Memory: An organism`s aty bilito stoer retain and recall information
... Interactions between species drive evolution and underlie many aspects of our world that we take for granted. Almost all plants and animals rely on other organisms to grow and survive: from fungal associations in the roots of land plants, to nutritional microbes living in animal guts, to bacteria th ...
... Interactions between species drive evolution and underlie many aspects of our world that we take for granted. Almost all plants and animals rely on other organisms to grow and survive: from fungal associations in the roots of land plants, to nutritional microbes living in animal guts, to bacteria th ...
S-8-9-2_Species Interactions Quiz
... Directions: Write the name of each type of species interaction next to the example provided. Use the terms in the box below. Each term will be used one time. ...
... Directions: Write the name of each type of species interaction next to the example provided. Use the terms in the box below. Each term will be used one time. ...
Interactions with Ecosystems
... • Populations of organisms can be categorized by how they acquire energy. • Food webs can be used to identify the relationships among producers, consumers and decomposers in an ecosystem. • All of the processes that take place within organisms require energy. • See below for additional enduring unde ...
... • Populations of organisms can be categorized by how they acquire energy. • Food webs can be used to identify the relationships among producers, consumers and decomposers in an ecosystem. • All of the processes that take place within organisms require energy. • See below for additional enduring unde ...
... • Estuaries-are areas where rivers meet the ocean. Detritus, shallow characteristics. Valuable as nursaries, migration stop • Salt marsh- temperate-zone estuaries where grasses are the dominant vegetation • Mangrove swamps-coastal wetlands, along tropical regions. Mangroves, seagrasses dominant vege ...
SAT2生物专业词汇
... the watery environments inside and outside of the cell. photic zone(透光层) Literally, zone with light. The photic zone is part of the marine pelagic zone and extends to 600 feet below the surface of the ocean. Photosynthetic plankton as well as bony fish, sharks, and whales inhabit this zone. 全国免费咨询电话 ...
... the watery environments inside and outside of the cell. photic zone(透光层) Literally, zone with light. The photic zone is part of the marine pelagic zone and extends to 600 feet below the surface of the ocean. Photosynthetic plankton as well as bony fish, sharks, and whales inhabit this zone. 全国免费咨询电话 ...
Habitat - Piscataway High School
... Coniferous trees: Keep their leaves (needles) all year long. ...
... Coniferous trees: Keep their leaves (needles) all year long. ...
Phosphorous Cycle
... Heterotrophs- needs at least one organic nutrient as a source of carbon for making other organic compounds ...
... Heterotrophs- needs at least one organic nutrient as a source of carbon for making other organic compounds ...
Ecology - Shaw Communications
... rejuvenates the prairie so that virtually all the biomass is living a month after a burn (right) ...
... rejuvenates the prairie so that virtually all the biomass is living a month after a burn (right) ...
Microsoft Word - Chapter 06
... pervasive ripple effects throughout the food web. Removal of predators at high trophic levels can result in increased prey abundance, which may cause decreased abundance of their food as they overgraze. Other species that have major effects because they physically modify the environment shared by co ...
... pervasive ripple effects throughout the food web. Removal of predators at high trophic levels can result in increased prey abundance, which may cause decreased abundance of their food as they overgraze. Other species that have major effects because they physically modify the environment shared by co ...
Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Limiting Factor - snc1p
... o species with broader tolerance ranges are able to adapt to a larger variety of conditions and are better suited to acting as an invasive species terrestrial abiotic factors include temperature, precipitation, nutrient availability and light aquatic abiotic factors include salinity, temperature ...
... o species with broader tolerance ranges are able to adapt to a larger variety of conditions and are better suited to acting as an invasive species terrestrial abiotic factors include temperature, precipitation, nutrient availability and light aquatic abiotic factors include salinity, temperature ...
see the key
... 400: The biological community produced at the end of succession 500: environmental disturbance (both intensity and frequency) Pollution and Environmental Changes 100: the “aging of lakes”. Increased nutrients, sediment into lakes, decreasing oxygen and visibility, caused by human disturbance 200: At ...
