Ecosystem and Ecology Powerpoint
... Every population has a different place to live and a different role to play in an ecosystem. Habitat: the place in which an organism lives and obtains the ...
... Every population has a different place to live and a different role to play in an ecosystem. Habitat: the place in which an organism lives and obtains the ...
2 Flow of Energy
... Consumers are organisms that depend on other organisms for food. They take in organic molecules by essentially “eating” other living things. They include all animals and fungi. (Fungi don’t really “eat”; they absorb nutrients from other organisms.) They also include many bacteria and even a few plan ...
... Consumers are organisms that depend on other organisms for food. They take in organic molecules by essentially “eating” other living things. They include all animals and fungi. (Fungi don’t really “eat”; they absorb nutrients from other organisms.) They also include many bacteria and even a few plan ...
deflected succession
... compete for exactly the same resources for an extended period of time. (G.F. Gause) • One will either migrate, become extinct, or partition the resource and utilize a sub-set of the same resource. • Given resource can only be partitioned a finite number of times. ...
... compete for exactly the same resources for an extended period of time. (G.F. Gause) • One will either migrate, become extinct, or partition the resource and utilize a sub-set of the same resource. • Given resource can only be partitioned a finite number of times. ...
Jeopardy
... The 10 percent rule limits population sizes in an ecosystem, since only about 10 percent of energy is transferred between trophic levels. (The rest of the energy is lost as waste/heat.) Since only 10 percent of energy is transferred, each trophic level has about 1/10th the population size of the pre ...
... The 10 percent rule limits population sizes in an ecosystem, since only about 10 percent of energy is transferred between trophic levels. (The rest of the energy is lost as waste/heat.) Since only 10 percent of energy is transferred, each trophic level has about 1/10th the population size of the pre ...
Biodiversity, Scale and Ecological Resilience
... Biosphere, Biogeochemical cycles, Solar Energy, Biodiversity, Earth Materials ...
... Biosphere, Biogeochemical cycles, Solar Energy, Biodiversity, Earth Materials ...
NOTES ON BIO 201 – GENERAL ECOLOGY INTRODUCTION
... set of BIOTIC and ABIOTIC conditions in which a species is able to persist and maintain stable population sizes. Two issues are recognizable from this definition (a) functional role of an organism (b) its position in time and space. ...
... set of BIOTIC and ABIOTIC conditions in which a species is able to persist and maintain stable population sizes. Two issues are recognizable from this definition (a) functional role of an organism (b) its position in time and space. ...
Wetlands!
... • Wetlands throughout the world have long been recognized as key habitats that provide many services to humankind. Unfortunately many of these services are not well recognized and are often taken for granted. ...
... • Wetlands throughout the world have long been recognized as key habitats that provide many services to humankind. Unfortunately many of these services are not well recognized and are often taken for granted. ...
Ecosystem Impacts Assessment Framework: Objectives, sub
... information requirement (National Standard 2) to include information on past, present, and possible future condition of the stocks, marine ecosystems, and fisheries being managed in the stock assessment and fishery evaluation reports provided to managers. ...
... information requirement (National Standard 2) to include information on past, present, and possible future condition of the stocks, marine ecosystems, and fisheries being managed in the stock assessment and fishery evaluation reports provided to managers. ...
Ecosystems - Trophic Levels
... This food chain shows the flow of energy from a producer, algae, to the consumers in the ecosystem. Minnows are primary consumers, salmon are secondary consumers, and bears are tertiary consumers. The arrows in a food chain or a food web represent the direction of energy flow. The arrow points from ...
... This food chain shows the flow of energy from a producer, algae, to the consumers in the ecosystem. Minnows are primary consumers, salmon are secondary consumers, and bears are tertiary consumers. The arrows in a food chain or a food web represent the direction of energy flow. The arrow points from ...
Information about Pond Wildlife
... Water or hoglouse – related to woodlouse, these live at the bottom of the pond feeding on dead organic matter. Water louse carry their eggs and small young on their tummies. Freshwater shrimp – smaller freshwater species of marine shrimps. They belong to the decapods as they have ten legs. Molluscs ...
... Water or hoglouse – related to woodlouse, these live at the bottom of the pond feeding on dead organic matter. Water louse carry their eggs and small young on their tummies. Freshwater shrimp – smaller freshwater species of marine shrimps. They belong to the decapods as they have ten legs. Molluscs ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... minerals and energy that then become available to other living organisms in that ecosystems. o Saprotrophs Secrete enzymes onto the dead organic matter, digestion takes places outside the decomposer and the digested material is then take in by the decomposer, although some remains in the ecosystem ...
... minerals and energy that then become available to other living organisms in that ecosystems. o Saprotrophs Secrete enzymes onto the dead organic matter, digestion takes places outside the decomposer and the digested material is then take in by the decomposer, although some remains in the ecosystem ...
Untitled
... are grouped according to their role and illustrated in a Trophic level pyramid. The first level (base) contains groups of producers, then the second levels are made up of mainly herbivore secondary consumers and the levels that follow consists of tertiary consumers that eat the herbivores and so on. ...
... are grouped according to their role and illustrated in a Trophic level pyramid. The first level (base) contains groups of producers, then the second levels are made up of mainly herbivore secondary consumers and the levels that follow consists of tertiary consumers that eat the herbivores and so on. ...
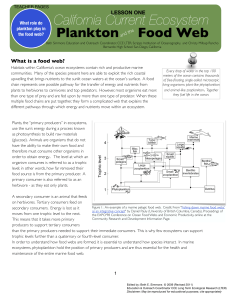
L3_fnl_Plankton Food Web_TEACHER
... Figure 1: An example of a marine pelagic food web. Credit: From "Fishing down marine food webs' secondary consumers. Energy is lost as it as an integrative concept" by Daniel Pauly (University of British Columbia, Canada), Proceedings of moves from one trophic level to the next. the EXPO'98 Conferen ...
... Figure 1: An example of a marine pelagic food web. Credit: From "Fishing down marine food webs' secondary consumers. Energy is lost as it as an integrative concept" by Daniel Pauly (University of British Columbia, Canada), Proceedings of moves from one trophic level to the next. the EXPO'98 Conferen ...
Final Review Answers BIOCHEMISTRY Chapter 3 Water and the
... 23. Heat must be absorbed to break hydrogen bonds and heat must be released to form hydrogen ...
... 23. Heat must be absorbed to break hydrogen bonds and heat must be released to form hydrogen ...
(Hg) Concentrations in the Blacktip Shark
... 2003). In the same study the researcher did statistically find high levels of mercury in neonatal and juvenile sharks that parent female sharks likely pass on high levels of (Hg) through the maternal fluid exchange (Adams et al. 2003). A study should be done to conclude the lifetime fluctuations in ...
... 2003). In the same study the researcher did statistically find high levels of mercury in neonatal and juvenile sharks that parent female sharks likely pass on high levels of (Hg) through the maternal fluid exchange (Adams et al. 2003). A study should be done to conclude the lifetime fluctuations in ...