The World of Plants in 41 Minutes
... companion cell whose nucleus and ribosomes serve both cells ...
... companion cell whose nucleus and ribosomes serve both cells ...
Plant Science - Aurora City Schools
... A meristem consists of cells that divide frequently, generating additional cells. Some products of this division remain in the meristem and produce still more cells, while others differentiate and are incorporated into tissues and organs of the growing plant. ...
... A meristem consists of cells that divide frequently, generating additional cells. Some products of this division remain in the meristem and produce still more cells, while others differentiate and are incorporated into tissues and organs of the growing plant. ...
Ch32
... CAM plants do the reverse. Light and dehydration also affect the opening or closing of the stomata. A low concentration of CO2 in the leaf induces stomata to open even in the dark. ...
... CAM plants do the reverse. Light and dehydration also affect the opening or closing of the stomata. A low concentration of CO2 in the leaf induces stomata to open even in the dark. ...
PLSC 210-Horticulture Science
... _____chloroplast), while respiration occurs in (_____ mitochondria, _____chloroplast). (check the correct terms.) 16. Which of the following is the correct nomenclature for “Crimson Sweet” watermelon? a. b. c. d. ...
... _____chloroplast), while respiration occurs in (_____ mitochondria, _____chloroplast). (check the correct terms.) 16. Which of the following is the correct nomenclature for “Crimson Sweet” watermelon? a. b. c. d. ...
Botany Worksheet Maryland Master Gardener Handbook Chapter 3
... _________________________, probing for nectar with their tongue. Beetles need ______________________ sturdy petals and wide access to the nectar. Wild ginger are at ground levels and can be pollinated by _______________, ______________________________ and ____________________. Hummingbirds can acces ...
... _________________________, probing for nectar with their tongue. Beetles need ______________________ sturdy petals and wide access to the nectar. Wild ginger are at ground levels and can be pollinated by _______________, ______________________________ and ____________________. Hummingbirds can acces ...
Cordyline fruticosa
... flowers turn to red berries and grow in panicles of 40-60cm in length. NOTE: Propagation from stem cuttings. Ethno Botany This ornamental plant has a very sweet starchy rhizome when mature. It can be eaten and is used in medicine. Tea, can be made from leaves, buds, or young shoots, used as a mouthw ...
... flowers turn to red berries and grow in panicles of 40-60cm in length. NOTE: Propagation from stem cuttings. Ethno Botany This ornamental plant has a very sweet starchy rhizome when mature. It can be eaten and is used in medicine. Tea, can be made from leaves, buds, or young shoots, used as a mouthw ...
Plant Form and Function
... - Root pressure results from water flowing into the stele (vascular tissue of root) from the soil as a result of the high mineral content in the root cells (known as guttation) - Transpirational pull can pull fluid up the tallest trees - Transpiration, the evaporation of water from leaves, causes ne ...
... - Root pressure results from water flowing into the stele (vascular tissue of root) from the soil as a result of the high mineral content in the root cells (known as guttation) - Transpirational pull can pull fluid up the tallest trees - Transpiration, the evaporation of water from leaves, causes ne ...
Organismal Biology Test 2 Notes Organism-of-the
... cells that conduct most of the water and minerals upward from the roots to the rest of the plant Phloem= vascular plant tissue consisting of living cells arranged into elongated tubes that transport sugar and other organic nutrients throughout the plant ...
... cells that conduct most of the water and minerals upward from the roots to the rest of the plant Phloem= vascular plant tissue consisting of living cells arranged into elongated tubes that transport sugar and other organic nutrients throughout the plant ...
Different Ways to Measure Growth
... compared, it can be seen that different parts of the body grow at different rates. ...
... compared, it can be seen that different parts of the body grow at different rates. ...
chapter27_Sections 6
... Plant Hormones • Plant hormones stimulate or inhibit development • When a plant hormone binds to a target cell, it may modify gene expression, change solute concentrations, affect enzyme activity, or activate another molecule in cytoplasm • Five types of plant hormones interact in plant development ...
