Methylation of histone H3-lysine 27 by EED-EZH2/ESC-E(Z)
... Figure S1. The monoclonal uH2A antibody recognizes uH2A from Drosophila SL2 cells. a, Sequence alignment of human and Drosophila H2A around the ubiquitination site. b, Western blotting of histone extracts from SL2 cells using a well-characterized monoclonal antibody (E6C5) against uH2A 1. c, Coomass ...
... Figure S1. The monoclonal uH2A antibody recognizes uH2A from Drosophila SL2 cells. a, Sequence alignment of human and Drosophila H2A around the ubiquitination site. b, Western blotting of histone extracts from SL2 cells using a well-characterized monoclonal antibody (E6C5) against uH2A 1. c, Coomass ...
Proteins for Growth and Repair
... Complete Proteins from Animal Foods: Complete proteins contain 9 of the 22 amino acids that are essential to life and must be added to the diet. They are found in animal foods like meat, fish, milk cheese and eggs. Vegans and vegetarians can get shortages of the essential amino acids lysine and thre ...
... Complete Proteins from Animal Foods: Complete proteins contain 9 of the 22 amino acids that are essential to life and must be added to the diet. They are found in animal foods like meat, fish, milk cheese and eggs. Vegans and vegetarians can get shortages of the essential amino acids lysine and thre ...
Proteins - CasimiroSBI4U
... There are 8 essential AA’s in human adults (9 in children) and the body must get these in the diet the others can be synthesized Protein Structure Polypeptide chains = polymers of amino acids, linked by peptide bonds, arranged in a specific linear sequence. Peptide bond = covalent bond forme ...
... There are 8 essential AA’s in human adults (9 in children) and the body must get these in the diet the others can be synthesized Protein Structure Polypeptide chains = polymers of amino acids, linked by peptide bonds, arranged in a specific linear sequence. Peptide bond = covalent bond forme ...
Anti-UBR1 Antibody
... Investigators intending to use an application that has not been verified can request a complimentary sample. ...
... Investigators intending to use an application that has not been verified can request a complimentary sample. ...
MTC25 - Intracellular Processing
... The smooth ER is so called because it is not studded with ribosomal sites like the rough ER and so has no SRP-related components; it participates in lipid synthesis and detoxification, e.g. of alcohol The most common genetic defect that causes CF, ΔF508 (deletion of three nucleotides resulting in th ...
... The smooth ER is so called because it is not studded with ribosomal sites like the rough ER and so has no SRP-related components; it participates in lipid synthesis and detoxification, e.g. of alcohol The most common genetic defect that causes CF, ΔF508 (deletion of three nucleotides resulting in th ...
Protein Metabolism
... internal proteolytic sites and two 19S regulatory particles (RP) that contain multiple ATPase active sites • CP of four stacked rings, composed of two different types of subunits (α and B) ...
... internal proteolytic sites and two 19S regulatory particles (RP) that contain multiple ATPase active sites • CP of four stacked rings, composed of two different types of subunits (α and B) ...
Biosynthesis and degradation of proteins
... Protein degradation systems Ubiquitin and proteasome Activation of proteases Protease inhibitors ...
... Protein degradation systems Ubiquitin and proteasome Activation of proteases Protease inhibitors ...
Intracellular Protein Degradation
... Lane 1- Fraction II + 125I- APF (no ATP) Lane 2- Fraction II + 125I-AFP + ATP Lane 3- Fraction II + 125I-AFP + ATP + unlabeled lysosome as substrate Lane 4 & 5 - Increasing conc of lysosome Lane 6- Fraction II + 125I-lysosome (no ATP) + unlabeled APF Lane 7- Same as lane 6 + ATP ...
... Lane 1- Fraction II + 125I- APF (no ATP) Lane 2- Fraction II + 125I-AFP + ATP Lane 3- Fraction II + 125I-AFP + ATP + unlabeled lysosome as substrate Lane 4 & 5 - Increasing conc of lysosome Lane 6- Fraction II + 125I-lysosome (no ATP) + unlabeled APF Lane 7- Same as lane 6 + ATP ...
WSB2 (Human) Recombinant Protein (Q01)
... page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: Store at -80°C. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and t ...
... page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: Store at -80°C. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and t ...
Questions for Discussion or Assignment to Accompany the Ubiquitin
... This assumes that the amplifier is linear and assumes that PL2 and PL1 represent attenuations (i.e. higher attenuation is less power). (c) Now calculate the 360 degree pulse at PL2. (d) Assuming a presaturation pulse of 4 seconds, how many revolutions does the water magnetization vector undergo if ...
