D3-4_Tool simulating the macroscopic properties of PU
... over time. This is caused by the fact that the blowing agents are diffusing out of the foam and the air instead diffuses into the foam. Since the air has generally higher thermal conductivity than the blowing agents, the thermal conductivity of the whole foam also increases. This effect can increase ...
... over time. This is caused by the fact that the blowing agents are diffusing out of the foam and the air instead diffuses into the foam. Since the air has generally higher thermal conductivity than the blowing agents, the thermal conductivity of the whole foam also increases. This effect can increase ...
A Pool Boiling Map: Water on a Horizontal Surface at
... bubble, the minimum surface temperature may be thought of as being slightly greater than the vapor temperature predicted by equation (!II-5.) The Situation Addressed For the situation where the nucleation site is filled with a gas, an expression for the superheat needed to form a ...
... bubble, the minimum surface temperature may be thought of as being slightly greater than the vapor temperature predicted by equation (!II-5.) The Situation Addressed For the situation where the nucleation site is filled with a gas, an expression for the superheat needed to form a ...
Molecular-Fluorescence Enhancement via Blue
... the absorption of MC molecules. Along with the quenching of scattering from AuNRs, the blue-shifted PIRET enhances the fluorescence of nearby molecules. On the basis of the fluorescence enhancement, we conclude that AuNRs can be used as donors with clear advantages to excite the fluorescence of molecul ...
... the absorption of MC molecules. Along with the quenching of scattering from AuNRs, the blue-shifted PIRET enhances the fluorescence of nearby molecules. On the basis of the fluorescence enhancement, we conclude that AuNRs can be used as donors with clear advantages to excite the fluorescence of molecul ...
Ch 15) The Laws of Thermodynamics
... great laws of physics, and its validity rests on experiments (such as Joule’s) to which no exceptions have been seen. Since Q and W represent energy transferred into or out of the system, the internal energy changes accordingly. Thus, the first law of thermodynamics is a general statement of the law ...
... great laws of physics, and its validity rests on experiments (such as Joule’s) to which no exceptions have been seen. Since Q and W represent energy transferred into or out of the system, the internal energy changes accordingly. Thus, the first law of thermodynamics is a general statement of the law ...
Thermal noise on capacitors
... Thermal noise accounts for 100% of kTC noise, whether it is attributed to the resistance or to the capacitance. In the extreme case of the reset noise left on a capacitor by opening an ideal switch, the resistance is infinite, yet the formula still applies; however, now the RMS must be interpreted ...
... Thermal noise accounts for 100% of kTC noise, whether it is attributed to the resistance or to the capacitance. In the extreme case of the reset noise left on a capacitor by opening an ideal switch, the resistance is infinite, yet the formula still applies; however, now the RMS must be interpreted ...
Thermochemistry Thermochemistry
... of matter and deduces a few general laws – It does not require any knowledge/assumptions of molecules CHEM 1000A 3.0 ...
... of matter and deduces a few general laws – It does not require any knowledge/assumptions of molecules CHEM 1000A 3.0 ...
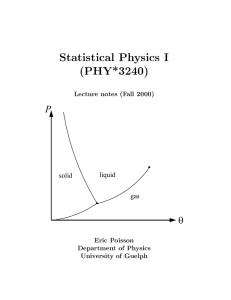
book - University of Guelph Physics
... Thermodynamics is the study of macroscopic systems for which thermal effects are important. These systems are normally assumed to be at equilibrium, or at least, close to equilibrium. Systems at equilibrium are easier to study, both experimentally and theoretically, because their physical properties ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of macroscopic systems for which thermal effects are important. These systems are normally assumed to be at equilibrium, or at least, close to equilibrium. Systems at equilibrium are easier to study, both experimentally and theoretically, because their physical properties ...
Basic Thermodynamics - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... engines if t1 t2 are fixed, different irreversible engines will depict different efficiencies. It is because of the fact that all reversible engines have the same efficiency when t1 and t2 are fixed. The efficiency of a reversible engine is a function of the two temperatures only. Now we will exploi ...
... engines if t1 t2 are fixed, different irreversible engines will depict different efficiencies. It is because of the fact that all reversible engines have the same efficiency when t1 and t2 are fixed. The efficiency of a reversible engine is a function of the two temperatures only. Now we will exploi ...
Energy Conservation in Ethanol-Water Distillation
... compressor to raise the energy level of vapour that is condensed in reboiler–condenser by exchange of heat with the bottoms. The condensate distillate is passed into reflux drum while the bottom product is vaporised into the column. Vapour recompression consists of taking the overhead vapour of a co ...
... compressor to raise the energy level of vapour that is condensed in reboiler–condenser by exchange of heat with the bottoms. The condensate distillate is passed into reflux drum while the bottom product is vaporised into the column. Vapour recompression consists of taking the overhead vapour of a co ...
The Fields Outside a Long Solenoid with a Time
... then ∂f/∂t = 0, and so the electric field should be constant in time. Apparently the approximation used in deriving eq. (10) is not completely correct. Either we should return to eq. (9) or continue on from eq. (14), both of which do not contain approximations. It appears to be more straightforward t ...
... then ∂f/∂t = 0, and so the electric field should be constant in time. Apparently the approximation used in deriving eq. (10) is not completely correct. Either we should return to eq. (9) or continue on from eq. (14), both of which do not contain approximations. It appears to be more straightforward t ...
Physcal Chemistry ERT 108 semester II 2010/2011
... undergoes no acceleration, and there is no turbulence within the system. 2. Material equilibrium • No net chemical reactions are occurring in the system, nor is there any net transfer of matter from one part of the system to another or between the system and its surroundings; the concentrations of t ...
... undergoes no acceleration, and there is no turbulence within the system. 2. Material equilibrium • No net chemical reactions are occurring in the system, nor is there any net transfer of matter from one part of the system to another or between the system and its surroundings; the concentrations of t ...
THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 3·5 So far we have
... Step 7: Determine the Required Properties and Unknowns The unknown properties at any state can be determined with the help of thermodynamic relations or tables. Thermodynamic relations are usually valid over some limited range, and therefore their validity should be checked before they are used, to ...
... Step 7: Determine the Required Properties and Unknowns The unknown properties at any state can be determined with the help of thermodynamic relations or tables. Thermodynamic relations are usually valid over some limited range, and therefore their validity should be checked before they are used, to ...
Amorphous Silicon Dioxide
... emitting diodes (LEDs), which are applications for which silicon is not well suited. Similarly, silicon carbide may be useful if high temperature operation is required since it has a much larger band gap than silicon. (Diamond also has similar semiconductor characteristics.) Other semiconductors, su ...
... emitting diodes (LEDs), which are applications for which silicon is not well suited. Similarly, silicon carbide may be useful if high temperature operation is required since it has a much larger band gap than silicon. (Diamond also has similar semiconductor characteristics.) Other semiconductors, su ...
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. An object with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change. This results in charge-acceleration and/or dipole oscillation which produces electromagnetic radiation, and the wide spectrum of radiation reflects the wide spectrum of energies and accelerations that occur even at a single temperature.Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, the infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution (infrared rather than visible) because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation. Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.