Plate Tectonics
... and forms a chain of volcanic islands Convergent oceanic and continental plates – oceanic is more dense and is subducted under the continental plate. Volcanoes on land are produced. Convergent continental and continental plate – 2 continental plates collide, crust buckles and ...
... and forms a chain of volcanic islands Convergent oceanic and continental plates – oceanic is more dense and is subducted under the continental plate. Volcanoes on land are produced. Convergent continental and continental plate – 2 continental plates collide, crust buckles and ...
Earthquake test review 8th grade Earthquake Review for
... ____________________11. Ocean crust sinks under continental crust because ocean crust is less dense. ...
... ____________________11. Ocean crust sinks under continental crust because ocean crust is less dense. ...
Plate Tectonics Part 1
... day continents “fit” together 2. Distribution of fossil species 3. Magnetic stripes in sea floor ...
... day continents “fit” together 2. Distribution of fossil species 3. Magnetic stripes in sea floor ...
To the September 16th Field Excursion Guide
... Palynological data is published from these localities in Tongiorgi et al. (2003) who identified a microflora comprising 52 taxa of acritarchs from the Tøyen Formation (Tremadocian−Floian). The preservation is generally poor but most taxa were identified to the species level. It was shown that sampl ...
... Palynological data is published from these localities in Tongiorgi et al. (2003) who identified a microflora comprising 52 taxa of acritarchs from the Tøyen Formation (Tremadocian−Floian). The preservation is generally poor but most taxa were identified to the species level. It was shown that sampl ...
Chapter 7:2 pages 198-201
... B. Mid-Ocean Ridges and Sea-Floor Spreading 1. A chain of submerged mountains runs through the center of the Atlantic Ocean…It is part of a worldwide system of mid-ocean ridges that are underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins. ...
... B. Mid-Ocean Ridges and Sea-Floor Spreading 1. A chain of submerged mountains runs through the center of the Atlantic Ocean…It is part of a worldwide system of mid-ocean ridges that are underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins. ...
Eons, Eras, Periods and Epochs Dating by radioactive isotopes
... •H2O increases in volume by 9% upon freezing •Repeated freezing and thawing breaks rocks apart •Humid continental, subarctic, polar and alpine environments Frost wedging pushes portions of rock apart. The loosened, angular rock falls from cliffs in steep areas and accumulates downslope, forming talu ...
... •H2O increases in volume by 9% upon freezing •Repeated freezing and thawing breaks rocks apart •Humid continental, subarctic, polar and alpine environments Frost wedging pushes portions of rock apart. The loosened, angular rock falls from cliffs in steep areas and accumulates downslope, forming talu ...
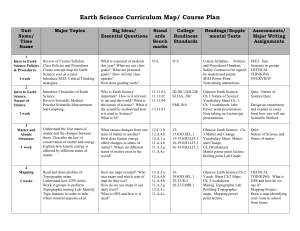
Earth Science Curriculum Map 11-12
... theories of the fate of the Universe. Analyze different types of galaxies and solar systems and how scientists study them in order to better understand the universe. Understand how Cosmic ...
... theories of the fate of the Universe. Analyze different types of galaxies and solar systems and how scientists study them in order to better understand the universe. Understand how Cosmic ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... The sea floor is continually being generated at mid-ocean ridges. II Earth was once covered by a massive continent. III The sea floor is continually being destroyed. A) I only B) I and II only C) I and III only D) I, II, and III ...
... The sea floor is continually being generated at mid-ocean ridges. II Earth was once covered by a massive continent. III The sea floor is continually being destroyed. A) I only B) I and II only C) I and III only D) I, II, and III ...
GTPlate Tectonics, Continental Drift and Seafloor Spreading
... • Many believed Wegener’s theory was just that, merely a theory. • Many said there was no mechanism to explain how the continents could have moved apart. • Until..... ...
... • Many believed Wegener’s theory was just that, merely a theory. • Many said there was no mechanism to explain how the continents could have moved apart. • Until..... ...
Earth Space Science - Laconia School District
... surface because the plates move and push the plates (together, apart ect.). They change the landforms because a big mountain hit by an earthquake might be so big anymore (might flatten out a little), a stream that has a mudslide come through it might become more of a river, and then from there maybe ...
... surface because the plates move and push the plates (together, apart ect.). They change the landforms because a big mountain hit by an earthquake might be so big anymore (might flatten out a little), a stream that has a mudslide come through it might become more of a river, and then from there maybe ...
Chapter 3 Plate Tectonics Theory & Evolution
... Historical Development of Plate Tectonics Earth’s layers Study of Plate Motions Summary of Plate Driving Forces ...
... Historical Development of Plate Tectonics Earth’s layers Study of Plate Motions Summary of Plate Driving Forces ...
notes symp
... In southern Death Valley normal and strike-slip faulting associated with extensional basin formation began less than 15 Ma ago and continues today. Geologic features such as: granitic plutons, dikes, sills, and volcanic fields are concurrent with extension (Calzia et al., 2000). This presentation ou ...
... In southern Death Valley normal and strike-slip faulting associated with extensional basin formation began less than 15 Ma ago and continues today. Geologic features such as: granitic plutons, dikes, sills, and volcanic fields are concurrent with extension (Calzia et al., 2000). This presentation ou ...
