Action Research - Hazleton Area School District
... Some scientists believe these microspheres took on more and more of the cells characteristics and eventually became what we know of as cells. Evolution of RNA and DNA Neither DNA or RNA can exist without each other. So which can first?????? Scientists think RNA existed first and gave way t ...
... Some scientists believe these microspheres took on more and more of the cells characteristics and eventually became what we know of as cells. Evolution of RNA and DNA Neither DNA or RNA can exist without each other. So which can first?????? Scientists think RNA existed first and gave way t ...
The history of life - Mrs. Stout's Website
... nucleic acids… which become surrounded by a membrane Sidney Fox – produced protocells (large ordered structure that carried out some activities of life such as growth, division, & metabolism) ...
... nucleic acids… which become surrounded by a membrane Sidney Fox – produced protocells (large ordered structure that carried out some activities of life such as growth, division, & metabolism) ...
File
... there will be a high % similarity of DNA strands. If two species are not closely related then they will have less similarity in their DNA (eg. a frog and a human would have low % similarity in their DNA than the human and the chimp). ...
... there will be a high % similarity of DNA strands. If two species are not closely related then they will have less similarity in their DNA (eg. a frog and a human would have low % similarity in their DNA than the human and the chimp). ...
Changes Over Time and Classification
... three important observations: The world includes a tremendous diversity of living things throughout a wide range of habitats Animal species, like those in the Galapagos Islands, that are related, can have different characteristics or occupy different habitats in the same area. Fossils — preserved re ...
... three important observations: The world includes a tremendous diversity of living things throughout a wide range of habitats Animal species, like those in the Galapagos Islands, that are related, can have different characteristics or occupy different habitats in the same area. Fossils — preserved re ...
Part 8 - glenbrook s hs
... • Sponges are the simplest animals, probably evolved very early from colonial protists • Range in height from about 1 cm to 2 meters. • Have no nerves or muscles, and consist of about 9,000 species. • About 100 species lives in fresh water and the rest are marine. • The body of a sponge resembles a ...
... • Sponges are the simplest animals, probably evolved very early from colonial protists • Range in height from about 1 cm to 2 meters. • Have no nerves or muscles, and consist of about 9,000 species. • About 100 species lives in fresh water and the rest are marine. • The body of a sponge resembles a ...
EARTH HISTORY
... THE GEOLOGIC RECORD The principle of Uniformitarianism states that processes observed on Earth today have operated throughout history, and have produced the rocks and fossils that we see. FOSSILS Fossils provide evidence about the ancient history of Earth and the extinct biota (life). ...
... THE GEOLOGIC RECORD The principle of Uniformitarianism states that processes observed on Earth today have operated throughout history, and have produced the rocks and fossils that we see. FOSSILS Fossils provide evidence about the ancient history of Earth and the extinct biota (life). ...
Chapter 17:
... Use pieces- rarely see whole organisms Look for similarities/differences between fossils and current organisms Date the fossil ...
... Use pieces- rarely see whole organisms Look for similarities/differences between fossils and current organisms Date the fossil ...
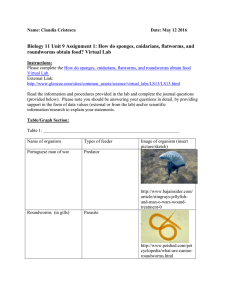
Biology 11 Unit 9 Assignment 1 How do sponges
... various invertebrates have adapted to feeding in their environment. Filter feeders filter bacteria, algae, protozoans and other bacteria from the water in which they live. Types of organisms with this method of feeding are usually sessile and relatively inactive. On the other hand organisms that are ...
... various invertebrates have adapted to feeding in their environment. Filter feeders filter bacteria, algae, protozoans and other bacteria from the water in which they live. Types of organisms with this method of feeding are usually sessile and relatively inactive. On the other hand organisms that are ...
Invertebrates: Phylum Porifera and Phylum Cnidarians
... Simplest of ALL Animals A. ____________________ – asymmetrical, pores all over body with large hole on top called an ____________________ where water is pumped through, Have no mouth or gut, Have no tissues or organs, Simple functions are carried out by a few specialized cells B. ___________________ ...
... Simplest of ALL Animals A. ____________________ – asymmetrical, pores all over body with large hole on top called an ____________________ where water is pumped through, Have no mouth or gut, Have no tissues or organs, Simple functions are carried out by a few specialized cells B. ___________________ ...
