Section 17.3 Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 1. Warms, _________________, and becomes _____________________ & ____________ 2. __________________________ material sinks due to gravity 3. Forms a cycle, or _____________________________ Mantle Convection Currents in the Asthenosphere: 1. ________________in the aesthenosphere is thought to cause t ...
... 1. Warms, _________________, and becomes _____________________ & ____________ 2. __________________________ material sinks due to gravity 3. Forms a cycle, or _____________________________ Mantle Convection Currents in the Asthenosphere: 1. ________________in the aesthenosphere is thought to cause t ...
Tectonic Plate Theory PowerPoint Study Guide
... Therefore the landmasses must have been in different locations in the past. ...
... Therefore the landmasses must have been in different locations in the past. ...
The Earth’s Layers - Welcome to Ms. George's Science Class
... very thin in comparison to the other layers. • The crust is 5-100 km. thick • There are two types of crust: Continental Crust and Oceanic Crust • Both continental crust and oceanic crust are made of the elements oxygen, silicon, and ...
... very thin in comparison to the other layers. • The crust is 5-100 km. thick • There are two types of crust: Continental Crust and Oceanic Crust • Both continental crust and oceanic crust are made of the elements oxygen, silicon, and ...
Name: Graphing Seafloor Spreading Lab Objective: Using ocean
... Name: ________________________________________________________________ Graphing Seafloor Spreading Lab Objective: Using ocean depth data you will construct an ocean bottom profile of the Atlantic Ocean. Using the profile, you will identify features of the ocean bottom in regions of diverging plate b ...
... Name: ________________________________________________________________ Graphing Seafloor Spreading Lab Objective: Using ocean depth data you will construct an ocean bottom profile of the Atlantic Ocean. Using the profile, you will identify features of the ocean bottom in regions of diverging plate b ...
Erosion
... Pacific Plates Pacific plate lies at the bottom of the ocean. Over time, the edges of these plates were forced under the edges of the plates surrounding the ...
... Pacific Plates Pacific plate lies at the bottom of the ocean. Over time, the edges of these plates were forced under the edges of the plates surrounding the ...
Earth, continental drift, plate tectonics, sea floor spreading
... parts are moving in opposite directions, carrying along the continents and oceans that rest on top of them. These pieces of Earth’s top layer are called tectonic plates. They are moving very slowly, but constantly. (Most plates are moving about as fast as your fingernails are growing -- not very fas ...
... parts are moving in opposite directions, carrying along the continents and oceans that rest on top of them. These pieces of Earth’s top layer are called tectonic plates. They are moving very slowly, but constantly. (Most plates are moving about as fast as your fingernails are growing -- not very fas ...
Ch. 11 Lecture1
... • Isostasy explains the vertical distribution of Earth's crust. George Bedell Airy proposed that the density of the crust is everywhere the same and the thickness of crustal material varies. Higher mountains are compensated by deeper roots. This explains the high elevations of most major mountain c ...
... • Isostasy explains the vertical distribution of Earth's crust. George Bedell Airy proposed that the density of the crust is everywhere the same and the thickness of crustal material varies. Higher mountains are compensated by deeper roots. This explains the high elevations of most major mountain c ...
Chapter 12 - Fill-in-the
... Acid rain is produced when __________ gases mix with water vapor in the atmosphere. Parts of a __________ o Magma collects in a magma __________ inside the Earth’s crust. o The opening where magma is forced up and flows onto the Earth’s surface is called a __________. o The __________-walled dep ...
... Acid rain is produced when __________ gases mix with water vapor in the atmosphere. Parts of a __________ o Magma collects in a magma __________ inside the Earth’s crust. o The opening where magma is forced up and flows onto the Earth’s surface is called a __________. o The __________-walled dep ...
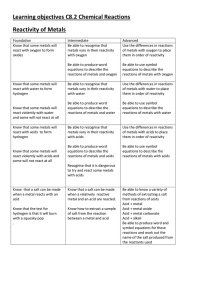
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... Understand that some metals are more reactive than others and this allows us to place the metals in order of reactivity Understand that the reactivity of a metal affects what it’s uses are ...
... Understand that some metals are more reactive than others and this allows us to place the metals in order of reactivity Understand that the reactivity of a metal affects what it’s uses are ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... • Rocks may also be subjected to differential stress which is unequal in different directions ...
... • Rocks may also be subjected to differential stress which is unequal in different directions ...
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
... Plate Tectonics: • The Earth’s crust is divided into _________major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to _____________________________ • ________________ against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “te ...
... Plate Tectonics: • The Earth’s crust is divided into _________major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to _____________________________ • ________________ against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “te ...
sample test1 - this is only for questions style
... a) The outer core is liquid. b) The core is approximately 1/4 the radius of the earth. c) The core is made of Fe. d) The core is approximately 1/8 the volume of the earth. e) All of the above describe the earth's core. Scientists have calculated Earth to be ______ billion years old by meteorites. a) ...
