Igneous Rocks II: Heat, magma generation, and differentiation
... T is different from the fluid (mass flux). Important near Earth’s surface due to fractured nature of crust. • Conduction: transfer of kinetic energy by atomic vibration. Cannot occur in a vacuum. For a given volume, heat is conducted away faster if the enclosing surface area is larger. ...
... T is different from the fluid (mass flux). Important near Earth’s surface due to fractured nature of crust. • Conduction: transfer of kinetic energy by atomic vibration. Cannot occur in a vacuum. For a given volume, heat is conducted away faster if the enclosing surface area is larger. ...
MEMO TO: Lisa A. Sarvestaney, M.A., Instructor FROM: Charles
... defined as a naturally occurring, inorganic solid element or compound with crystalline structure” (442). In plain English, a rock is a jumble of elements and minerals formed under high temperature, pressure, and time. A mineral can be a rock; however, a rock is not a mineral. The key qualifier is th ...
... defined as a naturally occurring, inorganic solid element or compound with crystalline structure” (442). In plain English, a rock is a jumble of elements and minerals formed under high temperature, pressure, and time. A mineral can be a rock; however, a rock is not a mineral. The key qualifier is th ...
“Milk Chocolate Movement” worksheet
... All of this activity occurs within the Earth’s rock mantle which is made liquid due to the intense heat from the Earth’s core. The crust then moves over the mantel and has fractured into seven major tectonic plates, which collide and grind past each other. Tectonic plates are responsible for the cre ...
... All of this activity occurs within the Earth’s rock mantle which is made liquid due to the intense heat from the Earth’s core. The crust then moves over the mantel and has fractured into seven major tectonic plates, which collide and grind past each other. Tectonic plates are responsible for the cre ...
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
... • Metamorphism of rocks occurs very slowly, it may take millions of years for a rock to convert to a metamorphic rock. • Uplift and exposure is usually relatively rapid and rocks cool quickly during uplift, this “freezes” in the metamorphic mineral assemblage. • Loss of volatiles during high grade m ...
... • Metamorphism of rocks occurs very slowly, it may take millions of years for a rock to convert to a metamorphic rock. • Uplift and exposure is usually relatively rapid and rocks cool quickly during uplift, this “freezes” in the metamorphic mineral assemblage. • Loss of volatiles during high grade m ...
Kump_Ch07_TH - Camosun College
... • Thick fill or unconsolidated sediment amplifies ground motion due to surface waves: local geology & proximity both affect amplitude • More ground motion, more & infrastructure building damage ...
... • Thick fill or unconsolidated sediment amplifies ground motion due to surface waves: local geology & proximity both affect amplitude • More ground motion, more & infrastructure building damage ...
Sr–Nd isotope geochemistry and tectonomagmatic setting of the
... the fields of high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic series on the K2O versus SiO2 discrimination diagram proposed by Peccerillo and Taylor (1976) (Fig. 7), showing a strong potassium enrichment (1.57–5.87 K2O wt%) from the most mafic to the most felsic compositions. Since the Na2O (2.32–3.65 wt%) tre ...
... the fields of high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic series on the K2O versus SiO2 discrimination diagram proposed by Peccerillo and Taylor (1976) (Fig. 7), showing a strong potassium enrichment (1.57–5.87 K2O wt%) from the most mafic to the most felsic compositions. Since the Na2O (2.32–3.65 wt%) tre ...
Chap 12 14e
... – When two oceanic plates collide, a trench ordinarily forms at the boundary between the two plates. – When an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, the continental plate usually rides up over the denser oceanic plate and pushes it down into the mantle in a process called subduction. – Th ...
... – When two oceanic plates collide, a trench ordinarily forms at the boundary between the two plates. – When an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, the continental plate usually rides up over the denser oceanic plate and pushes it down into the mantle in a process called subduction. – Th ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface
... Earth’s crust is like a jigsaw puzzle, made up of large and small sections called tectonic plates. Energy from the Earth’s core and mantle pushes them around so they are in constant, slow motion. The plates can cause earthquakes and ...
... Earth’s crust is like a jigsaw puzzle, made up of large and small sections called tectonic plates. Energy from the Earth’s core and mantle pushes them around so they are in constant, slow motion. The plates can cause earthquakes and ...
The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
... hydrides which are ionic in nature. 2Na(s) + H2(g) 2NaH(s) The ionic character of hydrides increases from Li to Cs. The stability of hydrides decreases from Li to Cs. The hydrides behave as strong reducing agents and the latter increases from Li to Cs. ...
