Lecture4
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
Radioactivity
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
The Atom: Quick Note Guide
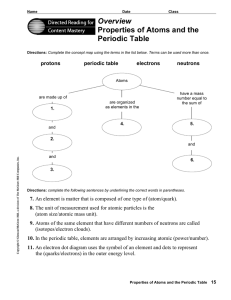
... Atomic Number Identifies number of protons in an element Can be found on the periodic tableperiodic table is organized according to increasing atomic number Because an atom is neutrally charged, number of positives has to equal number of negatives; number of protons has to equal number of electrons ...
... Atomic Number Identifies number of protons in an element Can be found on the periodic tableperiodic table is organized according to increasing atomic number Because an atom is neutrally charged, number of positives has to equal number of negatives; number of protons has to equal number of electrons ...
Unit 1: Atomic Structure & Electron Configuration
... Matter is composed of atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical to each other, but different from other elements. Atoms cannot be divided nor destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or re ...
... Matter is composed of atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical to each other, but different from other elements. Atoms cannot be divided nor destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or re ...
Structure of the atom
... • DEFINES identity of element For a given element, number of protons is fixed, but number of neutrons can vary. ...
... • DEFINES identity of element For a given element, number of protons is fixed, but number of neutrons can vary. ...
Physical Science Chapter 3 Test
... 1. The word atom comes from a Greek word that means "unable to be ____________________." 2. The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher ____________________. 3. John Dalton's atomic theory stated that atoms of the same ____________________ are exactly al ...
... 1. The word atom comes from a Greek word that means "unable to be ____________________." 2. The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher ____________________. 3. John Dalton's atomic theory stated that atoms of the same ____________________ are exactly al ...
Chapter 3 – Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter - Hatboro
... Joseph Louis Proust observed that Copper carbonate (CuCO3) occurs in nature as the mineral malachite (a), it forms as a patina on copper roofs (b) and bronze statues, and can also be synthesized in the laboratory (c). Regardless of its source, basic copper carbonate has the same composition. ...
... Joseph Louis Proust observed that Copper carbonate (CuCO3) occurs in nature as the mineral malachite (a), it forms as a patina on copper roofs (b) and bronze statues, and can also be synthesized in the laboratory (c). Regardless of its source, basic copper carbonate has the same composition. ...
3-ELEMENTS AND THE ATOMIC MODEL. C4.8A Identify the
... C4.8B Describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. C4.8C Recognize that protons repel each other and that a strong force needs to be present to keep the nucleus intact. C4.8i Descr ...
... C4.8B Describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. C4.8C Recognize that protons repel each other and that a strong force needs to be present to keep the nucleus intact. C4.8i Descr ...
The periodic table and the atom part 2
... what element it is. For example carbon atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. The number of protons in an atom also determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
... what element it is. For example carbon atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. The number of protons in an atom also determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
File - Ms M - EARL MARRIOTT SECONDARY
... Early discoveries of radiation relied on photographic equipment. Later, more sophisticated devices such as the Geiger-Müller counter were developed to more precisely measure radioactivity. Isotopes are different atoms of the same element, with the difference between the two atoms being the number of ...
... Early discoveries of radiation relied on photographic equipment. Later, more sophisticated devices such as the Geiger-Müller counter were developed to more precisely measure radioactivity. Isotopes are different atoms of the same element, with the difference between the two atoms being the number of ...
Atomic Structure
... • Number of Protons = Atomic Number • Number of Electrons = Number of Protons = Atomic Number • Number of Neutrons = Mass Number Atomic Number ...
... • Number of Protons = Atomic Number • Number of Electrons = Number of Protons = Atomic Number • Number of Neutrons = Mass Number Atomic Number ...
Rules for Naming Elements/Compounds
... – the atomic number . In the example, krypton's atomic number is 36. This tells us that an atom of krypton has 36 protons in its nucleus. ...
... – the atomic number . In the example, krypton's atomic number is 36. This tells us that an atom of krypton has 36 protons in its nucleus. ...
Chapter 9
... 5. The ____________ number on the periodic table tells you the number of protons. The _______ number indicates the number of ____________ and ______________. In a neutral atom, protons always equal ______________. 6. Energy level number (1) in an atom contains a maximum number of __________ electron ...
... 5. The ____________ number on the periodic table tells you the number of protons. The _______ number indicates the number of ____________ and ______________. In a neutral atom, protons always equal ______________. 6. Energy level number (1) in an atom contains a maximum number of __________ electron ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... The new periodic table has over 100 squares. ...
... The new periodic table has over 100 squares. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... The new periodic table has over 100 squares. ...
... The new periodic table has over 100 squares. ...
Name: _key Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 7. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? isotopes 8. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? 9. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? P-92, E-92, N-142 10. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proton ...
... 7. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? isotopes 8. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? 9. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? P-92, E-92, N-142 10. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proton ...
Atomic Structure
... mass spectrographic data to propose that many elements had more than one type of atom having different masses – isotopes. Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes: 1H, 2H, and 3H . ...
... mass spectrographic data to propose that many elements had more than one type of atom having different masses – isotopes. Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes: 1H, 2H, and 3H . ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.