... a) The outer core is liquid. b) The core is approximately 1/4 the radius of the earth. c) The core is made of Fe. d) The core is approximately 1/8 the volume of the earth. e) All of the above describe the earth's core. Scientists have calculated Earth to be ______ billion years old by meteorites. a) ...
PASS MOCK MIDTERM #2 – FOR PRACTICE ONLY
... Adiabatic temperature change is caused by the exchange of heat energy as the air parcel rises or falls. T / F Effusive volcanic eruptions are associated with sea-‐floor spreading centres and hot spo ...
... Adiabatic temperature change is caused by the exchange of heat energy as the air parcel rises or falls. T / F Effusive volcanic eruptions are associated with sea-‐floor spreading centres and hot spo ...
Jamies Group - Junee North Public School
... circles stones are 26 feet high and the outer circles stones are 10 feet high. There are two types of stones used in the construction of Stonehenge. The large outer circle is made of Sarsen which is sedimentary Sandstone and the inner circle is made of Bluestone which is a blend of Basalt and Gabbro ...
... circles stones are 26 feet high and the outer circles stones are 10 feet high. There are two types of stones used in the construction of Stonehenge. The large outer circle is made of Sarsen which is sedimentary Sandstone and the inner circle is made of Bluestone which is a blend of Basalt and Gabbro ...
File - Earth Science
... They are not made by humans Minerals are inorganic They have never been alive and are not made up from plants or animals Minerals are solids They are not liquids (like water), or gases (like the air around you) Minerals have a definite chemical composition Each one is made of a particular mix ...
... They are not made by humans Minerals are inorganic They have never been alive and are not made up from plants or animals Minerals are solids They are not liquids (like water), or gases (like the air around you) Minerals have a definite chemical composition Each one is made of a particular mix ...
Plate Tectonics
... started making detailed maps of the sea bed. • These discoveries gave evidence of continental drift and how the tectonic plates ...
... started making detailed maps of the sea bed. • These discoveries gave evidence of continental drift and how the tectonic plates ...
The Sea Floor
... 4. OCEAN SEDIMENTS are all the unconsolidated materials on the sea floor, loose fragments of rocks, minerals, ash, or organic material that are transported from their source and deposited by air, wind, ice, or water. Also some sediments are chemically precipitated from overlying water or form chemic ...
... 4. OCEAN SEDIMENTS are all the unconsolidated materials on the sea floor, loose fragments of rocks, minerals, ash, or organic material that are transported from their source and deposited by air, wind, ice, or water. Also some sediments are chemically precipitated from overlying water or form chemic ...
Chapter 3: Plate Tectonics
... supercontinent called Pangaea. • He thought the continents seemed to fit together as a puzzle. ...
... supercontinent called Pangaea. • He thought the continents seemed to fit together as a puzzle. ...
Internal Structure of the Earth
... How do we know there are four layers? • We don’t, it’s a theory! • Using earthquake waves, they can tell whether an object is a liquid or a solid, so by using that information, they theorized about the interior layers of the Earth ...
... How do we know there are four layers? • We don’t, it’s a theory! • Using earthquake waves, they can tell whether an object is a liquid or a solid, so by using that information, they theorized about the interior layers of the Earth ...
Quiz: Volcanoes Study Guide
... viscosity =the resistance of a liquid to flowing; low viscosity flows freely, high viscosity resist flowing silica = a compound made up of oxygen and silicon particles Where Volcanoes Form convergent boundary = two plates moving together; one plate subducts causing a volcano to form divergent bounda ...
... viscosity =the resistance of a liquid to flowing; low viscosity flows freely, high viscosity resist flowing silica = a compound made up of oxygen and silicon particles Where Volcanoes Form convergent boundary = two plates moving together; one plate subducts causing a volcano to form divergent bounda ...
Section 1
... • Temperature inside Earth increases as depth increases. • Beneath earth surface rock is cool, but 20 meters down the rock starts to get warmer. • For every 40 meters down , the temperature increases 1 Celsius degree. • The high temperatures inside Earth are the results of great rock pressure, energ ...
... • Temperature inside Earth increases as depth increases. • Beneath earth surface rock is cool, but 20 meters down the rock starts to get warmer. • For every 40 meters down , the temperature increases 1 Celsius degree. • The high temperatures inside Earth are the results of great rock pressure, energ ...
What is the Earth made of?
... rocks are formed; and then we will look at how rock is taken from the earth, by quarrying, and the effects of this on the people and the environment. After that we will look in a bit of detail as to what and how changed the shape of the earth’ surface. Having established the what and the how, we wil ...
... rocks are formed; and then we will look at how rock is taken from the earth, by quarrying, and the effects of this on the people and the environment. After that we will look in a bit of detail as to what and how changed the shape of the earth’ surface. Having established the what and the how, we wil ...