Living things need energy
... Animals that eat other animals are carnivores The red fox, coyote, gray fox, bobcat, Little Brown Bat Are examples of carnivores that can be found in CT. Fun fact, the Venus Flytrap plant is BOTH a producer and a consumer. It can convert energy from the sun through photosynthesis and from eating ins ...
... Animals that eat other animals are carnivores The red fox, coyote, gray fox, bobcat, Little Brown Bat Are examples of carnivores that can be found in CT. Fun fact, the Venus Flytrap plant is BOTH a producer and a consumer. It can convert energy from the sun through photosynthesis and from eating ins ...
Radiolarian biostratigraphy of the Conset Bay Series, Barbados
... Radiolarian biostratigraphy of the hemipelagic series of the Scotland Formation (or Basal Complex) and the suprajacent pelagic series of the Oceanic Formation at Conset Bay, Barbados, indicates that the sequence extends from the Middle to the late Eocene. The oldest assemblages can be correlated wit ...
... Radiolarian biostratigraphy of the hemipelagic series of the Scotland Formation (or Basal Complex) and the suprajacent pelagic series of the Oceanic Formation at Conset Bay, Barbados, indicates that the sequence extends from the Middle to the late Eocene. The oldest assemblages can be correlated wit ...
Chapter 11: Biogeography
... The generalist are in the majority- Why? Sometimes a species can change in its ecological niche: Humans are generalist, but can be carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores Succession and Climax Communities Autotrophs usually dictate the characteristics of terrestrial ecosystems These species are greatly ...
... The generalist are in the majority- Why? Sometimes a species can change in its ecological niche: Humans are generalist, but can be carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores Succession and Climax Communities Autotrophs usually dictate the characteristics of terrestrial ecosystems These species are greatly ...
Review Material for Ecology
... e. It is not possible to infer anything about future social conditions from age structure diagrams. ...
... e. It is not possible to infer anything about future social conditions from age structure diagrams. ...
Organism
... Competition- when two or more individuals or populations try to use the same limited resource such as food, water, shelter, space or sunlight There are 2 major reasons for competition: 1. carrying capacity- the largest population that an environment can support at any given time 2. limiting factor- ...
... Competition- when two or more individuals or populations try to use the same limited resource such as food, water, shelter, space or sunlight There are 2 major reasons for competition: 1. carrying capacity- the largest population that an environment can support at any given time 2. limiting factor- ...
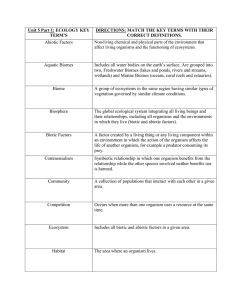
Ecosystems - Hardin County Schools
... *ex. 5 Kingdoms: plants, animals, protists, fungi, bacteria abiotic factors– All the nonliving things in an ecosystem. *ex. rocks, soil, air, sunlight, water, temperature, wind, weather… ...
... *ex. 5 Kingdoms: plants, animals, protists, fungi, bacteria abiotic factors– All the nonliving things in an ecosystem. *ex. rocks, soil, air, sunlight, water, temperature, wind, weather… ...
Ecosystems_Chapter_1_JEP - Copley
... This is the type of symbiosis where one organism benefits, while the other is not harmed. An example is the crab spider and a flower ...
... This is the type of symbiosis where one organism benefits, while the other is not harmed. An example is the crab spider and a flower ...
Biology Chapter 2 Test: Principles of Ecology
... 1. Living things are formed from carbon-containing molecules, so the carbon cycle is the only biogeochemical cycle that really affects humans. 2. Some plants have bacteria living in nodules on their roots that "fix" atmospheric nitrogen, converting it to a form of nitrogen the plant can use. Because ...
... 1. Living things are formed from carbon-containing molecules, so the carbon cycle is the only biogeochemical cycle that really affects humans. 2. Some plants have bacteria living in nodules on their roots that "fix" atmospheric nitrogen, converting it to a form of nitrogen the plant can use. Because ...
File
... The part of Earth where life exists ◦ The biosphere includes the top portion of Earth’s crust, all the waters that cover Earth’s surface, and the atmosphere that surrounds Earth. ...
... The part of Earth where life exists ◦ The biosphere includes the top portion of Earth’s crust, all the waters that cover Earth’s surface, and the atmosphere that surrounds Earth. ...
Communities, Ecosystems, and Biodiversity
... Very high T water, sulfur, other chemicals No light, low O2 Tube worms, bivalves, shrimp, crabs, eels Symbiotic relationship with sulfur-fixing bacteria Similar to photosynthesis, but some predation Nutrient input from smokers, detritus Organisms tightly coupled with environment Open or closed syste ...
... Very high T water, sulfur, other chemicals No light, low O2 Tube worms, bivalves, shrimp, crabs, eels Symbiotic relationship with sulfur-fixing bacteria Similar to photosynthesis, but some predation Nutrient input from smokers, detritus Organisms tightly coupled with environment Open or closed syste ...
Human Activities Can Alter Ecosystems
... The high levels of nitrogen, often along with phosphates, feed the rapid growth of algae in these bodies of water, a condition called eutrophication. As the algae die, the bacteria decomposing them can use up so much of the oxygen in the water that there is no longer enough to support other orga ...
... The high levels of nitrogen, often along with phosphates, feed the rapid growth of algae in these bodies of water, a condition called eutrophication. As the algae die, the bacteria decomposing them can use up so much of the oxygen in the water that there is no longer enough to support other orga ...
L01 Ecosystems crossword
... secondary consumer is greater than that from the producer to primary consumer. It is because the ……… found in a primary consumer is better for energy transfer compared to the carbohydrates found in the producer. 11. An environmental or abiotic factor that is increased in lakes for fish farming as it ...
... secondary consumer is greater than that from the producer to primary consumer. It is because the ……… found in a primary consumer is better for energy transfer compared to the carbohydrates found in the producer. 11. An environmental or abiotic factor that is increased in lakes for fish farming as it ...