... This assumes that the amplifier is linear and assumes that PL2 and PL1 represent attenuations (i.e. higher attenuation is less power). (c) Now calculate the 360 degree pulse at PL2. (d) Assuming a presaturation pulse of 4 seconds, how many revolutions does the water magnetization vector undergo if ...
IB2.14.3 Building a protein
... proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen ...
... proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen ...
answers
... PanB and PanC are close in the genomic region. Sequences are in a row next to each other suggesting that they form an operon ...
... PanB and PanC are close in the genomic region. Sequences are in a row next to each other suggesting that they form an operon ...
Biosynthesis and degradation of proteins
... A domain of the inhibitor protein interacts with the catalytic Zn++. • Cystatins are inhibitors of lysosomal cathepsins. Some of these (also called stefins) are found in the cytosol and others in the extracellular space. Cystatins protect cells against cathepsins that may escape from lysosomes. • Se ...
... A domain of the inhibitor protein interacts with the catalytic Zn++. • Cystatins are inhibitors of lysosomal cathepsins. Some of these (also called stefins) are found in the cytosol and others in the extracellular space. Cystatins protect cells against cathepsins that may escape from lysosomes. • Se ...
Poster
... ExoU, encoded by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In cooperation with MSOE, the Brown Deer SMART Team (Students Modeling A Research Topic) has modeled ExoU using 3D printing technology to have a better grasp on how the toxin interacts with eukaryotic cells. This soil bacterium infects those wit ...
... ExoU, encoded by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In cooperation with MSOE, the Brown Deer SMART Team (Students Modeling A Research Topic) has modeled ExoU using 3D printing technology to have a better grasp on how the toxin interacts with eukaryotic cells. This soil bacterium infects those wit ...
The_Structure_of_Protein_Activity
... a) The solubility of many proteins in water. b) The precise 3D structure of those enzymes which are proteins. c) The eleasticity of natural fibres such as wool and silk? ...
... a) The solubility of many proteins in water. b) The precise 3D structure of those enzymes which are proteins. c) The eleasticity of natural fibres such as wool and silk? ...
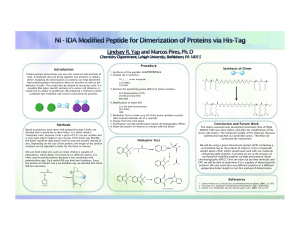
Introduction Methods Procedure Conclusion and Future Work
... cells. A molecule that can bring together two proteins is called a dimer. Studying the dimerization or proteins can help determine how protein-protein interactions alters its function as well as the behavior of cells. This could also be related to cancerous cells. It is possible that when specific p ...
... cells. A molecule that can bring together two proteins is called a dimer. Studying the dimerization or proteins can help determine how protein-protein interactions alters its function as well as the behavior of cells. This could also be related to cancerous cells. It is possible that when specific p ...
intracellular protein synthesis, post
... Alfred L. G o l d b u . Dept. of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, U.S.A. ...
... Alfred L. G o l d b u . Dept. of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, U.S.A. ...
abstract - UBC Blogs
... are abundant in the middle lamella that holds plant cells together. Their degree of methylesterification (DM) impacts wall strength and cell adhesion since unesterified pectin regions can cross-link via Ca2+ ions to form stronger gels. Here, we characterize flying saucer1 (fly1), a novel Arabidopsis ...
... are abundant in the middle lamella that holds plant cells together. Their degree of methylesterification (DM) impacts wall strength and cell adhesion since unesterified pectin regions can cross-link via Ca2+ ions to form stronger gels. Here, we characterize flying saucer1 (fly1), a novel Arabidopsis ...
Poster
... Modeling A Research Topic) Team is working with Dr. Frank from the Medical College of Wisconsin to model the bacterial toxin ExoU using MSOE’s 3D printer. ExoU is a phospholipase that destroys both organelle and plasma membranes by cleaving the phospholipids. The toxin is delivered into host cells b ...
... Modeling A Research Topic) Team is working with Dr. Frank from the Medical College of Wisconsin to model the bacterial toxin ExoU using MSOE’s 3D printer. ExoU is a phospholipase that destroys both organelle and plasma membranes by cleaving the phospholipids. The toxin is delivered into host cells b ...
