Matter and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answer Key
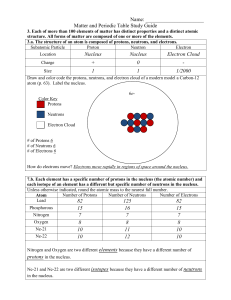
... 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound List the number of each type of atom making up the compound NH4 1 Nit ...
... 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound List the number of each type of atom making up the compound NH4 1 Nit ...
chapter-7-explore-page-248-protons-neutrons
... The Parts of the Atom Protons and neutrons have about the same mass. The mass of electrons is much smaller than the mass of protons or neutrons. That means that most of the mass of an atom is found in the nucleus. Different Elements --- Different Numbers of Protons The number of protons in the ...
... The Parts of the Atom Protons and neutrons have about the same mass. The mass of electrons is much smaller than the mass of protons or neutrons. That means that most of the mass of an atom is found in the nucleus. Different Elements --- Different Numbers of Protons The number of protons in the ...
1 - Bal Bharati Public School
... Q.18. Briefly describe the features of the Rutherford Model of an atom. what are the drawbacks ? Q.19. How do isotopes and isobars differ? Write three applications of isotopes. Q. 20. What observations in scattering experiment led Rutherford to make the following conclusions: (i) Most of the space i ...
... Q.18. Briefly describe the features of the Rutherford Model of an atom. what are the drawbacks ? Q.19. How do isotopes and isobars differ? Write three applications of isotopes. Q. 20. What observations in scattering experiment led Rutherford to make the following conclusions: (i) Most of the space i ...
Notes in PowerPoint form
... • Concluded there was small positive center and called it the nucleus • “discovered” and named the nucleus • 1908- Nobel Prize ...
... • Concluded there was small positive center and called it the nucleus • “discovered” and named the nucleus • 1908- Nobel Prize ...
Topic 7. 1 Atomic Structure
... Imagine a pea in the center of a football field with the track being the orbits. Protons and Neutrons have very similar mass. Protons and Neutrons are about 1800 times bigger than electrons. ****IB DATA*** See the data book for actual values. 7.1.2 Outline the evidence that supports a nuclear ...
... Imagine a pea in the center of a football field with the track being the orbits. Protons and Neutrons have very similar mass. Protons and Neutrons are about 1800 times bigger than electrons. ****IB DATA*** See the data book for actual values. 7.1.2 Outline the evidence that supports a nuclear ...
physics - Keith E. Holbert
... • isotope: nuclides with equal number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons • isotone: nuclides with equal number of neutrons, but different number of protons • isobars: nuclides with same total number of protons and neutrons, different combinations of Z & N • element (particular Z, any N) v ...
... • isotope: nuclides with equal number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons • isotone: nuclides with equal number of neutrons, but different number of protons • isobars: nuclides with same total number of protons and neutrons, different combinations of Z & N • element (particular Z, any N) v ...
atomic number.
... But atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. Some helium nuclei, for example, have two neutrons; others have only one. The mass number (atomic weight) of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus. The two-neutron atom of helium has a ma ...
... But atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. Some helium nuclei, for example, have two neutrons; others have only one. The mass number (atomic weight) of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus. The two-neutron atom of helium has a ma ...
Friday, Feb 3, 2006
... carbon (Period 2, Group 4A) hydrogen (Period 1, Group 1A) nitrogen (Period 2, Group 5A) calcium (Period 4, Group 2A) pg 122 35) Democritus’ ideas were not helpful in explaining chemical behavior because ...
... carbon (Period 2, Group 4A) hydrogen (Period 1, Group 1A) nitrogen (Period 2, Group 5A) calcium (Period 4, Group 2A) pg 122 35) Democritus’ ideas were not helpful in explaining chemical behavior because ...
Chapter 3
... 6. In 1808, an English schoolteacher named _________________________________ proposed an explanation for the law of the conservation of mass. 7. Finish these statements that sum up his theory. a. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called ________________. ...
... 6. In 1808, an English schoolteacher named _________________________________ proposed an explanation for the law of the conservation of mass. 7. Finish these statements that sum up his theory. a. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called ________________. ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... 3. An unknown sample is malleable and ductile. Where on the periodic table would the sample most likely be found? a. To the right of the zig-zag line. b. Bordering right on the zig-zag line. c. To the left of the zig-zag line. d. There are no elements that are both malleable and ductile found on the ...
... 3. An unknown sample is malleable and ductile. Where on the periodic table would the sample most likely be found? a. To the right of the zig-zag line. b. Bordering right on the zig-zag line. c. To the left of the zig-zag line. d. There are no elements that are both malleable and ductile found on the ...
Packet 5
... Protons – Positive charge, found in the nucleus and have a mass of 1 amu. ( Identify) Neutrons- No charge, found in the nucleus, and have a mass of 1 amu ( Isotopes) Electrons- Negative charge, found in the energy levels outside of the nucleus, have relatively no mass ( Ions) ...
... Protons – Positive charge, found in the nucleus and have a mass of 1 amu. ( Identify) Neutrons- No charge, found in the nucleus, and have a mass of 1 amu ( Isotopes) Electrons- Negative charge, found in the energy levels outside of the nucleus, have relatively no mass ( Ions) ...
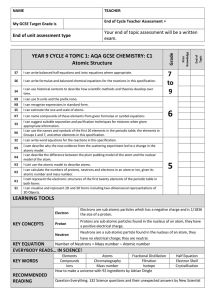
Cycle 4 Topic 1 C1 Atomic Structure Cycle Sheet
... I can use the atomic model to describe atoms. I can calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom or ion, given its atomic number and mass number. I can represent the electronic structures of the first twenty elements of the periodic table in both forms I can visualise and repr ...
... I can use the atomic model to describe atoms. I can calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom or ion, given its atomic number and mass number. I can represent the electronic structures of the first twenty elements of the periodic table in both forms I can visualise and repr ...
chapter 19 - Celina City Schools
... REFER to the National Geographic section entitled, “Visualizing the Atomic Model” (p.582) Section 2 – Masses of Atoms I. Atomic ____________ A) Atomic ____________ The number of protons (p+) in an atom Protons identify an ____________ B) Mass ____________ The sum of the number of protons and ...
... REFER to the National Geographic section entitled, “Visualizing the Atomic Model” (p.582) Section 2 – Masses of Atoms I. Atomic ____________ A) Atomic ____________ The number of protons (p+) in an atom Protons identify an ____________ B) Mass ____________ The sum of the number of protons and ...
Chapter 5 “Atomic Structure and the Periodic table”
... Contain the symbol of the element, the mass number and the atomic number. ...
... Contain the symbol of the element, the mass number and the atomic number. ...
Chapter 3 study guide answers
... Because a few alpha particles bounced back from the foil, Rutherford concluded that they were ...
... Because a few alpha particles bounced back from the foil, Rutherford concluded that they were ...
elements_and_the_periodic_table_2011
... Atoms are the smallest part of an element that has all the properties of an element. ...
... Atoms are the smallest part of an element that has all the properties of an element. ...
AtomsIntro His
... number. • Mass numbers are found by adding the protons and neutrons. • Atomic mass of an element is the average mass of all the isotopes of that element. ...
... number. • Mass numbers are found by adding the protons and neutrons. • Atomic mass of an element is the average mass of all the isotopes of that element. ...
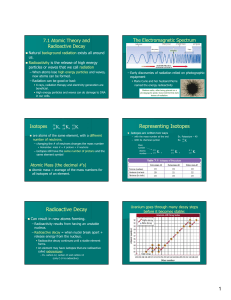
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.