... 400: The biological community produced at the end of succession 500: environmental disturbance (both intensity and frequency) Pollution and Environmental Changes 100: the “aging of lakes”. Increased nutrients, sediment into lakes, decreasing oxygen and visibility, caused by human disturbance 200: At ...
Chapter 1 and 2 Review
... 8) Be able to read a food chain or food web. Practice: draw a simple food web and describe the trophic level of particular organisms within the food web. 9) Describe the three different types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each 10) Explain how and why biomass and available energy ...
... 8) Be able to read a food chain or food web. Practice: draw a simple food web and describe the trophic level of particular organisms within the food web. 9) Describe the three different types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each 10) Explain how and why biomass and available energy ...
204FinalSG_AA_W05
... - In the barnacle example, are you saying that Balanus is better suited to the environment and that if desiccation was not a problem at the higher water level, they would force out the Chthamalus? - Assuming two species occupy the same ecological niche, why couldn’t they both co-exist assuming they ...
... - In the barnacle example, are you saying that Balanus is better suited to the environment and that if desiccation was not a problem at the higher water level, they would force out the Chthamalus? - Assuming two species occupy the same ecological niche, why couldn’t they both co-exist assuming they ...
Principles of Ecology - Mrs. Jacob's Science Class
... classification within ecology and differentiate between food chains and food webs ...
... classification within ecology and differentiate between food chains and food webs ...
Principles of Ecology
... Determined by primarily the depth, flow, temperature, and chemistry of the overlying water Grouped by abiotic factors that affect them Freshwater ecosystems divided into 2 types- flowing water and standing water ecosystem Plankton- tiny, free-floating organisms live in freshwater and saltwat ...
... Determined by primarily the depth, flow, temperature, and chemistry of the overlying water Grouped by abiotic factors that affect them Freshwater ecosystems divided into 2 types- flowing water and standing water ecosystem Plankton- tiny, free-floating organisms live in freshwater and saltwat ...
Study Guide Lesson 2
... Organization of the environment: Living systems move toward order or death. The movement toward order or equilibrium is ecological succession. Ex. Forest Fire Critical factor Adaptations Carrying capacity Habitat and niche Relationships between organisms: Competition, predation, symbiosis Symbiosis: ...
... Organization of the environment: Living systems move toward order or death. The movement toward order or equilibrium is ecological succession. Ex. Forest Fire Critical factor Adaptations Carrying capacity Habitat and niche Relationships between organisms: Competition, predation, symbiosis Symbiosis: ...
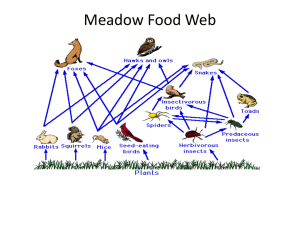
Meadow Food Web, Ecology pp
... • Computer models of interactions may predict outcomes of environmental change ...
... • Computer models of interactions may predict outcomes of environmental change ...
MARKING SCHEME BIOLOGY P1 231/1 1. a)Cohesion Water
... b)Lack of Anti - diuretic hormone / vasopressin therefore less water is reabsorbed; 13. Results in adaptations that enable organisms to exploit different ecological niches; Leads to the formation of new species; 14.(a) Aquatic ecosystem; (b) The shorter the food chain, the more energy can be derived ...
... b)Lack of Anti - diuretic hormone / vasopressin therefore less water is reabsorbed; 13. Results in adaptations that enable organisms to exploit different ecological niches; Leads to the formation of new species; 14.(a) Aquatic ecosystem; (b) The shorter the food chain, the more energy can be derived ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... parental care. Ex. Rabbits, bacteria k strategy – A reproductive strategy characterized by more prolonged development and larger offspring that parents invest more energy into raising. Ex. Humans, elephants ...
... parental care. Ex. Rabbits, bacteria k strategy – A reproductive strategy characterized by more prolonged development and larger offspring that parents invest more energy into raising. Ex. Humans, elephants ...