An Unifying Basis for all the Nuclear Reactions
... subjected to any kind of nuclear reactions. To make the hydrogen atoms to release energy, first we need to compress the atoms to the state of plasma and then that plasma should be subjected to an expansion. Energy will be consumed in the compression of the gaseous hydrogen before it ever releases th ...
... subjected to any kind of nuclear reactions. To make the hydrogen atoms to release energy, first we need to compress the atoms to the state of plasma and then that plasma should be subjected to an expansion. Energy will be consumed in the compression of the gaseous hydrogen before it ever releases th ...
Periodicity - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... THE ORIGINS OF NATURALLY OCCURING ELEMENTS Natural and synthetic elements are created in different ways ...
... THE ORIGINS OF NATURALLY OCCURING ELEMENTS Natural and synthetic elements are created in different ways ...
Jeopardy Nuclear Physics
... number of neutrons passing from one fuel rod to another. Back to Jeopardy ...
... number of neutrons passing from one fuel rod to another. Back to Jeopardy ...
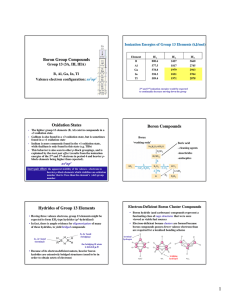
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier pblock elements being higher than expected). ...
... This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier pblock elements being higher than expected). ...
View - Rutgers Physics
... from atoms to the nucleus of the atom. Nuclear physics began with the observation of various kinds of radiation of much higher energy than the atomic spectra that come from atomic energy levels. We now understand that these come from decays of unstable atomic nuclei. The three observed kinds of radi ...
... from atoms to the nucleus of the atom. Nuclear physics began with the observation of various kinds of radiation of much higher energy than the atomic spectra that come from atomic energy levels. We now understand that these come from decays of unstable atomic nuclei. The three observed kinds of radi ...
The Structure of the Atom
... All matter is made of . . . Atoms cannot be . . . Atoms of a given element . . . Atoms of different elements . . . In a chemical reaction atoms are ...
... All matter is made of . . . Atoms cannot be . . . Atoms of a given element . . . Atoms of different elements . . . In a chemical reaction atoms are ...
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 8. identify significant figures in measurements and know how to determine them. 9. use the rules for determining the number of significant figures required in answers to calculations. 10. distinguish between accuracy and precision in experimental results. 11. use density as another physical property ...
... 8. identify significant figures in measurements and know how to determine them. 9. use the rules for determining the number of significant figures required in answers to calculations. 10. distinguish between accuracy and precision in experimental results. 11. use density as another physical property ...
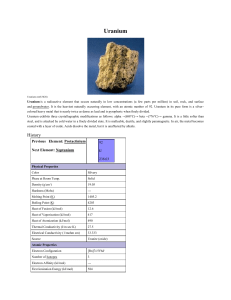
Uranium
... uranium-238 is about 4.5 billion years, which means it is not very radioactive. In fact, its very long half-life (and thus low radioactivity) is the reason uranium still exists on the Earth. Three additional isotopes of uranium are not naturally present but can be produced by nuclear transformations ...
... uranium-238 is about 4.5 billion years, which means it is not very radioactive. In fact, its very long half-life (and thus low radioactivity) is the reason uranium still exists on the Earth. Three additional isotopes of uranium are not naturally present but can be produced by nuclear transformations ...
Nuclear Force - International Journal of Science and Technology
... *Range of nuclear force :- To show that the range of force is related to the mass of exchanged particle, It is assumed that the π0-meson is contained virtually in a proton. If this virtual particle travels with the velocity of light as might be expected for a field particle, then the greatest distan ...
... *Range of nuclear force :- To show that the range of force is related to the mass of exchanged particle, It is assumed that the π0-meson is contained virtually in a proton. If this virtual particle travels with the velocity of light as might be expected for a field particle, then the greatest distan ...
How to Balance Chemical Equations
... 3. Example of how to balance a chemical equation a) Write a balanced chemical equation of hydrogen combining with oxygen to produce water. Hydrogen ...
... 3. Example of how to balance a chemical equation a) Write a balanced chemical equation of hydrogen combining with oxygen to produce water. Hydrogen ...
Chapter 2 1
... and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. Protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge – leading to electrostatic attraction between the two particles. Neutrons do not have a charge or are neutral. Neutral atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons. If an atom loses electr ...
... and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. Protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge – leading to electrostatic attraction between the two particles. Neutrons do not have a charge or are neutral. Neutral atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons. If an atom loses electr ...
Chemistry –Worksheet: Atomic structure
... 21. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of tungsten-184 which has an atomic number of 74? # of neutrons:_________________ 22. Which of the following combinations of particles represents an ion of net charge -1 and of mass number 82? (A) 46 neutrons, 35 protons, 36 electrons (C) 46 neutro ...
... 21. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of tungsten-184 which has an atomic number of 74? # of neutrons:_________________ 22. Which of the following combinations of particles represents an ion of net charge -1 and of mass number 82? (A) 46 neutrons, 35 protons, 36 electrons (C) 46 neutro ...
