The Chemical Context of Life
... together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons For example H:H (H–H) • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons For example O::O (O=O) Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publi ...
... together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons For example H:H (H–H) • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons For example O::O (O=O) Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publi ...
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations
... * because there is oxygen in every compound in the equation, it may be helpful to count the number of a polyatomic ion, rather than splitting the polyatomic ion into its elements and then counting.* EXAMPLE #6: ...
... * because there is oxygen in every compound in the equation, it may be helpful to count the number of a polyatomic ion, rather than splitting the polyatomic ion into its elements and then counting.* EXAMPLE #6: ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
... 46) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have A) different atomic numbers. B) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of protons. C) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of electrons. D) the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. E) the same atomic mass but diff ...
... 46) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have A) different atomic numbers. B) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of protons. C) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of electrons. D) the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. E) the same atomic mass but diff ...
Lecture 2 - TCD Chemistry
... Material particles which cannot be divided into smaller particles, but they can react to give other elementary particles Protons, neutron, electrons (valid for nearly all atoms: exception the hydrogen atom) ...
... Material particles which cannot be divided into smaller particles, but they can react to give other elementary particles Protons, neutron, electrons (valid for nearly all atoms: exception the hydrogen atom) ...
PCSD General Chemistry Pacing Guide
... Explain the history and models of the atomic theory through Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr, and the electron cloud model Describe how Dalton’s atomic theory has changed over time Identify the parts of the atom Define atomic number, mass number, and atomic mass and use these ...
... Explain the history and models of the atomic theory through Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr, and the electron cloud model Describe how Dalton’s atomic theory has changed over time Identify the parts of the atom Define atomic number, mass number, and atomic mass and use these ...
First Grade Science Pacing
... into energy, releasing large amounts of energy compared with chemical reactions. Fission is the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller pieces. Fusion is the joining of nuclei and is the process that generates energy in the Sun and other stars. ...
... into energy, releasing large amounts of energy compared with chemical reactions. Fission is the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller pieces. Fusion is the joining of nuclei and is the process that generates energy in the Sun and other stars. ...
Science - Pasco School District
... into energy, releasing large amounts of energy compared with chemical reactions. Fission is the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller pieces. Fusion is the joining of nuclei and is the process that generates energy in the Sun and other stars. ...
... into energy, releasing large amounts of energy compared with chemical reactions. Fission is the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller pieces. Fusion is the joining of nuclei and is the process that generates energy in the Sun and other stars. ...
Utilization of Thermal Neutrons
... measure gamma-rays with energies from 60 KeV to 3.0 MeV. Figure 3 shows typical gamma-ray spectra from an irradiated pottery specimen.[17] Most common and efficient neutron sources are nuclear reactors, that can produce thermal neutron flux of around 1012 − 1014 neutrons/cm2 s at maximum power. Hig ...
... measure gamma-rays with energies from 60 KeV to 3.0 MeV. Figure 3 shows typical gamma-ray spectra from an irradiated pottery specimen.[17] Most common and efficient neutron sources are nuclear reactors, that can produce thermal neutron flux of around 1012 − 1014 neutrons/cm2 s at maximum power. Hig ...
Tamene Hailu - Addis Ababa University Institutional Repository
... German physicist Bothe and Becker continuing Rutherford’s experiment on alpha particle bombardment of light atoms and observation of nuclear reaction discovered that when some elements such as ,lithium ,beryllium, or boron are exposed to alpha radiation there appears a strongly penetrating radiation ...
... German physicist Bothe and Becker continuing Rutherford’s experiment on alpha particle bombardment of light atoms and observation of nuclear reaction discovered that when some elements such as ,lithium ,beryllium, or boron are exposed to alpha radiation there appears a strongly penetrating radiation ...
Atomic Theory and the Nuclear Atom
... 1. Atoms having low atomic numbers (up to about ___) are more stable when the neutron-proton ratio is ________. 2. Atoms having large atomic numbers are more stable when there are greater numbers of _______________ than ________________. 3. No stable nuclides exist for atoms with atomic numbers grea ...
... 1. Atoms having low atomic numbers (up to about ___) are more stable when the neutron-proton ratio is ________. 2. Atoms having large atomic numbers are more stable when there are greater numbers of _______________ than ________________. 3. No stable nuclides exist for atoms with atomic numbers grea ...
2 - grade11chemistry
... The Categories • The elements are organized in three categories: the metals (left and centre of the periodic table), the non-metals (on the right side of the periodic table), and the metalloids (the staircase of ...
... The Categories • The elements are organized in three categories: the metals (left and centre of the periodic table), the non-metals (on the right side of the periodic table), and the metalloids (the staircase of ...
8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... (metal hydroxide plus acid gives solution of a salt plus water) (metal oxide plus acid gives solution of a salt plus water) "Describe and justify the criteria used to place metals into an order of activity based on their ease of reaction with oxygen, water and dilute acids". "Perform a first hand in ...
... (metal hydroxide plus acid gives solution of a salt plus water) (metal oxide plus acid gives solution of a salt plus water) "Describe and justify the criteria used to place metals into an order of activity based on their ease of reaction with oxygen, water and dilute acids". "Perform a first hand in ...
Chemistry - School District of Springfield Township
... Unit III: The Organization of Matter • The Periodic Table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways to compare and organize the elements. o Elements with similar properties have been placed into groups. o The physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular patt ...
