EE4302 Fl04 Class Sy..
... *Homework and notes handed in after the due date will not be counted! (This means that the homework can be slid under my door that night. I usually arrive at ~8 AM.) ...
... *Homework and notes handed in after the due date will not be counted! (This means that the homework can be slid under my door that night. I usually arrive at ~8 AM.) ...
Anticipation Guide: Electricity from Magnetism
... Before Reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark () if you agree or think the statement is true or an (X) if you disagree or think the statement is false. During or After Reading: Add new check marks or cross-through the X’s for which you have changed your mind. Keep i ...
... Before Reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark () if you agree or think the statement is true or an (X) if you disagree or think the statement is false. During or After Reading: Add new check marks or cross-through the X’s for which you have changed your mind. Keep i ...
Chapter 3
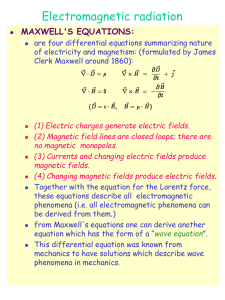
... Assuming the E-field information propagates at speed c. Gauss’s law suggests that the field lines are curved when the charge is accelerated. The transverse component of the electric field will propagate outward. A non-uniformly moving charge produces electromagnetic waves. ...
... Assuming the E-field information propagates at speed c. Gauss’s law suggests that the field lines are curved when the charge is accelerated. The transverse component of the electric field will propagate outward. A non-uniformly moving charge produces electromagnetic waves. ...
Lecture18
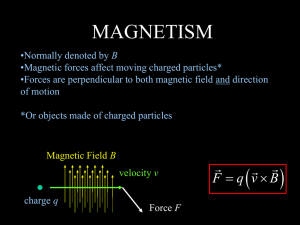
... Magnetic Force •Can only affect moving particles! •Force depends on charge just like electric fields •Force is maximum when the velocity and field are perpendicular, and zero when they are parallel •When the velocity and field are neither perpendicular nor parallel, the force still exists! ...
... Magnetic Force •Can only affect moving particles! •Force depends on charge just like electric fields •Force is maximum when the velocity and field are perpendicular, and zero when they are parallel •When the velocity and field are neither perpendicular nor parallel, the force still exists! ...
Course Specifications
... structure of matter, the atom, electric potential, energy relations in an electric field, electric current, electric dipole, higher order electric multipoles. Chapter II : Magnetic Interactions Magnetic force on an moving charge, motion of a charge in a magnetic field, equipment in which charged par ...
... structure of matter, the atom, electric potential, energy relations in an electric field, electric current, electric dipole, higher order electric multipoles. Chapter II : Magnetic Interactions Magnetic force on an moving charge, motion of a charge in a magnetic field, equipment in which charged par ...
Al-Balqa Applied University
... To introduce the basic elements of electromagnetic needed in the understanding of electricity and magnetism. Course Objectives: At completing this module the student should be able to: 1- Understand the basic vectors and calculus used in describing the field theory. 2- Understand the basic principle ...
... To introduce the basic elements of electromagnetic needed in the understanding of electricity and magnetism. Course Objectives: At completing this module the student should be able to: 1- Understand the basic vectors and calculus used in describing the field theory. 2- Understand the basic principle ...
Phys2102 Spring 2002
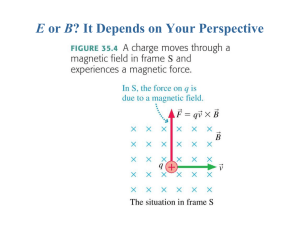
... and Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later. ...
... and Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later. ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... electronics undergraduate students and is composed of two parts – lectures and laboratory works. During lectures the electrical and magnetic phenomena have been discussed and analyzed – static electricity, electric current, magnetism, electromagnetic induction, electromagnetic waves. Mathematics is ...
... electronics undergraduate students and is composed of two parts – lectures and laboratory works. During lectures the electrical and magnetic phenomena have been discussed and analyzed – static electricity, electric current, magnetism, electromagnetic induction, electromagnetic waves. Mathematics is ...
Course Title
... To introduce the basic elements of electromagnetic needed in the understanding of electricity and magnetism. Course Objectives: At completing this module the student should be able to: 1- Understand the basic vectors and calculus used in describing the field theory. 2- Understand the basic principle ...
... To introduce the basic elements of electromagnetic needed in the understanding of electricity and magnetism. Course Objectives: At completing this module the student should be able to: 1- Understand the basic vectors and calculus used in describing the field theory. 2- Understand the basic principle ...
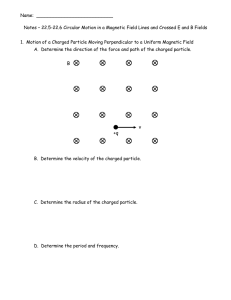
Name: Notes – 22.5-22.6 Circular Motion in a Magnetic Field Lines
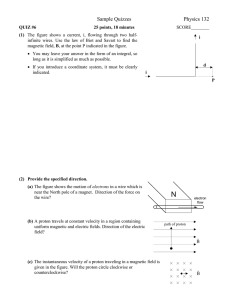
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...