Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Goals : To gain an understanding of : 1. Atoms and their structure. 2. The development of the atomic theory. 3. The periodic table. NOTES: An atom is the smallest part of an element that retains the properties of that element. The concept of an atom goes a long way back. It was first suggested by an ...
... Goals : To gain an understanding of : 1. Atoms and their structure. 2. The development of the atomic theory. 3. The periodic table. NOTES: An atom is the smallest part of an element that retains the properties of that element. The concept of an atom goes a long way back. It was first suggested by an ...
Atomic Theory 1
... Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutrons in its nuclei. (This does NOT alter the identity of the element (#p same), but DOES make the element heavier or li ...
... Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutrons in its nuclei. (This does NOT alter the identity of the element (#p same), but DOES make the element heavier or li ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... Charge to mass ration • e/m = 1.758820 X 108 C/g e is the magnitude of the charge in coulomb C, and m is mass in grams. R. A. Millikan (1868 – 1953) devised a method for measuring the mass of the electron. Oil mist spayed into a chamber allowed to drop between two plates. Mass from falling rate. X- ...
... Charge to mass ration • e/m = 1.758820 X 108 C/g e is the magnitude of the charge in coulomb C, and m is mass in grams. R. A. Millikan (1868 – 1953) devised a method for measuring the mass of the electron. Oil mist spayed into a chamber allowed to drop between two plates. Mass from falling rate. X- ...
09/09/03 lecture
... • A neutral atom (i.e., one with no net charge) will have the same number of electrons as protons). • Most chemical properties are determined by the number and arrangement of electrons (more on this later). ...
... • A neutral atom (i.e., one with no net charge) will have the same number of electrons as protons). • Most chemical properties are determined by the number and arrangement of electrons (more on this later). ...
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
... We know that atoms are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. This sheet will discuss how we show the composition of atoms: How many p, e, and n a particular atom has. We will also relate the makeup of each element’s atoms to the periodic table. Key terms to know, covered on this sheet: Atomic nu ...
... We know that atoms are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. This sheet will discuss how we show the composition of atoms: How many p, e, and n a particular atom has. We will also relate the makeup of each element’s atoms to the periodic table. Key terms to know, covered on this sheet: Atomic nu ...
1-Three states of matter . A: density, volume and weight B: solid
... 4- Identify the elements in each chemical formula and tell how many atoms of each are present. a. K2Cr2O7 b. C5H8NNaO4 (MSG, fl avor enhancer) c. C10H16N2O3S (vitamin B7) 5- Identify the element that fi ts each description. a. an alkali metal in period 6 b. a transition metal in period 5, group 8 c. ...
... 4- Identify the elements in each chemical formula and tell how many atoms of each are present. a. K2Cr2O7 b. C5H8NNaO4 (MSG, fl avor enhancer) c. C10H16N2O3S (vitamin B7) 5- Identify the element that fi ts each description. a. an alkali metal in period 6 b. a transition metal in period 5, group 8 c. ...
Adventures in Chemistry Julie T. Millard, Colby College
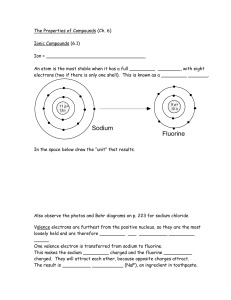
... Definitions Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electron ...
... Definitions Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electron ...
File
... Compounds are formed when different atoms link to form “compound atoms” (now called molecules). In a compound all “compound atoms” are alike. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. ...
... Compounds are formed when different atoms link to form “compound atoms” (now called molecules). In a compound all “compound atoms” are alike. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Review WS
... charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Later, after searching in vain for a positively charged particle nearly the same size as an electron, Rutherford’s experiments led him to the fact that the positively charged particle he was searching for, eventually named the proton, is 1840 times mo ...
... charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Later, after searching in vain for a positively charged particle nearly the same size as an electron, Rutherford’s experiments led him to the fact that the positively charged particle he was searching for, eventually named the proton, is 1840 times mo ...
Periodic Table Trends - Magoffin County Schools
... atoms are generally larger than group 18 atoms. • This is because, within a period, the number of principle energy levels (PELs) in each element generally remains constant. • For example, all elements in Period 3 have three energy levels. However, the nucleus gains protons as atomic number increases ...
... atoms are generally larger than group 18 atoms. • This is because, within a period, the number of principle energy levels (PELs) in each element generally remains constant. • For example, all elements in Period 3 have three energy levels. However, the nucleus gains protons as atomic number increases ...
atomic number
... Electrons move from the cathode (negative electrode) to the anode (positive electrode). The tube contains a glass screen (set diagonally to the electron beam) that fluoresces, showing the path of the ...
... Electrons move from the cathode (negative electrode) to the anode (positive electrode). The tube contains a glass screen (set diagonally to the electron beam) that fluoresces, showing the path of the ...
Johnston Middle School Lesson Plan 2015-2016
... TSW describe the structure of atoms including the masses, electrical charges and locations of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. TSW identify that protons determine an element's identity, and valence electrons determine its chemical properties and reactivity TSW ...
... TSW describe the structure of atoms including the masses, electrical charges and locations of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. TSW identify that protons determine an element's identity, and valence electrons determine its chemical properties and reactivity TSW ...
