Study Questions - Geocycles, communities, populations
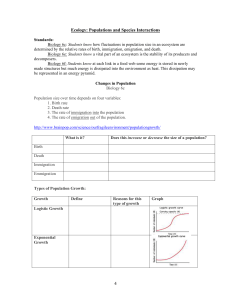
... 5. What is exponential growth of populations? What shape does this growth curve often take? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of exponential growth. 6. What is logistic growth? What does a graph of this type of growth look like? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of this type. 7. ...
... 5. What is exponential growth of populations? What shape does this growth curve often take? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of exponential growth. 6. What is logistic growth? What does a graph of this type of growth look like? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of this type. 7. ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... Energy Transfer Each time one organism eats another, energy is transferred Ecosystems are all about energy flowing from one organism to another ...
... Energy Transfer Each time one organism eats another, energy is transferred Ecosystems are all about energy flowing from one organism to another ...
Biosphere Review
... Bacteria take carbon dioxide from the atomosphere and fix it in a form plants can use. This is TRUE about nitrogen NOT CARBON DIOXIDE Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere naturally from respiration and volcanic activity . TRUE Human activities such as mining, cutting and burning forests, and burning ...
... Bacteria take carbon dioxide from the atomosphere and fix it in a form plants can use. This is TRUE about nitrogen NOT CARBON DIOXIDE Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere naturally from respiration and volcanic activity . TRUE Human activities such as mining, cutting and burning forests, and burning ...
Critical Thinking Questions
... A) No heat energy is lost in an ecosystem. B) There are fewer primary producers than secondary consumers. C) There is more available energy in secondary consumers than primary consumers. D) Ninety percent of the energy is transformed at each level. ...
... A) No heat energy is lost in an ecosystem. B) There are fewer primary producers than secondary consumers. C) There is more available energy in secondary consumers than primary consumers. D) Ninety percent of the energy is transformed at each level. ...
organic
... Bacteria take carbon dioxide from the atomosphere and fix it in a form plants can use. This is TRUE about nitrogen NOT CARBON DIOXIDE Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere naturally from respiration and volcanic activity . TRUE Human activities such as mining, cutting and burning forests, and burning ...
... Bacteria take carbon dioxide from the atomosphere and fix it in a form plants can use. This is TRUE about nitrogen NOT CARBON DIOXIDE Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere naturally from respiration and volcanic activity . TRUE Human activities such as mining, cutting and burning forests, and burning ...
Practice Ecology Test
... 8. A stable ecosystem would not contain A) materials being cycled B) consumers without producers C) decomposers D) a constant source of energy 9. For a natural ecosystem to be self-sustaining, many essential chemical elements must be A) converted to energy B) changed into fossil fuels such as oil an ...
... 8. A stable ecosystem would not contain A) materials being cycled B) consumers without producers C) decomposers D) a constant source of energy 9. For a natural ecosystem to be self-sustaining, many essential chemical elements must be A) converted to energy B) changed into fossil fuels such as oil an ...
Unit III- Ecology (Guided Notes)
... All organisms need energy in order to grow, reproduce, and perform the activities necessary for survival. The amount of organic matter in an ecosystem is its biomass. The rate at which an ecosystem’s producers build biomass is the ecosystem’s primary productivity. Define primary productivity: ...
... All organisms need energy in order to grow, reproduce, and perform the activities necessary for survival. The amount of organic matter in an ecosystem is its biomass. The rate at which an ecosystem’s producers build biomass is the ecosystem’s primary productivity. Define primary productivity: ...
Salt Water Biome
... affect many animals. It can kill the tiny planktonic larvae and eggs of adult fish, shrimp, jellyfish, squid, and numerous other species. ...
... affect many animals. It can kill the tiny planktonic larvae and eggs of adult fish, shrimp, jellyfish, squid, and numerous other species. ...
Ecosystem Interactions
... on it. The tree provides nectar and a home for the ants. Another symbiotic relationship in which one organism derives benefit at the expense of the other is called parasitism. Parasites have evolved in such a way that they harm, but usually do not kill, the hose. An example of a parasite is a tick ...
... on it. The tree provides nectar and a home for the ants. Another symbiotic relationship in which one organism derives benefit at the expense of the other is called parasitism. Parasites have evolved in such a way that they harm, but usually do not kill, the hose. An example of a parasite is a tick ...
Ecology Core and Ecology Option
... • Describe what is meant by a food chain, giving three examples, each with at least three linkages (four organisms) (2) • Describe what is meant by a food web (2) • Deduce the trophic level of organisms in food chain and a food web (3) • Construct a food web containing up to 10 organisms, using appr ...
... • Describe what is meant by a food chain, giving three examples, each with at least three linkages (four organisms) (2) • Describe what is meant by a food web (2) • Deduce the trophic level of organisms in food chain and a food web (3) • Construct a food web containing up to 10 organisms, using appr ...
Ecology and Human Impact Test Takers Review
... Deforestation: cutting down trees in mass amounts Direct harvesting: taking a species from their original habitat (overfishing would be an example of this) Renewable resource: source of energy that can be used over and over ...
... Deforestation: cutting down trees in mass amounts Direct harvesting: taking a species from their original habitat (overfishing would be an example of this) Renewable resource: source of energy that can be used over and over ...
Ecosystems - Varsity Field
... Ecosystems vary greatly in the their structural complexity as well as the clarity of their boundaries What all ecosystems therefore have in common is NOT size or shape, but processes which give them the ability to sustain life ...
... Ecosystems vary greatly in the their structural complexity as well as the clarity of their boundaries What all ecosystems therefore have in common is NOT size or shape, but processes which give them the ability to sustain life ...
A combined approach of photogrammetrical methods and field
... 1998). Investigations at the Lower River Spree (Schulz et al., 2003) agree with these statements. They demonstrated that during the vegetation period of 2001, phosphorus retention due to deposition amounted to approximately 12% of total phosphorus load. In comparison to those results, we found nutri ...
... 1998). Investigations at the Lower River Spree (Schulz et al., 2003) agree with these statements. They demonstrated that during the vegetation period of 2001, phosphorus retention due to deposition amounted to approximately 12% of total phosphorus load. In comparison to those results, we found nutri ...
Exam Answers
... 2. Compare and contrast a ciliate grazer and a euphausiid grazer, with respect to: a) sloppy feeding, b) ammonia excretion, c) contribution to vertical carbon flux, and d) basal metabolism. (20 pts) a) sloppy feeding: The ciliate engulfs prey whole, so does not contribute to sloppy feeding. Euphaus ...
... 2. Compare and contrast a ciliate grazer and a euphausiid grazer, with respect to: a) sloppy feeding, b) ammonia excretion, c) contribution to vertical carbon flux, and d) basal metabolism. (20 pts) a) sloppy feeding: The ciliate engulfs prey whole, so does not contribute to sloppy feeding. Euphaus ...
Tides - Feiro Marine Life Center
... with respect to the land, produced by the gravitational attraction of the moon and the sun. To a much smaller extent, tides also occur in large lakes, the atmosphere, and within the solid crust of the earth, acted upon by these same gravitational forces of the moon and sun. Additional nonastronomica ...
... with respect to the land, produced by the gravitational attraction of the moon and the sun. To a much smaller extent, tides also occur in large lakes, the atmosphere, and within the solid crust of the earth, acted upon by these same gravitational forces of the moon and sun. Additional nonastronomica ...