ppt
... The network is a black box… ...so what can I do 1. We want the users to be able to diagnose their paths ...
... The network is a black box… ...so what can I do 1. We want the users to be able to diagnose their paths ...
ppt - The Fengs
... – If time permits, we may cover this at the end of the course….or someone should do a research paper on this. ...
... – If time permits, we may cover this at the end of the course….or someone should do a research paper on this. ...
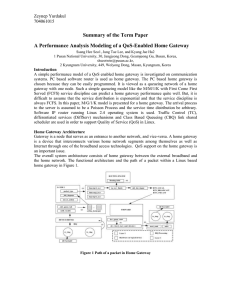
A performance analysis modeling of a QoS
... The first drop of packets was started at 1.4M bandwidth. In case of 1.4M, the only UDP1 traffic was dropped. This means that the QoS mechanism was achieved. Since the UDP1 traffic has the lowest priority although the UDP1 traffic has the lowest sending rate. Also, UDP1 and VoIP traffic were dropped ...
... The first drop of packets was started at 1.4M bandwidth. In case of 1.4M, the only UDP1 traffic was dropped. This means that the QoS mechanism was achieved. Since the UDP1 traffic has the lowest priority although the UDP1 traffic has the lowest sending rate. Also, UDP1 and VoIP traffic were dropped ...
Thursday, October 25th
... Analogous to the transport-layer services, but: service: host-to-host no choice: network provides one or the other implementation: in network core ...
... Analogous to the transport-layer services, but: service: host-to-host no choice: network provides one or the other implementation: in network core ...
notes
... Circuit Switching • Circuit switching – physical path set up from source to destination before any data transmitted, e.g., phone system – Adv: no congestion problem, only delay is propagation time – Disadv: unused bandwidth on allocated circuit is wasted ...
... Circuit Switching • Circuit switching – physical path set up from source to destination before any data transmitted, e.g., phone system – Adv: no congestion problem, only delay is propagation time – Disadv: unused bandwidth on allocated circuit is wasted ...
Quality of Service
... depending on the traffic at the moment the packet is sent. There is no guarantee that the packets arrive at the destination in order. This model is not quite as simple as it looks. Some issues have to be considered such as: The multiprotocol routers can translate from packet format to another when t ...
... depending on the traffic at the moment the packet is sent. There is no guarantee that the packets arrive at the destination in order. This model is not quite as simple as it looks. Some issues have to be considered such as: The multiprotocol routers can translate from packet format to another when t ...
Convergence Technology Chapter Objectives
... identify the protocols on which they rely Run and interpret the output of simple TCP/IP ...
... identify the protocols on which they rely Run and interpret the output of simple TCP/IP ...
Lektion 1-Introduktion
... ○ The cells are 53 bytes long (48 bytes payload + 5 bytes header) ○ The length of the cell compromise between American and European telephone companies (average of 32 and 64) ...
... ○ The cells are 53 bytes long (48 bytes payload + 5 bytes header) ○ The length of the cell compromise between American and European telephone companies (average of 32 and 64) ...
4. Data-link layer
... A broadband network simultaneously transmits multiple signals over a single medium. Packet switching enables computers to share a baseband medium. ...
... A broadband network simultaneously transmits multiple signals over a single medium. Packet switching enables computers to share a baseband medium. ...
ppt
... etc., handshaking: setup (prepare for) data transfer ahead of time – Hello, hello back human protocol – set up “state” in two communicating hosts ...
... etc., handshaking: setup (prepare for) data transfer ahead of time – Hello, hello back human protocol – set up “state” in two communicating hosts ...
Chapter 5
... – Various adaptive routing algorithms are possible. – It can be used over subnets that do not use virtual circuits inside. ...
... – Various adaptive routing algorithms are possible. – It can be used over subnets that do not use virtual circuits inside. ...
ppt
... Tolerance of reordering and duplication Ability to fragment fragments Reassembly done at the endpoint Puts pressure on the receiver, not network interior Consequences of fragmentation: Loss of any fragments causes loss of entire packet Need to time-out reassembly when any fragments lost ...
... Tolerance of reordering and duplication Ability to fragment fragments Reassembly done at the endpoint Puts pressure on the receiver, not network interior Consequences of fragmentation: Loss of any fragments causes loss of entire packet Need to time-out reassembly when any fragments lost ...
Chapter 4.1 Network Layer
... the best way to get there – outgoing port and address of next-hop router. The router looks at the IP address of a packet. It decides which network this ...