The Atom - TeacherWeb
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses (ie same protons, different neutrons) Isotopes are written using the name of the element followed by a hyphen and then the mass number. Ex: Hydrogen-1, Hydrogen-2, & Hydrogen-3 are isotopes ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses (ie same protons, different neutrons) Isotopes are written using the name of the element followed by a hyphen and then the mass number. Ex: Hydrogen-1, Hydrogen-2, & Hydrogen-3 are isotopes ...
Regents Chemistry Study Tips
... Mass no. is the sum of protons and neutrons Atomic mass is weighted avg of isotopes of that atom Bohr’s model of the atom is commonly accepted as a common model of the atom The energy levels are named K,L,M,N,O,P etc or 1.2.3.4.5 etc These energy levels are also know as principal quantum numbers Eac ...
... Mass no. is the sum of protons and neutrons Atomic mass is weighted avg of isotopes of that atom Bohr’s model of the atom is commonly accepted as a common model of the atom The energy levels are named K,L,M,N,O,P etc or 1.2.3.4.5 etc These energy levels are also know as principal quantum numbers Eac ...
Understanding the Properties of Elements – Chapter 5
... 2. Name the non-metal ion second. The end of its name will change to “-ide”. 3. If the proportion of one element to the other is not 1:1, a subscript is required to indicate the proportion of the element that is more abundant. e.g. For 1 Magnesium atom, there are 2 chlorine atoms: MgCl2. ...
... 2. Name the non-metal ion second. The end of its name will change to “-ide”. 3. If the proportion of one element to the other is not 1:1, a subscript is required to indicate the proportion of the element that is more abundant. e.g. For 1 Magnesium atom, there are 2 chlorine atoms: MgCl2. ...
early_Atomic Theory notes_academic - wths
... abundance of each isotope by its atomic mass and summing these products. Because 75.78% = 0.7578 and 24.22% = 0.2422 we have Average atomic mass = (0.7578)(34.969 amu) + (0.2422)(36.966 amu) = 26.50 amu + 8.953 amu = 35.45 amu ...
... abundance of each isotope by its atomic mass and summing these products. Because 75.78% = 0.7578 and 24.22% = 0.2422 we have Average atomic mass = (0.7578)(34.969 amu) + (0.2422)(36.966 amu) = 26.50 amu + 8.953 amu = 35.45 amu ...
Chapter 4 - Atomic Structure - A
... Atoms in the same element are identical; atoms from 1 element are different form atoms of another element Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically combine in whole-number ratios Chemical reactions = atoms joined, separated, or rearranged. Atoms of 1 element NEVER change into atom ...
... Atoms in the same element are identical; atoms from 1 element are different form atoms of another element Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically combine in whole-number ratios Chemical reactions = atoms joined, separated, or rearranged. Atoms of 1 element NEVER change into atom ...
Unit 4 Packet
... 11. How many protons are in the nuclei of the following atoms? a. Sulfur b. Hydrogen c. Phosphorus d. Cadmium e. Calcium 12. How do the three isotopes of hydrogen (H–1, H–2, H–3) compare in terms of the numbers of subatomic particles in each? 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Ide ...
... 11. How many protons are in the nuclei of the following atoms? a. Sulfur b. Hydrogen c. Phosphorus d. Cadmium e. Calcium 12. How do the three isotopes of hydrogen (H–1, H–2, H–3) compare in terms of the numbers of subatomic particles in each? 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Ide ...
1.3 Biochemistry: Chemistry basics notes ppt
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change; comes mainly from the rapid movement of electrons • Potential energy (energy of position) is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energ ...
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change; comes mainly from the rapid movement of electrons • Potential energy (energy of position) is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energ ...
Zn 8 p + 8 p + 30 p + 8 n 8 n 35 n 8 e
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
Slides - RibisiChem.com
... • How does the neutron to proton ratio change when polonium-210 decays into lead-206? What type of decay does polonium-210 undergo? (Low atomic # elements are happy with a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons. Heavier elements need a 1.5:1 ratio and all elements above 82 are radioactive.) ...
... • How does the neutron to proton ratio change when polonium-210 decays into lead-206? What type of decay does polonium-210 undergo? (Low atomic # elements are happy with a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons. Heavier elements need a 1.5:1 ratio and all elements above 82 are radioactive.) ...
Powerpoint Unit 4
... • Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons • Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons • The number of protons is give by the Atomic Number ...
... • Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons • Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons • The number of protons is give by the Atomic Number ...
Getting to Know: Atomic Structure and Elements
... What are some other properties of elements and atoms? An atom cannot be divided further and still be identified as an atom of a particular element. For example, if a silver atom were split into protons, neutrons, and electrons, it would no longer be silver. It would just be a collection of subatomic ...
... What are some other properties of elements and atoms? An atom cannot be divided further and still be identified as an atom of a particular element. For example, if a silver atom were split into protons, neutrons, and electrons, it would no longer be silver. It would just be a collection of subatomic ...
2.1 Atoms and Bonds
... electrons in an atom Procedure: 1. Write the atomic symbol 2. Determine the number of valence electrons 3. Place the valence electrons (dots) around all 4 sides of the atomic symbol – not pairing up until necessary! ...
... electrons in an atom Procedure: 1. Write the atomic symbol 2. Determine the number of valence electrons 3. Place the valence electrons (dots) around all 4 sides of the atomic symbol – not pairing up until necessary! ...
Atomic Structure
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged ...