Electricity - WordPress.com
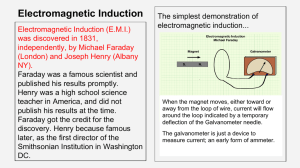
... Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and the flow of electrical current. In addition, electricity permits the cre ...
... Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and the flow of electrical current. In addition, electricity permits the cre ...
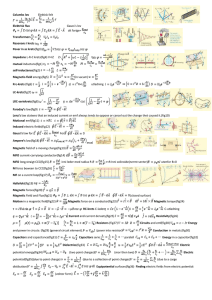
A brief history of Ampere`s law
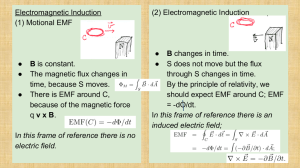
... ∫ l = − dtM where φM is the magnetic flux) that a changing magnetic field can create an electric field. Maxwell realized that the combination of these two laws meant that it was possible for a self-sustaining electromagnetic wave to propagate through a vacuum – the changing electric field creates a ...
... ∫ l = − dtM where φM is the magnetic flux) that a changing magnetic field can create an electric field. Maxwell realized that the combination of these two laws meant that it was possible for a self-sustaining electromagnetic wave to propagate through a vacuum – the changing electric field creates a ...
SurveyMotors
... perpendicular to the magnetic field and perpendicular to the current. (If the current is in the same direction as the field, there is no force.) ...
... perpendicular to the magnetic field and perpendicular to the current. (If the current is in the same direction as the field, there is no force.) ...
suggested contents (prof. Bury)
... - More about electrostatic properties of a conductor 4. Capacitance, electric energy, and properties of insulators - Capacitors and capacitance - Capacitors in series and parallel - Electric energy and energy density - Electrostatic properties of insulators - Atomic description of the properties of ...
... - More about electrostatic properties of a conductor 4. Capacitance, electric energy, and properties of insulators - Capacitors and capacitance - Capacitors in series and parallel - Electric energy and energy density - Electrostatic properties of insulators - Atomic description of the properties of ...
เนื้อหาของรายวิชา 2304104 GEN PHYS II
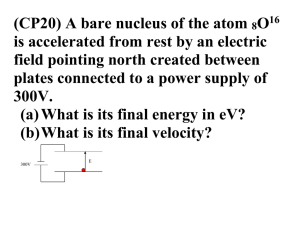
... Coulomb’s law Electric field Gauss’ law The electric potential Electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distribution and dipole Calculating the field from the potential Capacitance and Dielectric Electric current and electromotive force Conductivity of materia ...
... Coulomb’s law Electric field Gauss’ law The electric potential Electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distribution and dipole Calculating the field from the potential Capacitance and Dielectric Electric current and electromotive force Conductivity of materia ...



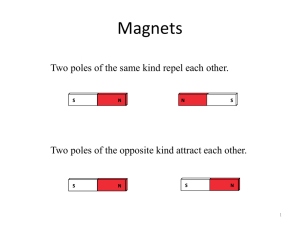
![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-300x300.png)