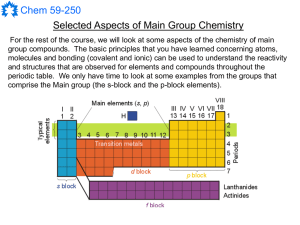
Main Group Notes 1
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 16 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np4 electron configuration, neutral group 16 compounds can form up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state f ...
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 16 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np4 electron configuration, neutral group 16 compounds can form up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state f ...
Earth Science Chapter 9 Section 4 Review
... Hot spots are relatively stationary plumes of molten rock rising from Earth’s mantle. According to the theory of plate tectonics, as a plate moves over a hot spot, magma often penetrates the surface, generating volcanic activity. If the volcanic activity continues, an island will form. In the case o ...
... Hot spots are relatively stationary plumes of molten rock rising from Earth’s mantle. According to the theory of plate tectonics, as a plate moves over a hot spot, magma often penetrates the surface, generating volcanic activity. If the volcanic activity continues, an island will form. In the case o ...
Formulae/ Equations homework - St Peter the Apostle High School
... lead (I) oxide copper (II) iodide copper (I) sulphide ...
... lead (I) oxide copper (II) iodide copper (I) sulphide ...
Section: Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... ______ 2. The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called a. seismology. c. deformation. b. elasticity. d. re-formation. ______ 3. When stress squeezes an object it is called a. compression. c. convergence. b. re-formation. d. tension. ______ 4. When stress stretches an ...
... ______ 2. The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called a. seismology. c. deformation. b. elasticity. d. re-formation. ______ 3. When stress squeezes an object it is called a. compression. c. convergence. b. re-formation. d. tension. ______ 4. When stress stretches an ...
Density of Earth Materials Lab - Mercer Island School District
... represent pieces of the mantle brought up to the surface during eruptions. A final piece of evidence used to determine the mantle's composition comes from stony meteorites (chondrites), since they are thought to be remnants of material left over from the formation of the solar system, and have ...
... represent pieces of the mantle brought up to the surface during eruptions. A final piece of evidence used to determine the mantle's composition comes from stony meteorites (chondrites), since they are thought to be remnants of material left over from the formation of the solar system, and have ...
Plate Tectonics Notes
... This is where molten rock reaches the surface, cools, and forms new crust As this new crust forms the magnetic minerals in the crust align in relation to Earth’s current magnetic field Scientists can look at the sea floor to get a history of Earth’s magnetic reversals (we will talk about how this wo ...
... This is where molten rock reaches the surface, cools, and forms new crust As this new crust forms the magnetic minerals in the crust align in relation to Earth’s current magnetic field Scientists can look at the sea floor to get a history of Earth’s magnetic reversals (we will talk about how this wo ...
Science Study Guide - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The organisms that are better suited to the environment will survive and reproduce. 64.What defines the members of a species? Should be able to reproduce. 65.Marine fossils have been found in exposed rock layers in South Carolina. What would be a good interpretation of this discovery? South Carolina ...
... The organisms that are better suited to the environment will survive and reproduce. 64.What defines the members of a species? Should be able to reproduce. 65.Marine fossils have been found in exposed rock layers in South Carolina. What would be a good interpretation of this discovery? South Carolina ...
File
... Describe Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift. Be specific and very detailed! About 225 million years ago, all the continents were one huge supercontinent, called Pangaea. Pangaea split and the continents drifted into their current positions. Describe all the types of evidence that supports ...
... Describe Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift. Be specific and very detailed! About 225 million years ago, all the continents were one huge supercontinent, called Pangaea. Pangaea split and the continents drifted into their current positions. Describe all the types of evidence that supports ...
0113295 390 2b 0/.
... The coast of the lower part of Lake Erie and the upper part of Lake Ontario, as well as the country back from Toronto to the exit of Lake Simcoe and Matchedash Bay. The Ottawa from its mouth near Montreal to the head of Lake Temiscamang, a distance of 400 miles, with many of its tributaries on the r ...
... The coast of the lower part of Lake Erie and the upper part of Lake Ontario, as well as the country back from Toronto to the exit of Lake Simcoe and Matchedash Bay. The Ottawa from its mouth near Montreal to the head of Lake Temiscamang, a distance of 400 miles, with many of its tributaries on the r ...
Final Review Answers - Academic Computer Center
... _____ 3. The tilt of Earth’s axis is responsible for its seasons. _____ 4. An eclipse of the Moon occurs approximately every 28 days. False, because of the tilt of the Moon’s orbit it will not always fall in the Earth’s shadow _____ 5. The amount of the lunar surface that is illuminated by the Sun c ...
... _____ 3. The tilt of Earth’s axis is responsible for its seasons. _____ 4. An eclipse of the Moon occurs approximately every 28 days. False, because of the tilt of the Moon’s orbit it will not always fall in the Earth’s shadow _____ 5. The amount of the lunar surface that is illuminated by the Sun c ...
Layers of The Earth
... The Earth has several distinct layers: The crust – the outermost layer of the Earth, comprised of 2 types of crust - continental and oceanic. The crust has a variable thickness, being 35-70 km thick in the continents and 5-10 km thick in the ocean basins. Continental crust has a varying thickness, b ...
... The Earth has several distinct layers: The crust – the outermost layer of the Earth, comprised of 2 types of crust - continental and oceanic. The crust has a variable thickness, being 35-70 km thick in the continents and 5-10 km thick in the ocean basins. Continental crust has a varying thickness, b ...