110 EXAM Review MATERIALTro
... Density measures how closely the mass of a given substance is packed in a given volume ...
... Density measures how closely the mass of a given substance is packed in a given volume ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements The Representative
... configuration is ns2np1 (n is the period number). Boron and aluminum almost always have an oxidation number of +3. The heavier elements of the group are more likely to keep their s electrons and can have oxidation numbers of +1 ...
... configuration is ns2np1 (n is the period number). Boron and aluminum almost always have an oxidation number of +3. The heavier elements of the group are more likely to keep their s electrons and can have oxidation numbers of +1 ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements
... All group 2 elements except for beryllium react with water and the vigor of the reaction increases going down the group. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
... All group 2 elements except for beryllium react with water and the vigor of the reaction increases going down the group. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
KNIGHT Physics for Scientists and Engineers
... has six protons and six neutrons in the nucleus, is written and pronounced "carbon twelve." The radioactive form of carbon used in carbon dating is 14C.It has six protons. makine it carbon. and eieht neutrons. More th& 3000 isotopes a& known. The majority of these are radioactive, meaning that the n ...
... has six protons and six neutrons in the nucleus, is written and pronounced "carbon twelve." The radioactive form of carbon used in carbon dating is 14C.It has six protons. makine it carbon. and eieht neutrons. More th& 3000 isotopes a& known. The majority of these are radioactive, meaning that the n ...
Predicting Products online assistance #3
... 3. single replacement - an element replaces another in a compound. 4. double replacement - the elements in two compounds switch partners to form two new compounds. Writing Balanced Equations A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different sub ...
... 3. single replacement - an element replaces another in a compound. 4. double replacement - the elements in two compounds switch partners to form two new compounds. Writing Balanced Equations A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different sub ...
Matter - GEOCITIES.ws
... 3. In a compound, the constituent elements are present in a definite proportion by weight. 4. A compound has a fixed boiling point and a fixed melting point. 5. A compound is a homogenous substance, i.e. a compound is such a substance which is same in its properties and composition. Mixture: A mixtu ...
... 3. In a compound, the constituent elements are present in a definite proportion by weight. 4. A compound has a fixed boiling point and a fixed melting point. 5. A compound is a homogenous substance, i.e. a compound is such a substance which is same in its properties and composition. Mixture: A mixtu ...
File
... *amu is the atomic mass unit (u, μ or amu), which is defined as 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This value is arbitrary and simply provides a reference point for measuring relative atomic masses. Stable vs. Unstable Isotopes There may be several isotopes of the same element. Some of these isoto ...
... *amu is the atomic mass unit (u, μ or amu), which is defined as 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This value is arbitrary and simply provides a reference point for measuring relative atomic masses. Stable vs. Unstable Isotopes There may be several isotopes of the same element. Some of these isoto ...
Lecture 1.
... Many protons stay together inside a small nucleus. Electric forces do not destroy the nucleus. Why?? The protons do not scatter into the space. Why?? Conclusion: Due to the nucleus exists and the nucleus stays in one volume, there must be a force which stick the protons together. Definition (force i ...
... Many protons stay together inside a small nucleus. Electric forces do not destroy the nucleus. Why?? The protons do not scatter into the space. Why?? Conclusion: Due to the nucleus exists and the nucleus stays in one volume, there must be a force which stick the protons together. Definition (force i ...
Nuclear Physics - Thierry Karsenti
... PRE-REQUISITE KNOWLEDGE: In this section you are provided with information regarding the specific pre-requisite knowledge and skills you require to start the module. Carefully look into the requirements as this will help you to decide whether you require some revision work or not. TIME REQUIRED: It ...
... PRE-REQUISITE KNOWLEDGE: In this section you are provided with information regarding the specific pre-requisite knowledge and skills you require to start the module. Carefully look into the requirements as this will help you to decide whether you require some revision work or not. TIME REQUIRED: It ...
Atomic Structure Tick Sheet
... I can use symbols like 23Na to work out the protons, neutrons and electrons ...
... I can use symbols like 23Na to work out the protons, neutrons and electrons ...
atoms
... Unfortunately, there is no alternative: The names and charges of the common polyatomic ions must be memorized. (a) Lithium nitrate Lithium (group 1A) forms only the Li+ ion and does not need a Roman numeral. (b) Potassium hydrogen sulfate (potassium bisulfate) Potassium (group 1A) forms only the K+ ...
... Unfortunately, there is no alternative: The names and charges of the common polyatomic ions must be memorized. (a) Lithium nitrate Lithium (group 1A) forms only the Li+ ion and does not need a Roman numeral. (b) Potassium hydrogen sulfate (potassium bisulfate) Potassium (group 1A) forms only the K+ ...
U4 Project
... onic%20Charges%29.pdf and complete the chart below. Some elements may form more than once charge. You only need to select one of them to fill in the data below. Krypton does not have an ionic charge because of its stability. If you were assigned krypton, you will use a +1 charge to complete this par ...
... onic%20Charges%29.pdf and complete the chart below. Some elements may form more than once charge. You only need to select one of them to fill in the data below. Krypton does not have an ionic charge because of its stability. If you were assigned krypton, you will use a +1 charge to complete this par ...