PATHOLOGY NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
... Yet, not everyone expected this family of orphan proteins to wield power over so many important cellular processes. Pagano's research group has revealed that F-box proteins help control cell proliferation, DNA-damage checkpoints, chromosomal stability, ribosomal biogenesis, protein synthesis, apopto ...
... Yet, not everyone expected this family of orphan proteins to wield power over so many important cellular processes. Pagano's research group has revealed that F-box proteins help control cell proliferation, DNA-damage checkpoints, chromosomal stability, ribosomal biogenesis, protein synthesis, apopto ...
the ubiquitin system and a putative stimulatory role
... Among eukaryotes, ubiquitin is highly conserved, meaning that the amino acid sequence does not differ much when very different organisms are compared. Ub is a heat-stable protein that folds up into a compact globular structure. It is found throughout the cell and can exist either in free form or as ...
... Among eukaryotes, ubiquitin is highly conserved, meaning that the amino acid sequence does not differ much when very different organisms are compared. Ub is a heat-stable protein that folds up into a compact globular structure. It is found throughout the cell and can exist either in free form or as ...
Protein Engineering
... • Eliminate the need for cofactor in enzymatic reaction •Change substrate binding site to increase specificity •Change the thermal tolerance •Change the pH stability •Increase proteins resistance to proteases (purification) •Signal sequences - secretion •rare codon changes ...
... • Eliminate the need for cofactor in enzymatic reaction •Change substrate binding site to increase specificity •Change the thermal tolerance •Change the pH stability •Increase proteins resistance to proteases (purification) •Signal sequences - secretion •rare codon changes ...
Protein Degradation As discussed in last the last lecture, newly
... 1. E1- ubiquitin – a thioester bond is formed between the C-terminal amino acids of ubiquitin and an internal Cys residue of E1, the ubiquitin activating enzyme. This is an ATP dependent process. 2. E2- ubiquitin – an exchange reaction occurs, and the ubiquitin is transferred to a sulfhydryl group o ...
... 1. E1- ubiquitin – a thioester bond is formed between the C-terminal amino acids of ubiquitin and an internal Cys residue of E1, the ubiquitin activating enzyme. This is an ATP dependent process. 2. E2- ubiquitin – an exchange reaction occurs, and the ubiquitin is transferred to a sulfhydryl group o ...
Ubiquitin ligases and beyond EDITORIAL Open Access Ivan Dikic
... ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, to which the ubiquitin is transferred from the E1; and E3 is the ubiquitin ligase, which binds the target protein and directly or indirectly catalyzes its ligation to the ubiquitin. The E3 therefore determines the substrate specificity of ubiquitination, and the diversi ...
... ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, to which the ubiquitin is transferred from the E1; and E3 is the ubiquitin ligase, which binds the target protein and directly or indirectly catalyzes its ligation to the ubiquitin. The E3 therefore determines the substrate specificity of ubiquitination, and the diversi ...
Ubiquitin

Ubiquitin is a small (8.5 kDa) regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues (ubiquitously) of eukaryotic organisms. It was discovered in 1975 by Goldstein and further characterized throughout the 1970s and 1980s. There are four genes in the human genome that produce ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A.The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: It can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitination is carried out in three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade binds ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond or to the amino group of the protein's N-terminus via a peptide bond.The protein modifications can be either a single ubiquitin protein (monoubiquitination) or a chain of ubiquitin (polyubiquitination). The ubiquitination bonds are always formed with one of the seven lysine residues from the ubiquitin molecule. These 'linking' lysines are represented by a ""K"" (which is the one-letter amino acid notation of lysine) and a number, referring to its position in the ubiquitin molecule. First, a ubiquitin molecule is bonded by its C-terminus to a specific lysine residue (e.g. K48, K29, K63,...) on the target protein. Poly-ubiquitination occurs when the C-terminus of another ubiquitin, will be linked again to a lysine residue (for example again K48 or K29) on the previously added ubiquitin molecule, forming a chain. This process repeats several times, leading to the addition of several ubiquitins. Only poly-ubiquitination on defined lysines, mostly on K48 and K29, is related to degradation with the proteasome (referred to as the ""molecular kiss of death""), while other polyubiquitinations (e.g. on K63, K11, K6) and monoubiquitinations may regulate processes such as endocytic trafficking, inflammation, translation and DNA repair.Lysine 48-linked chains have been much-studied. They are the forms of chains that signal proteins to the proteasome, which destroys and recycles proteins. This discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004.