... Unit III: The Organization of Matter • The Periodic Table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways to compare and organize the elements. o Elements with similar properties have been placed into groups. o The physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular patt ...
Review Unit 5
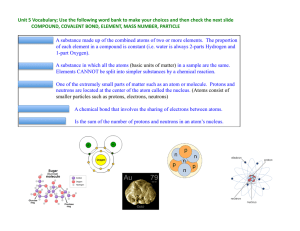
... COMPOUND, COVALENT BOND, ELEMENT, MASS NUMBER, PARTICLE COMPOUND: A substance made up of the combined atoms of two or more elements. The proportion of each element in a compound is constant (i.e. water is always 2-parts Hydrogen and 1-part Oxygen). ELEMENT: ...
... COMPOUND, COVALENT BOND, ELEMENT, MASS NUMBER, PARTICLE COMPOUND: A substance made up of the combined atoms of two or more elements. The proportion of each element in a compound is constant (i.e. water is always 2-parts Hydrogen and 1-part Oxygen). ELEMENT: ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... molecules of oxygen To produce: 1 molecule of carbon dioxide and 2 molecules of water ...
... molecules of oxygen To produce: 1 molecule of carbon dioxide and 2 molecules of water ...
Chapter 2
... The Nuclear Atom • Rutherford postulated a very small, positive, dense nucleus with the electrons around the outside of the atom. • Most of the volume of the atom is empty space. ...
... The Nuclear Atom • Rutherford postulated a very small, positive, dense nucleus with the electrons around the outside of the atom. • Most of the volume of the atom is empty space. ...
First Semester complete review with answers
... The difference between an exothermic chemical reaction and an endothermic chemical reaction o Exothermic = releases energy in the form of heat or light (found in the products of the reaction) o Endothermic = takes in energy in the form of heat or light (found in the reactants of the reaction) Un ...
... The difference between an exothermic chemical reaction and an endothermic chemical reaction o Exothermic = releases energy in the form of heat or light (found in the products of the reaction) o Endothermic = takes in energy in the form of heat or light (found in the reactants of the reaction) Un ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... discovered the radioactivity. He was working with compounds containing the element uranium. Becqeurel found that photographic plates covered to keep out light became fogged, or partially exposed, when these uranium compounds were anywhere near the plates. Two years after Becquerel’s discovery, Pierr ...
... discovered the radioactivity. He was working with compounds containing the element uranium. Becqeurel found that photographic plates covered to keep out light became fogged, or partially exposed, when these uranium compounds were anywhere near the plates. Two years after Becquerel’s discovery, Pierr ...
BS5-Ch 2.
... the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. • cements the idea that atoms react as complete (whole) particles. • chemical formulas indicate whole numbers of atoms- not fractions ...
... the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. • cements the idea that atoms react as complete (whole) particles. • chemical formulas indicate whole numbers of atoms- not fractions ...
Radiant Energy Research Manual 3.0.0
... added to its ferrite core. The high-voltage, high-frequency is the result of the transformer being driven into resonance at about 143Khz. The flyback transformer T1 outputs around 10KV, 15KV peak to peak at the above mentioned frequency and is inputted to a solid-state multiplier section. The multip ...
... added to its ferrite core. The high-voltage, high-frequency is the result of the transformer being driven into resonance at about 143Khz. The flyback transformer T1 outputs around 10KV, 15KV peak to peak at the above mentioned frequency and is inputted to a solid-state multiplier section. The multip ...
39 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... followed—first with natural bombarding particles from radioactive elements. Later, scientists used more energetic particles hurled by giant atom-smashing particle accelerators. The elements beyond uranium in the periodic table have been produced through artificial transmutation. These elements have ...
... followed—first with natural bombarding particles from radioactive elements. Later, scientists used more energetic particles hurled by giant atom-smashing particle accelerators. The elements beyond uranium in the periodic table have been produced through artificial transmutation. These elements have ...
EOCT Physical Science Atomic Theory
... B. a single neutron. C. one proton and one electron. D. one neutron and one proton. 13. By using electrolysis, salt can be separated into sodium metal and chlorine gas, and water can be separated into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. No further physical or chemical techniques can be used to change any o ...
... B. a single neutron. C. one proton and one electron. D. one neutron and one proton. 13. By using electrolysis, salt can be separated into sodium metal and chlorine gas, and water can be separated into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. No further physical or chemical techniques can be used to change any o ...
The structure of the nucleus - Assets
... nucleus of an atom spontaneously changes into a different nuclide, emitting radiation as it does so. Because it emits radiation, the original unstable nucleus is called a radionuclide. For example: ...
... nucleus of an atom spontaneously changes into a different nuclide, emitting radiation as it does so. Because it emits radiation, the original unstable nucleus is called a radionuclide. For example: ...
An Unifying Basis for all the Nuclear Reactions
... subjected to any kind of nuclear reactions. To make the hydrogen atoms to release energy, first we need to compress the atoms to the state of plasma and then that plasma should be subjected to an expansion. Energy will be consumed in the compression of the gaseous hydrogen before it ever releases th ...
... subjected to any kind of nuclear reactions. To make the hydrogen atoms to release energy, first we need to compress the atoms to the state of plasma and then that plasma should be subjected to an expansion. Energy will be consumed in the compression of the gaseous hydrogen before it ever releases th ...