... the best way to get there – outgoing port and address of next-hop router. The router looks at the IP address of a packet. It decides which network this ...
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication
... A sequence of VCs is set up from source through one or more gateways to destination Each gateway maintains tables of information of VCs Best when all networks have roughly the same properties ...
... A sequence of VCs is set up from source through one or more gateways to destination Each gateway maintains tables of information of VCs Best when all networks have roughly the same properties ...
ppt
... Add UDP to TCP to better support other types of applications - e.g., “real-time” applications ...
... Add UDP to TCP to better support other types of applications - e.g., “real-time” applications ...
EQ23854856
... [2]. Using the information captured by the packet sniffer an administrator can identify erroneous packets and use the data to pinpoint bottlenecks and help maintain efficient network data transmission. This is unlike standard network hosts that only receive traffic sent specifically to them. The sec ...
... [2]. Using the information captured by the packet sniffer an administrator can identify erroneous packets and use the data to pinpoint bottlenecks and help maintain efficient network data transmission. This is unlike standard network hosts that only receive traffic sent specifically to them. The sec ...
Tuesday, October 21st - University of Pittsburgh
... Analogous to the transport-layer services, but: service: host-to-host no choice: network provides one or the other implementation: in network core ...
... Analogous to the transport-layer services, but: service: host-to-host no choice: network provides one or the other implementation: in network core ...
Lecture 1 - Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical
... transmitted as a flow of discrete bits – bit ...
... transmitted as a flow of discrete bits – bit ...
Module 6 - ITE technical support
... Cellular networking uses a digital mobile phone for Internet access. Mobile phones with Cellular digital data plans use cellular calls to connect to the Internet. You can install a cellular adapter in a notebook computer to provide cellular access. Satellite networking uses radio signals sent and re ...
... Cellular networking uses a digital mobile phone for Internet access. Mobile phones with Cellular digital data plans use cellular calls to connect to the Internet. You can install a cellular adapter in a notebook computer to provide cellular access. Satellite networking uses radio signals sent and re ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1 - Universidad de Sevilla
... link bandwidth, switch capacity dedicated resources: no sharing circuit-like (guaranteed) performance call setup required ...
... link bandwidth, switch capacity dedicated resources: no sharing circuit-like (guaranteed) performance call setup required ...
List six access technologies
... at the receiver]. The network layer runs the routing protocols that calculate the best (or shortest) paths to get the packets from any point in the network to any other point, based on IP addresses. These protocols also re-calculate routes after failures, and sometime provide load balancing by routi ...
... at the receiver]. The network layer runs the routing protocols that calculate the best (or shortest) paths to get the packets from any point in the network to any other point, based on IP addresses. These protocols also re-calculate routes after failures, and sometime provide load balancing by routi ...
Overview of High Speed Network Technologies
... when there is no data being transferred. If there is no enough resources for a connection establishment, the connection request is blocked or denied. The delay in each node is not meaningful. It is not well-suited for bursty traffic. It is proper for transmission of isochronous signals, such as voic ...
... when there is no data being transferred. If there is no enough resources for a connection establishment, the connection request is blocked or denied. The delay in each node is not meaningful. It is not well-suited for bursty traffic. It is proper for transmission of isochronous signals, such as voic ...
ppt
... output buffer switching rate: rate at which packets can be transfer from inputs to outputs often measured as multiple of input/output line rate ...
... output buffer switching rate: rate at which packets can be transfer from inputs to outputs often measured as multiple of input/output line rate ...
Packet switching

Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data into suitably sized blocks, called packets, which are transmitted via a medium that may be shared by multiple simultaneous communication sessions. Packet switching increases network efficiency, robustness and enables technological convergence of many applications operating on the same network.Packets are composed of a header and payload. Information in the header is used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination where the payload is extracted and used by application software.Starting in the late 1950s, American computer scientist Paul Baran developed the concept Distributed Adaptive Message Block Switching with the goal to provide a fault-tolerant, efficient routing method for telecommunication messages as part of a research program at the RAND Corporation, funded by the US Department of Defense. This concept contrasted and contradicted the heretofore established principles of pre-allocation of network bandwidth, largely fortified by the development of telecommunications in the Bell System. The new concept found little resonance among network implementers until the independent work of Donald Davies at the National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom) (NPL) in the late 1960s. Davies is credited with coining the modern name packet switching and inspiring numerous packet switching networks in Europe in the decade following, including the incorporation of the concept in the early ARPANET in the United States.