Full Text
... of Stanford University’s Global Climate and Energy Project and a professor (research) in the Department of Energy Resources Engineering in the School of Earth Sciences. She is an internationally recognized expert in the storage of carbon dioxide in geological formations and was a coordinating lead a ...
... of Stanford University’s Global Climate and Energy Project and a professor (research) in the Department of Energy Resources Engineering in the School of Earth Sciences. She is an internationally recognized expert in the storage of carbon dioxide in geological formations and was a coordinating lead a ...
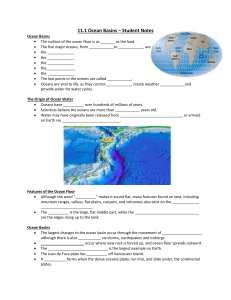
11.1 OCEAN BASINS - STUDENT NOTES
... are the edges rising up to the land. Ocean Basins The largest changes to the ocean basin occur through the movement of ___________________, although there is also ___________ via storms, earthquakes and icebergs. _____________________ occur where new rock is forced up, and ocean floor spreads ou ...
... are the edges rising up to the land. Ocean Basins The largest changes to the ocean basin occur through the movement of ___________________, although there is also ___________ via storms, earthquakes and icebergs. _____________________ occur where new rock is forced up, and ocean floor spreads ou ...
Nickel
... its abundance in Earth lie between 17,000 and 19,000 ppm. Most of this is concentrated in the Earth’s core; analyses of iron meteorites suggest the core contains ca 5 wt% Ni (McDonough, 2014), leaving ca 1860 ppm in the mantle (Palme and O’Neill, 2014) and 47 ppm in the continental crust (Rudnick an ...
... its abundance in Earth lie between 17,000 and 19,000 ppm. Most of this is concentrated in the Earth’s core; analyses of iron meteorites suggest the core contains ca 5 wt% Ni (McDonough, 2014), leaving ca 1860 ppm in the mantle (Palme and O’Neill, 2014) and 47 ppm in the continental crust (Rudnick an ...
Earth`s Surface:
... the Earth’s active surface geology. Volcanoes and earthquakes, expressions of Earth’s restless crust, are observed to be clustered along plate boundaries. Earthquakes occur when pieces of the crust or upper mantle suddenly release accumulated strain caused by plate tectonics. Energy propagates from ...
... the Earth’s active surface geology. Volcanoes and earthquakes, expressions of Earth’s restless crust, are observed to be clustered along plate boundaries. Earthquakes occur when pieces of the crust or upper mantle suddenly release accumulated strain caused by plate tectonics. Energy propagates from ...
Wanganui High School
... Weathering is the slow breaking down of rocks into smaller and smaller fragments and it can occur in many different ways. (i) physical weathering e.g. water freezes in rock cracks, and expands as it turns to ice which cracks the rocks apart; continuous battering of rock surfaces with dust and sand p ...
... Weathering is the slow breaking down of rocks into smaller and smaller fragments and it can occur in many different ways. (i) physical weathering e.g. water freezes in rock cracks, and expands as it turns to ice which cracks the rocks apart; continuous battering of rock surfaces with dust and sand p ...
Plate Tectonics - Helena High School
... Evidence from Rock Formations - Same rocks are found in the Appalachians and also in Greenland and Europe. - Rock formations (ex. mountain ranges) fractured as the continents separated. ...
... Evidence from Rock Formations - Same rocks are found in the Appalachians and also in Greenland and Europe. - Rock formations (ex. mountain ranges) fractured as the continents separated. ...
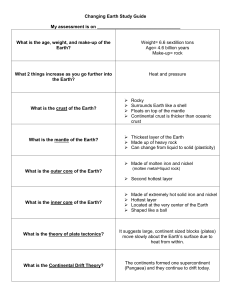
Changing Earth Study Guide My assessment is on What is the age
... Made up of heavy rock Can change from liquid to solid (plasticity) Made of molten iron and nickel (molten metal=liquid rock) ...
