Adventures in Nature
... 3.3 Describe ways in which biodiversity within species is important for maintaining the resilience of those species 3.4 describe ways in which biodiversity within and among communities are important for maintaining the resilience of these communities 3.5 Describe interrelationships within species, b ...
... 3.3 Describe ways in which biodiversity within species is important for maintaining the resilience of those species 3.4 describe ways in which biodiversity within and among communities are important for maintaining the resilience of these communities 3.5 Describe interrelationships within species, b ...
Ecology Review
... 10. What is an ecological pyramid? _a diagram showing relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web 11. When does competition occur? _when organisms of the same or different species attempt to use a resource at the same time in the same place 12 ...
... 10. What is an ecological pyramid? _a diagram showing relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web 11. When does competition occur? _when organisms of the same or different species attempt to use a resource at the same time in the same place 12 ...
lec4.dsc
... ecology as to whether “top-down” or “bottom-up” process control ecosystems? 7. Critically evaluate the concept of “carrying capacity of species richness” as summarized in the Hansen et al. 2011 paper. 8. Think of abiotic factors in terms of your project. How might abiotic factors influence or affect ...
... ecology as to whether “top-down” or “bottom-up” process control ecosystems? 7. Critically evaluate the concept of “carrying capacity of species richness” as summarized in the Hansen et al. 2011 paper. 8. Think of abiotic factors in terms of your project. How might abiotic factors influence or affect ...
Robinson`s Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 10/19
... you have interacted with in the last two days (include foods and clothing). ...
... you have interacted with in the last two days (include foods and clothing). ...
The Effects of Invasive Green Crabs on Native Species, presentation
... • Reduces abundance of invertebrate prey • Predation linked to collapse of softshell clam industry in Maine during 1950’s Competition: • Competition for food with other predators, e.g. crabs, fishes • Competition for habitat Habitat disturbance: • Digs up eelgrass and sediments ...
... • Reduces abundance of invertebrate prey • Predation linked to collapse of softshell clam industry in Maine during 1950’s Competition: • Competition for food with other predators, e.g. crabs, fishes • Competition for habitat Habitat disturbance: • Digs up eelgrass and sediments ...
Biology Class Presentation Questions CH 4 Ecosystems
... 1. How are aquatic ecosystems classified? 2. List three factors that determines the chemistry of an ecosystem. 3. What are the two types of freshwater ecosystems? List examples of each. 4. Define PLANKTON & give examples of each. 5. Define wetland. 6. Why are most wetlands considered “productive”? 7 ...
... 1. How are aquatic ecosystems classified? 2. List three factors that determines the chemistry of an ecosystem. 3. What are the two types of freshwater ecosystems? List examples of each. 4. Define PLANKTON & give examples of each. 5. Define wetland. 6. Why are most wetlands considered “productive”? 7 ...
Meningie-Tailem Bend
... purpose of the contents, and shall not be liable for any loss or damage that may be occasioned directly or indirectly through the use of or reliance on the contents of this publication. Reference to any company, product or service in this publication should not be taken as a Department endorsement o ...
... purpose of the contents, and shall not be liable for any loss or damage that may be occasioned directly or indirectly through the use of or reliance on the contents of this publication. Reference to any company, product or service in this publication should not be taken as a Department endorsement o ...
ECOLOGY
... -- feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
... -- feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
Ecology- Powerpoint
... -- feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
... -- feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
Document
... -- feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
... -- feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
Biotic Factors
... is another important biotic factor which helps to limit the size of populations within an ecosystem. Predation occurs when one animal (the predator) eats another living animal (the prey) to utilize (or use) the energy and nutrients from the body of the prey for its own growth, maintenance, or re ...
... is another important biotic factor which helps to limit the size of populations within an ecosystem. Predation occurs when one animal (the predator) eats another living animal (the prey) to utilize (or use) the energy and nutrients from the body of the prey for its own growth, maintenance, or re ...
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... Biomagnification refers to the process in which pollutants not only accumulate, but also become more concentrated at each trophic level. Organisms at lower trophic levels may be affected by the pollutant, but primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers will be more affected, because levels will build ...
... Biomagnification refers to the process in which pollutants not only accumulate, but also become more concentrated at each trophic level. Organisms at lower trophic levels may be affected by the pollutant, but primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers will be more affected, because levels will build ...
Use this Ecology packet to supplement the information in the
... 3. Niche and Community Interactions – Read pages 94 – 104. a. What is a niche? Why does each organism have its own niche within an ecosystem? b. Community Interactions – How do different populations interact with each other within ecosystems? List and define the types of relationships (competition, ...
... 3. Niche and Community Interactions – Read pages 94 – 104. a. What is a niche? Why does each organism have its own niche within an ecosystem? b. Community Interactions – How do different populations interact with each other within ecosystems? List and define the types of relationships (competition, ...
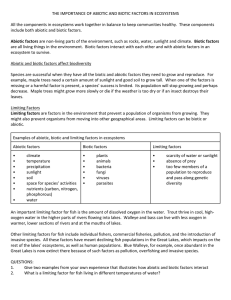
THE IMPORTANCE OF ABIOTIC AND BIOTIC FACTORS IN
... include both abiotic and biotic factors. Abiotic factors are non-living parts of the environment, such as rocks, water, sunlight and climate. Biotic factors are all living things in the environment. Biotic factors interact with each other and with abiotic factors in an ecosystem to survive. Abiotic ...
... include both abiotic and biotic factors. Abiotic factors are non-living parts of the environment, such as rocks, water, sunlight and climate. Biotic factors are all living things in the environment. Biotic factors interact with each other and with abiotic factors in an ecosystem to survive. Abiotic ...
Species Relationships ppt Worksheet
... • If the parasite kills the _________ then it may die too, so it does not usually do this. • Examples: ________________ and hookworms that live inside of an animal (the host) and get nutrients from them. • This interaction is also called parasite – host. Video Link Predation • An interaction where o ...
... • If the parasite kills the _________ then it may die too, so it does not usually do this. • Examples: ________________ and hookworms that live inside of an animal (the host) and get nutrients from them. • This interaction is also called parasite – host. Video Link Predation • An interaction where o ...
Organisms - St. Michael Catholic School
... population that includes other members of its species.The population belongs to a community of different species.The community and abiotic factors together form an ecosystem. • Any change affects all the different populations that live there. • Ecology: the study of how organisms interact with each ...
... population that includes other members of its species.The population belongs to a community of different species.The community and abiotic factors together form an ecosystem. • Any change affects all the different populations that live there. • Ecology: the study of how organisms interact with each ...