Name: ___________ Date: Period: ______ Science Mr. Vorstadt
... 30- ___________________________ evolution different groups evolve from one ancestor. 31- ___________________________ evolution two or more different groups evolve so that they resemble one another strongly. 32- ___________________________ radiation organisms spread into new environments and become a ...
... 30- ___________________________ evolution different groups evolve from one ancestor. 31- ___________________________ evolution two or more different groups evolve so that they resemble one another strongly. 32- ___________________________ radiation organisms spread into new environments and become a ...
Changes Over Time - twpunionschools.org
... Adaptation: A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce. ...
... Adaptation: A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce. ...
Evolution Test Review
... 11. The first word is the genus of the organism. What is the second? 12. What is a taxon? 13. Name Linnaeus’ 7 taxonomic categories from largest to smallest. 14. Why is it important to have a universal scientific name for an organism? 15. What tool do scientists use to identify the scientific name o ...
... 11. The first word is the genus of the organism. What is the second? 12. What is a taxon? 13. Name Linnaeus’ 7 taxonomic categories from largest to smallest. 14. Why is it important to have a universal scientific name for an organism? 15. What tool do scientists use to identify the scientific name o ...
Evolution Test Review
... 11. The first word is the genus of the organism. What is the second? 12. What is a taxon? 13. Name Linnaeus’ 7 taxonomic categories from largest to smallest. 14. Why is it important to have a universal scientific name for an organism? 15. What tool do scientists use to identify the scientific name o ...
... 11. The first word is the genus of the organism. What is the second? 12. What is a taxon? 13. Name Linnaeus’ 7 taxonomic categories from largest to smallest. 14. Why is it important to have a universal scientific name for an organism? 15. What tool do scientists use to identify the scientific name o ...
Unifying Themes in Biology Represent recurring patterns
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
File
... Sponges are ideal habitats for marine life because they’re irregular and large. Their relationship with algae, bacteria, and plant like protists is symbiotic; organisms on or inside the sponge provide the food and oxygen for it while the sponge provides protection for the organisms living on or in ...
... Sponges are ideal habitats for marine life because they’re irregular and large. Their relationship with algae, bacteria, and plant like protists is symbiotic; organisms on or inside the sponge provide the food and oxygen for it while the sponge provides protection for the organisms living on or in ...
Sponge and Cnidarian Test: Zoology B
... 51. The classification of sponges is Kingdom 52. Sponge collar cells contain ...
... 51. The classification of sponges is Kingdom 52. Sponge collar cells contain ...
sci 7 study guide
... Genus-group of species; when a scientist discovers a new species, it is placed with the species with which it shares the most characteristics Structure and Function of Living Organisms: From Cells to Organisms Cells: smallest, or lowest, level of organization of the human body Organelles/parts: nucl ...
... Genus-group of species; when a scientist discovers a new species, it is placed with the species with which it shares the most characteristics Structure and Function of Living Organisms: From Cells to Organisms Cells: smallest, or lowest, level of organization of the human body Organelles/parts: nucl ...
Evolution Notes
... Geographic Distribution of Species: Examining similar but unrelated species on different continents suggesting common ancestor but descent with modification Homologous Structures: Structures from the same embryonic tissue but having various forms in the mature organism (human arm, bird wing, fish fl ...
... Geographic Distribution of Species: Examining similar but unrelated species on different continents suggesting common ancestor but descent with modification Homologous Structures: Structures from the same embryonic tissue but having various forms in the mature organism (human arm, bird wing, fish fl ...
Precambrian body plans

Until the late 1950’s, the Precambrian era was not believed to have hosted multicellular organisms. However, with radiometric dating techniques, it has been found that fossils initially found in the Ediacara Hills in Southern Australia date back to the late Precambrian era. These fossils are body impressions of organisms shaped like disks, fronds and some with ribbon patterns that were most likely tentacles.These are the earliest multicellular organisms in Earth’s history, despite the fact that unicellularity had been around for a long time before that. The requirements for multicellularity were embedded in the genes of some of these cells, specifically choanoflagellates. These are thought to be the precursors for all multicellular organisms. They are highly related to sponges (Porifera), which are the simplest multicellular organisms.In order to understand the transition to multicellularity during the Precambrian, it is important to look at the requirements for multicellularity—both biological and environmental.