ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Theory of the Atom _______________, a famous Greek teacher who lived in the 4th Century B.C., first suggested the idea of the atom. • Said that all matter is composed of tiny, _____________ particles called __________ (atoms) In 1803, _______________ studied experiments and ...
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Theory of the Atom _______________, a famous Greek teacher who lived in the 4th Century B.C., first suggested the idea of the atom. • Said that all matter is composed of tiny, _____________ particles called __________ (atoms) In 1803, _______________ studied experiments and ...
Name___________________________________ Physical
... B) Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. C) The mass of a neutron nearly equals the mass of a proton. D) Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. E) Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. ...
... B) Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. C) The mass of a neutron nearly equals the mass of a proton. D) Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. E) Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. ...
- Catalyst
... 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determine the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass number, but not in chemical behavior (much). A sample of the element is treated as though its atom ...
... 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determine the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass number, but not in chemical behavior (much). A sample of the element is treated as though its atom ...
Atomic mass - cloudfront.net
... For example, the vast majority of carbon atoms have 6 protons and 6 neutrons, but a small percentage of carbon atoms have 6 protons andT neutrons, and an even smaller percentage have 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Since the vast majority of carbon atoms have a mass very close to 12, and only a small perc ...
... For example, the vast majority of carbon atoms have 6 protons and 6 neutrons, but a small percentage of carbon atoms have 6 protons andT neutrons, and an even smaller percentage have 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Since the vast majority of carbon atoms have a mass very close to 12, and only a small perc ...
AP Chemistry Name_____________________________________
... 16. He studied matter in cathode ray tubes. 17. His philosophical idea included the term “atomos”. 18. He added to the atomic theory the idea that atoms had positive and negative parts. ...
... 16. He studied matter in cathode ray tubes. 17. His philosophical idea included the term “atomos”. 18. He added to the atomic theory the idea that atoms had positive and negative parts. ...
Chapter 5
... -Millikan calculated the weight and charge of the electron in 1916 Protons and Neutrons -Protons (Goldstein 1886)are Positive and about 1840 times the size of an electron -Neutrons (Chadwick 1932) are Neutral and have about the same weight as a proton Rutherford 1911: Most of an atom is empty space, ...
... -Millikan calculated the weight and charge of the electron in 1916 Protons and Neutrons -Protons (Goldstein 1886)are Positive and about 1840 times the size of an electron -Neutrons (Chadwick 1932) are Neutral and have about the same weight as a proton Rutherford 1911: Most of an atom is empty space, ...
1. Of the three major categories of elements (metals, non
... They are called groups or families. 12. What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called? They are called periods. 13. Explain the relationship between elements in the same group. They have similar chemical and physical properties because each one has the same number of valence electrons. ...
... They are called groups or families. 12. What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called? They are called periods. 13. Explain the relationship between elements in the same group. They have similar chemical and physical properties because each one has the same number of valence electrons. ...
The Atom.jet.2013 - Petal School District
... all available isotopes of the element, based on percent occurrence Nomenclature to distinguish isotopes: C-12 is “carbon twelve” ◦ ______ protons and ______ neutrons ...
... all available isotopes of the element, based on percent occurrence Nomenclature to distinguish isotopes: C-12 is “carbon twelve” ◦ ______ protons and ______ neutrons ...
Nuclear Notes
... Deflected by electric or magnetic fields More penetrating than alpha particles Example: ...
... Deflected by electric or magnetic fields More penetrating than alpha particles Example: ...
atomic number
... – Proton - a positively charged particle – Neutron - a neutral particle – Electron - a negatively charged particle (much lighter than a Proton or Neutron) ...
... – Proton - a positively charged particle – Neutron - a neutral particle – Electron - a negatively charged particle (much lighter than a Proton or Neutron) ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... Look at the atomic weights of a few different elements on your periodic table. Do you notice that very few of the elements have atomic weights that are close to being nice whole numbers? Do you know why this is? After all, for our purposes, the mass of both the proton and the neutron are almost exac ...
... Look at the atomic weights of a few different elements on your periodic table. Do you notice that very few of the elements have atomic weights that are close to being nice whole numbers? Do you know why this is? After all, for our purposes, the mass of both the proton and the neutron are almost exac ...
AP Chem
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
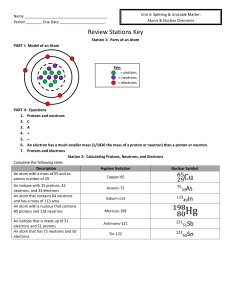
Name Period ______ Due Date Review Stations Key Station 1
... The isotope shown above has 16 protons,16 electrons, 18 neutrons, and a mass number of 34. I and III &II and IV Station 4: Average Atomic Mass 10.811 amu 28.088 amu 79.90 amu a. 35.45 amu b. Chlorine (Cl) Potassium-39 because the average atomic mass is closer to 39 than 41. ...
... The isotope shown above has 16 protons,16 electrons, 18 neutrons, and a mass number of 34. I and III &II and IV Station 4: Average Atomic Mass 10.811 amu 28.088 amu 79.90 amu a. 35.45 amu b. Chlorine (Cl) Potassium-39 because the average atomic mass is closer to 39 than 41. ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass and chemical properties. 3. Atoms of different elements are different. 4. Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass and chemical properties. 3. Atoms of different elements are different. 4. Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically ...
Structure of the atom
... Each proton has a mass of how many atomic mass units (amu)? (p. 319) Each neutron has a mass of how many atomic mass units (amu)? (p. 319) How does the mass of an electron compare to protons and neutrons? (p. 320) An atom is neutral if the number An atom is neutral if the number of protons and of pr ...
... Each proton has a mass of how many atomic mass units (amu)? (p. 319) Each neutron has a mass of how many atomic mass units (amu)? (p. 319) How does the mass of an electron compare to protons and neutrons? (p. 320) An atom is neutral if the number An atom is neutral if the number of protons and of pr ...
Chapter 10 Test A
... b. Atoms of different elements may have the same number of protons in the nucleus. c. All atoms of the same element have the same number of electrons and protons but may have different numbers of neutrons. d. The number of neutrons is equal to the number of protons. ____ 14. Which of the following s ...
... b. Atoms of different elements may have the same number of protons in the nucleus. c. All atoms of the same element have the same number of electrons and protons but may have different numbers of neutrons. d. The number of neutrons is equal to the number of protons. ____ 14. Which of the following s ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms
... Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms: Atom- smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction Atomic Mass-weighted avg mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample (isotopes) Atomic Mass Unit (amu)-unit of mass of a proton or neutron ( ...
... Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms: Atom- smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction Atomic Mass-weighted avg mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample (isotopes) Atomic Mass Unit (amu)-unit of mass of a proton or neutron ( ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.