lecture #7 ppt
... Footnote: Derivation of relations between A, B, assumed thermal radiation. The relations hold so long as either the radiation field or the molecules are randomly oriented in space—not necessarily for solids interacting with lasers. ...
... Footnote: Derivation of relations between A, B, assumed thermal radiation. The relations hold so long as either the radiation field or the molecules are randomly oriented in space—not necessarily for solids interacting with lasers. ...
Jan. 27 - Feb. 5
... Sun radiates most strongly at roughly 500nm and thus T = 3 x 106/500nm = 6000K Creation of electromagnetic radiation Bohr model of the atom Nucleus with protons (+) and neutrons Electron cloud (-) 2s, 6p, 6d etc. (periodic table) Possible energy levels for an electron (Quantized) Whole number multip ...
... Sun radiates most strongly at roughly 500nm and thus T = 3 x 106/500nm = 6000K Creation of electromagnetic radiation Bohr model of the atom Nucleus with protons (+) and neutrons Electron cloud (-) 2s, 6p, 6d etc. (periodic table) Possible energy levels for an electron (Quantized) Whole number multip ...
Lecture 5
... Physical mechanism: When a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. The part of the fluid in contact with the hot object has a temperature higher than that of the surrounding cooler fluid, hence that fluid becomes less dense; buoyant forces cause it r ...
... Physical mechanism: When a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. The part of the fluid in contact with the hot object has a temperature higher than that of the surrounding cooler fluid, hence that fluid becomes less dense; buoyant forces cause it r ...
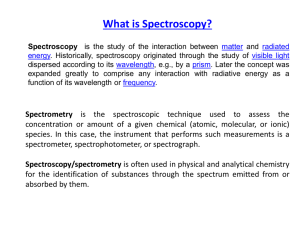
Physical and Chemical Tests
... the transmitted beam is detected and recorded. Frequencies that are absorbed by the sample appear as peaks deviating from a baseline value. ...
... the transmitted beam is detected and recorded. Frequencies that are absorbed by the sample appear as peaks deviating from a baseline value. ...
document
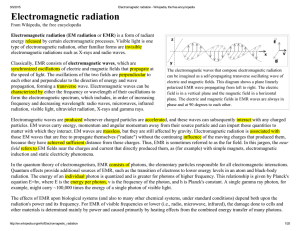
... In (a) the wave has long wavelength and low frequency In (b) the wave has shorter wavelength and higher frequency ...
... In (a) the wave has long wavelength and low frequency In (b) the wave has shorter wavelength and higher frequency ...
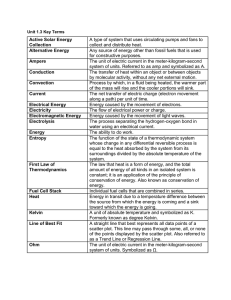
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
Convective heat transfer
... convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold. Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and diff ...
... convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold. Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and diff ...
Electromagnetic Radiation and Computers
... lives. As a result, users are exposed to electromagnetic radiation emitted by these machines. Should we be concerned? What is electromagnetic radiation? Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) are invisible lines of force that occur whenever electricity is being conducted. These forces occur from both natural ...
... lives. As a result, users are exposed to electromagnetic radiation emitted by these machines. Should we be concerned? What is electromagnetic radiation? Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) are invisible lines of force that occur whenever electricity is being conducted. These forces occur from both natural ...
Keeping Warm in Winter - University of Mount Union
... have excellent insulation. Birds are literally wearing a thick down jacket. When it is especially cold they fluff up their down to further improve their insulation. Underneath their outer feathers is a layer of soft, fuzzy down feathers that trap air and prevent convection from carrying away much of ...
... have excellent insulation. Birds are literally wearing a thick down jacket. When it is especially cold they fluff up their down to further improve their insulation. Underneath their outer feathers is a layer of soft, fuzzy down feathers that trap air and prevent convection from carrying away much of ...
Chap 7 - College of Science | Oregon State University
... - There are 100 degrees between these two points. Fahrenheit based on human body temperature and freezing point of a mixture of water and salt. - Water freezes at 32oF; boils at 212oF. - There are 180 degrees between these two points. Kelvin based on absolute zero. - Also called absolute scale. - Ab ...
... - There are 100 degrees between these two points. Fahrenheit based on human body temperature and freezing point of a mixture of water and salt. - Water freezes at 32oF; boils at 212oF. - There are 180 degrees between these two points. Kelvin based on absolute zero. - Also called absolute scale. - Ab ...
Modern Atomic Theory (aka the electron chapter!)
... The Electric Pickle • Excited atoms can emit light. • Here the solution in a pickle is excited electrically. The Na+ ions in the pickle juice give off light characteristic of that element. ...
... The Electric Pickle • Excited atoms can emit light. • Here the solution in a pickle is excited electrically. The Na+ ions in the pickle juice give off light characteristic of that element. ...
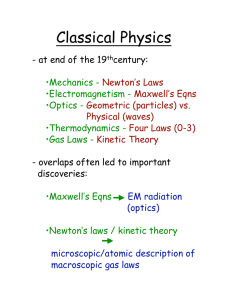
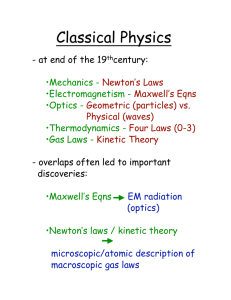
Classical Physics
... along with the medium. •Fluid near heat source becomes hot, expands, and rises. Surrounding cooler fluid takes its place. Etc. ...
... along with the medium. •Fluid near heat source becomes hot, expands, and rises. Surrounding cooler fluid takes its place. Etc. ...
4.4 Heat transfer by radiation 4.4.1 Black body radiation f c λ = c f = 1
... from the initial incoming solar radiation. A second example of the light scattering is a laser beam which we observe. Without the scattering medium (gas molecules) we would not see it, as it is, for example, in space. It should be emphasized that all bodies emit (thermal) radiation even if they had ...
... from the initial incoming solar radiation. A second example of the light scattering is a laser beam which we observe. Without the scattering medium (gas molecules) we would not see it, as it is, for example, in space. It should be emphasized that all bodies emit (thermal) radiation even if they had ...
LIGHT AND COLOR
... UV (suntan, sunburn) IR ( skin can detect IR) Microwaves and Radio Waves Long Term exposure, Cell phones and Power Lines? ...
... UV (suntan, sunburn) IR ( skin can detect IR) Microwaves and Radio Waves Long Term exposure, Cell phones and Power Lines? ...
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. An object with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change. This results in charge-acceleration and/or dipole oscillation which produces electromagnetic radiation, and the wide spectrum of radiation reflects the wide spectrum of energies and accelerations that occur even at a single temperature.Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, the infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution (infrared rather than visible) because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation. Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.