... hydrides which are ionic in nature. 2Na(s) + H2(g) 2NaH(s) The ionic character of hydrides increases from Li to Cs. The stability of hydrides decreases from Li to Cs. The hydrides behave as strong reducing agents and the latter increases from Li to Cs. ...
Lecture 13.
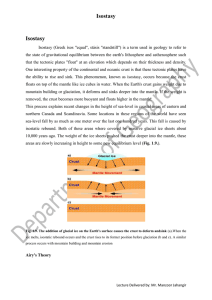
... Isostasy (Greek ísos "equal", stásis "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. One interesting proper ...
... Isostasy (Greek ísos "equal", stásis "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. One interesting proper ...
INTERIOR STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
... relative sizes of the mantle and core. Interestingly, there are two cores noted (the inner and the outer). Notice also how the chemical composition of the Earth varies with depth; near the surface, the Earth is dominated by silicon and oxygen. In fact, 74% of the crust of the Earth consists of the a ...
... relative sizes of the mantle and core. Interestingly, there are two cores noted (the inner and the outer). Notice also how the chemical composition of the Earth varies with depth; near the surface, the Earth is dominated by silicon and oxygen. In fact, 74% of the crust of the Earth consists of the a ...
THE CONTINTENTAL DRIFT IDEA
... the Earth's crust. If the idea was correct, however, mountains would be spread evenly over the Earth's surface. We know this is not the case. ...
... the Earth's crust. If the idea was correct, however, mountains would be spread evenly over the Earth's surface. We know this is not the case. ...
Geotechnical Properties of the Rodessa Formation in East
... samples from the Rodessa Formation will be taken from the Stephen F. Austin State University Core Lab Repository and tested at the University of Texas at El Paso. Parameters such as water absorption, dry density, saturation density, and bulk density will be experimentally determined using procedures ...
... samples from the Rodessa Formation will be taken from the Stephen F. Austin State University Core Lab Repository and tested at the University of Texas at El Paso. Parameters such as water absorption, dry density, saturation density, and bulk density will be experimentally determined using procedures ...
Name - OnCourse
... 3. Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift because it shows that continents move with the oceanic ...
... 3. Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift because it shows that continents move with the oceanic ...
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING
... SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950’s and early 1960’s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information: Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine ridge system that extended around the globe. These became known as MID-OCEAN RIDGES. Sam ...
... SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950’s and early 1960’s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information: Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine ridge system that extended around the globe. These became known as MID-OCEAN RIDGES. Sam ...
Word format
... C. convection in the mantle provides a driving force to move the plates around D. subduction of old crust makes room for new crust forming at mid-ocean ridges E. all of the above 10. The Earth has a magnetic field because: A. the liquid outer core creates an electric current which induces a magnetic ...
... C. convection in the mantle provides a driving force to move the plates around D. subduction of old crust makes room for new crust forming at mid-ocean ridges E. all of the above 10. The Earth has a magnetic field because: A. the liquid outer core creates an electric current which induces a magnetic ...
Mantle Convection
... Scientists are not in complete agreement as to what causes plate motion, but one suggestion is that convection currents within Earth’s interior provide the driving mechanism. Many scientists think convection occurs in the asthenosphere due to heat generated from Earth’s interior. A convection curren ...
... Scientists are not in complete agreement as to what causes plate motion, but one suggestion is that convection currents within Earth’s interior provide the driving mechanism. Many scientists think convection occurs in the asthenosphere due to heat generated from Earth’s interior. A convection curren ...
Layers of the Earth PPT
... * The core of the Earth is like a ball of very hot metals. * The outer core is liquid. * The outer core is made up of iron and is very dense. ...
... * The core of the Earth is like a ball of very hot metals. * The outer core is liquid. * The outer core is made up of iron and is very dense. ...
Earth Science - Gilbert Public Schools
... Another comparison of the amt. of water available to us. ...
... Another comparison of the amt. of water available to us. ...
Earthquakes - collazocove
... 2. It depends how far the plates move apart to how powerful the earthquake will be. ...
... 2. It depends how far the plates move apart to how powerful the earthquake will be. ...
plates How many major sections is Earth`s crust divided into?
... How many major sections is Earth’s crust divided into? ...
... How many major sections is Earth’s crust divided into? ...
CHAPTERS FROM GEOLOGY
... Igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of molten or partly molten mobile material termed magma. The nature of magma cannot be directly observed because it originates from the partial melting of the lower crust and upper mantle of the Earth, usually at depths between 50 and 200 km below the s ...
... Igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of molten or partly molten mobile material termed magma. The nature of magma cannot be directly observed because it originates from the partial melting of the lower crust and upper mantle of the Earth, usually at depths between 50 and 200 km below the s ...