Unit 2 Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
... organisms, cannot make own food Decomposer: breaks down dead or decaying organisms, recycles matter ...
... organisms, cannot make own food Decomposer: breaks down dead or decaying organisms, recycles matter ...
1. From Basics to the Extremophiles
... a mile deep on the Pacific Ocean floor near hydrothermal vents. They may grow to about 3 meters (8 ft) long. The worms’ white tube home is made of a tough, natural material called chitin (pronounced “kite-in”). These tubeworms have no mouth, eyes, or stomach (“gut”). Their survival depends on a symb ...
... a mile deep on the Pacific Ocean floor near hydrothermal vents. They may grow to about 3 meters (8 ft) long. The worms’ white tube home is made of a tough, natural material called chitin (pronounced “kite-in”). These tubeworms have no mouth, eyes, or stomach (“gut”). Their survival depends on a symb ...
Biomes and Aquatic Ecosystems
... • Littoral zone – area closest to the shore • Limnetic zone – open water that is well lit • Profundal zone – deepest area with little light and oxygen ...
... • Littoral zone – area closest to the shore • Limnetic zone – open water that is well lit • Profundal zone – deepest area with little light and oxygen ...
Ecology ppt notes
... Abiotic Factors The __________________ components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. Examples of Abiotic Factors: ...
... Abiotic Factors The __________________ components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. Examples of Abiotic Factors: ...
f79a37ba92a097a0f5b27bc72f25014e51cb8a00
... finds two of 1 species of tree side by side.Bengal tiger, Chimpanzee, African forest ...
... finds two of 1 species of tree side by side.Bengal tiger, Chimpanzee, African forest ...
Chapter 18
... Populations cannot grow indefinitely because the environment contains only so much food, water, living space and other resources When one or more becomes scarce, it becomes a limiting factor ...
... Populations cannot grow indefinitely because the environment contains only so much food, water, living space and other resources When one or more becomes scarce, it becomes a limiting factor ...
Ch. 4 - Ecosystems and Communities
... Organisms interact constantly in their community and help shape the ecosystem. ...
... Organisms interact constantly in their community and help shape the ecosystem. ...
Life Science Study Guide
... 7. Explain why there are more producers in an ecosystem than top consumers. There are more producers because not very much energy is passed on to the next level when they are being consumed (10%). The energy pyramid is not very efficient. 7. Define the following terms. Producer – plants, they make t ...
... 7. Explain why there are more producers in an ecosystem than top consumers. There are more producers because not very much energy is passed on to the next level when they are being consumed (10%). The energy pyramid is not very efficient. 7. Define the following terms. Producer – plants, they make t ...
Name
... 11B: Investigate and analyze how organisms, populations, and communities respond to external factors. 11C: Summarize the role of microorganisms in both maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems. 11D: Describe how events and processes that occur during ecological successi ...
... 11B: Investigate and analyze how organisms, populations, and communities respond to external factors. 11C: Summarize the role of microorganisms in both maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems. 11D: Describe how events and processes that occur during ecological successi ...
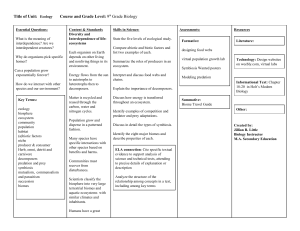
Title of Unit: Ecology Course and Grade Level: 9th Grade Biology
... State the five levels of ecological study. Compare abiotic and biotic factors and list two examples of each. Summarize the roles of producers in an ecosystem. ...
... State the five levels of ecological study. Compare abiotic and biotic factors and list two examples of each. Summarize the roles of producers in an ecosystem. ...
Ecology - SharpSchool
... or animals and therefore must depend on other organisms for food • Get energy through the process of cellular respiration C6H12O6+6O2 6CO2+6H2O+ATP • Consumers that eat producers are considered to be primary consumers since they are the primary (first) things to eat in the food chain. • When you e ...
... or animals and therefore must depend on other organisms for food • Get energy through the process of cellular respiration C6H12O6+6O2 6CO2+6H2O+ATP • Consumers that eat producers are considered to be primary consumers since they are the primary (first) things to eat in the food chain. • When you e ...
附件1: 试卷编制样式(统一使用B5纸出卷)
... B. In marine environments, often the standing biomass increases with increasing primary productivity. C. Although grasslands have lower rates of primary productivity than do forests, grasslands accumulate more biomass per individual than do forests. D. In terrestrial ecosystems, generally less stand ...
... B. In marine environments, often the standing biomass increases with increasing primary productivity. C. Although grasslands have lower rates of primary productivity than do forests, grasslands accumulate more biomass per individual than do forests. D. In terrestrial ecosystems, generally less stand ...
Interactions of life Energy Living need a constant supply of . Energy
... species has its own ____________________. An organism’s ____________________ is its role in its environment – how it obtains food and shelter, finds a mate, cares for its young, and avoids danger. Predator and Prey An organism’s niche includes how it avoids being eaten and how it finds or captures ...
... species has its own ____________________. An organism’s ____________________ is its role in its environment – how it obtains food and shelter, finds a mate, cares for its young, and avoids danger. Predator and Prey An organism’s niche includes how it avoids being eaten and how it finds or captures ...
Ecology Definitions
... Niche – A specific area or function within a habitat Photosynthesis – The chemical process by which plants use the Sun’s energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugar ...
... Niche – A specific area or function within a habitat Photosynthesis – The chemical process by which plants use the Sun’s energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugar ...
INTRO TO ECOLOGY
... mites find all they need to survive in the tiny follicles of eyelashes. Magnified here 225 times, these creatures measure 0.4 mm in length and can be seen only with a microscope. ...
... mites find all they need to survive in the tiny follicles of eyelashes. Magnified here 225 times, these creatures measure 0.4 mm in length and can be seen only with a microscope. ...