... Plant Hormones • Plant hormones stimulate or inhibit development • When a plant hormone binds to a target cell, it may modify gene expression, change solute concentrations, affect enzyme activity, or activate another molecule in cytoplasm • Five types of plant hormones interact in plant development ...
flowering plants
... new roots and upright stems at various points Rhizomes – an under ground stem that produces new roots and upright stems at various points ...
... new roots and upright stems at various points Rhizomes – an under ground stem that produces new roots and upright stems at various points ...
Teacher Quality Grant - Gulf Coast State College
... Stems support plants, transport materials, and provide storage. • Stems have many functions. – support leaves and flowers – house most of the vascular system – store water ...
... Stems support plants, transport materials, and provide storage. • Stems have many functions. – support leaves and flowers – house most of the vascular system – store water ...
Plants Power Point - Panhandle Area Educational Consortium
... Stems support plants, transport materials, and provide storage. • Stems have many functions. – support leaves and flowers – house most of the vascular system – store water ...
... Stems support plants, transport materials, and provide storage. • Stems have many functions. – support leaves and flowers – house most of the vascular system – store water ...
Chapter Two
... They lose less water than wide leaves. Their smell attracts insects. They help the tree retain heat in cold climates. ...
... They lose less water than wide leaves. Their smell attracts insects. They help the tree retain heat in cold climates. ...
invited review: in vitro morphogenesis in plants – recent
... manipulation of explant size to induce and optimize regeneration, has been used for many years with dicotyledonous species to study in vitro morphogenesis. Thin cell layer cultures can be manipulated for rigorously controlled programming of different morphogenic responses: callus formation, shoot or ...
... manipulation of explant size to induce and optimize regeneration, has been used for many years with dicotyledonous species to study in vitro morphogenesis. Thin cell layer cultures can be manipulated for rigorously controlled programming of different morphogenic responses: callus formation, shoot or ...
Unit 3 Plants
... circumference of a tree. This stops the sugar from the leaves from reaching the roots which causes the roots, and thus the whole tree to die. In woody stems, a layer of meristematic cells in the cortex becomes active (the cork cambium) and makes a waterproof layer of cork, commonly called bark or pe ...
... circumference of a tree. This stops the sugar from the leaves from reaching the roots which causes the roots, and thus the whole tree to die. In woody stems, a layer of meristematic cells in the cortex becomes active (the cork cambium) and makes a waterproof layer of cork, commonly called bark or pe ...
OPERCULINA TURPETHUM(L.) SILVA MANSO. Research Article
... presence of glycosides, saponins flavanoids, steroids and carbohydrates and the results of the study entered in Table 5. Microscopic characters Stem T.S. Of young stem, the epidermis consists of a single layer of tubular cells, the outer and radial walls of which are thickened(10). A narrow parenchy ...
... presence of glycosides, saponins flavanoids, steroids and carbohydrates and the results of the study entered in Table 5. Microscopic characters Stem T.S. Of young stem, the epidermis consists of a single layer of tubular cells, the outer and radial walls of which are thickened(10). A narrow parenchy ...
grade 3 – science and technology – plants
... - STEM helps take water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and flowers of the plant Kidney Bean Experiment helped us learn about WHAT A PLANT NEEDS TO GROW - to grow well, a plant needs WATER, SUN AND A WARM PLACE Carrot and Chrysanthemum Experiment we learned about the difference betwee ...
... - STEM helps take water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and flowers of the plant Kidney Bean Experiment helped us learn about WHAT A PLANT NEEDS TO GROW - to grow well, a plant needs WATER, SUN AND A WARM PLACE Carrot and Chrysanthemum Experiment we learned about the difference betwee ...
chapter 35 - Fort Bend ISD
... Concept 35.1 Plants have a hierarchical organization consisting of organs, tissues, and cells. ...