... Made up of heavy rock Can change from liquid to solid (plasticity) Made of molten iron and nickel (molten metal=liquid rock) ...
Earth`s Interior - Union Beach School District
... four different layers. » The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. » The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. » The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble ...
... four different layers. » The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. » The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. » The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble ...
Practice01 e - Kean University
... a. Send an e-mail to csmart@kean.edu by 5pm tomorrow. Use an e-mail address you check daily. The subject line MUST be Geology 1200. The body (the message) must include your name. b. Browse to http://www.kean.edu/~csmart/Lectures/ Open and print out the next homework, Practice02_3.doc. Bring it to cl ...
... a. Send an e-mail to csmart@kean.edu by 5pm tomorrow. Use an e-mail address you check daily. The subject line MUST be Geology 1200. The body (the message) must include your name. b. Browse to http://www.kean.edu/~csmart/Lectures/ Open and print out the next homework, Practice02_3.doc. Bring it to cl ...
Metamorphic Rocks ppt
... If not foliated, named on composition If foliated, determine type of foliation, then modify name based on composition ...
... If not foliated, named on composition If foliated, determine type of foliation, then modify name based on composition ...
Slide 1
... • Makes up most of Earth’s volume • Composed of hot solid material – Silicon, oxygen, iron, aluminum, and magnesium – 1,800 miles think and extremely high pressure – Heat moves upward through mantle ...
... • Makes up most of Earth’s volume • Composed of hot solid material – Silicon, oxygen, iron, aluminum, and magnesium – 1,800 miles think and extremely high pressure – Heat moves upward through mantle ...
The Rock Cycle and the three rock types File
... All rock can be heated. But where does the heat come from? Inside Earth there is heat from pressure (push your hands together very hard and feel the heat). There is heat from friction (rub your hands together and feel the heat). There is also heat from radioactive decay (the process that gives us nu ...
... All rock can be heated. But where does the heat come from? Inside Earth there is heat from pressure (push your hands together very hard and feel the heat). There is heat from friction (rub your hands together and feel the heat). There is also heat from radioactive decay (the process that gives us nu ...
chapter 14 - TeamCFA school
... affected by national policies that subsidize exploration or restrict exports/imports. C. New technologies can increase the mining of low-grade ores at affordable prices, but harmful environmental effects can limit this approach. In 1900, the average copper ore mined in the U.S. was about 5% copper b ...
... affected by national policies that subsidize exploration or restrict exports/imports. C. New technologies can increase the mining of low-grade ores at affordable prices, but harmful environmental effects can limit this approach. In 1900, the average copper ore mined in the U.S. was about 5% copper b ...
the layers of the earth - NATSCI-A7
... the crust composes of 15.3% of the total mantle-crust mass and is made of crystalline forms of Olivine (Mg,Fe)2SiO4 and pyroxene (Mg,Fe)SiO3. • The upper mantle makes up 10.3% of the Earth's mass, extending a depth of 6-250 miles (10-400 kilometers). • A relatively large portion when compared to the ...
... the crust composes of 15.3% of the total mantle-crust mass and is made of crystalline forms of Olivine (Mg,Fe)2SiO4 and pyroxene (Mg,Fe)SiO3. • The upper mantle makes up 10.3% of the Earth's mass, extending a depth of 6-250 miles (10-400 kilometers). • A relatively large portion when compared to the ...
Earth Science, 12e (Tarbuck/Lutgens)
... structure; in a rock, the atoms are randomly bonded without any geometric pattern. C) In a mineral the constituent atoms are bonded in a regular, repetitive, internal structure; a rock is a lithified or consolidated aggregate of different mineral grains. D) A rock consists of atoms bonded in a regul ...
... structure; in a rock, the atoms are randomly bonded without any geometric pattern. C) In a mineral the constituent atoms are bonded in a regular, repetitive, internal structure; a rock is a lithified or consolidated aggregate of different mineral grains. D) A rock consists of atoms bonded in a regul ...