula is a polyatomic anion containing oxygen (an oxy-anion) Rule: The name of a polyatomic acid is derived from its anion -- the ending of the anion name is modified ...
... -- the chemical formula of a polyatomic acid begins with H -- the second part of the formula is a polyatomic anion containing oxygen (an oxy-anion) Rule: The name of a polyatomic acid is derived from its anion -- the ending of the anion name is modified ...
Acid K a
... K+ - worthless, I- - worthless, neutral Li+ - worthless, C2H3O2- - weak base, basic Cl- - worthless, C6H5NH3+ - weak acid, acidic K+ - worthless, F- - weak base, basic Na+ - worthless, NO3- - worthless, neutral HClO4 – strong acid, acidic Ca(OH)2 – strong base, basic KaNH < KbCN - basic KaNH = KbC H ...
... K+ - worthless, I- - worthless, neutral Li+ - worthless, C2H3O2- - weak base, basic Cl- - worthless, C6H5NH3+ - weak acid, acidic K+ - worthless, F- - weak base, basic Na+ - worthless, NO3- - worthless, neutral HClO4 – strong acid, acidic Ca(OH)2 – strong base, basic KaNH < KbCN - basic KaNH = KbC H ...
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. A hydroxide attached to a strongly electropositive center may itself ionize, liberating a hydrogen cation (H+), making the parent compound an acid.The corresponding electrically neutral compound •HO is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently-bound group -OH of atoms is the hydroxyl group.Hydroxide ion and hydroxyl group are nucleophiles and can act as a catalyst in organic chemistry.Many inorganic substances which bear the word ""hydroxide"" in their names are not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which contain hydroxyl groups.