... Concept 35.1 Plants have a hierarchical organization consisting of organs, tissues, and cells. ...
the process of converting light energy into chemical energy using
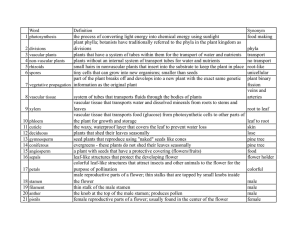
... vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to stems and leaves vascular tissue that transports food (glucose) from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth and storage the waxy, waterproof layer that covers the leaf to prevent water loss plants that sh ...
... vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to stems and leaves vascular tissue that transports food (glucose) from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth and storage the waxy, waterproof layer that covers the leaf to prevent water loss plants that sh ...
Sensory Systems in Plants
... • Promotes elongation of the stem (This helps a plant grow torwards a light source). • Plant cells that are in shade have more auxin because the auxin migrates from the light side to the dark side therefore growing faster than cells in the light causing the plant to bend. (As shown in Frit Went's ex ...
... • Promotes elongation of the stem (This helps a plant grow torwards a light source). • Plant cells that are in shade have more auxin because the auxin migrates from the light side to the dark side therefore growing faster than cells in the light causing the plant to bend. (As shown in Frit Went's ex ...
Master Gardener 2015 Basic Botany
... produce sugars, cool the plant, can be animal attractants Dermal Vascular Ground Stems: support leaves and fruits, conduct Stem sugars, water and nutrients (translocate), storage Dermal Vascular Roots: Ground anchor, absorb water and nutrients, Root conduct water ...
... produce sugars, cool the plant, can be animal attractants Dermal Vascular Ground Stems: support leaves and fruits, conduct Stem sugars, water and nutrients (translocate), storage Dermal Vascular Roots: Ground anchor, absorb water and nutrients, Root conduct water ...
23 Plant Structure and Function teacher ppt
... Growth and Plants Hormones Other (Sunlight, Temperature, and Gravity) ...
... Growth and Plants Hormones Other (Sunlight, Temperature, and Gravity) ...
Meristem

A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells), found in zones of the plant where growth can take place.Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. The shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function.The term meristem was first used in 1858 by Karl Wilhelm von Nägeli (1817–1891) in his book Beiträge zur Wissenschaftlichen Botanik. It is derived from the Greek word merizein (μερίζειν), meaning to divide, in recognition of its inherent function.In general, differentiated plant cells cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Therefore, cell division in the meristem is required to provide new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body.Meristematic cells are incompletely or not at all differentiated, and are capable of continued cellular division (youthful). Furthermore, the cells are small and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The vacuoles are extremely small. The cytoplasm does not contain differentiated plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), although they are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together without intercellular cavities. The cell wall is a very thin primary cell wall.Maintenance of the cells requires a balance between two antagonistic processes: organ initiation and stem cell population renewal.Apical meristems are the completely undifferentiated (indeterminate) meristems in a plant. These differentiate into three kinds of primary meristems. The primary meristems in turn produce the two secondary meristem types. These secondary meristems are also known as lateral meristems because they are involved in lateral growth.At the meristem summit, there is a small group of slowly dividing cells, which is commonly called the central zone. Cells of this zone have a stem cell function and are essential for meristem maintenance. The proliferation and growth rates at the meristem summit usually differ considerably from those at the periphery.Meristems also are induced in the roots of legumes such as soybean, Lotus japonicus, pea, and Medicago truncatula after infection with soil bacteria commonly called Rhizobium. Cells of the inner or outer cortex in the so-called ""window of nodulation"" just behind the developing root tip are induced to divide. The critical signal substance is the lipo-oligosaccharide Nod-factor, decorated with side groups to allow specificity of interaction. The Nod factor receptor proteins NFR1 and NFR5 were cloned from several legumes including Lotus japonicus, Medicago truncatula and soybean (Glycine max). Regulation of nodule meristems utilizes long distance regulation commonly called ""Autoregulation of Nodulation"" (AON). This process involves a leaf-vascular tissue located LRR receptor kinases (LjHAR1, GmNARK and MtSUNN), CLE peptide signalling, and KAPP interaction, similar to that seen in the CLV1,2,3 system. LjKLAVIER also exhibits a nodule regulation phenotype though it is not yet known how this relates to the other AON receptor kinases.