Seafloor Spreading Lab with Makeup
... Elsewhere, one plate slides under another, or subducts, and deep ocean trenches are formed. Rock on the subducting plate becomes part of the asthenosphere. Oceanic crust is denser and thinner than continental crust, so all seafloor rock is eventually destroyed in this way. Thus, the oldest seafloor ...
... Elsewhere, one plate slides under another, or subducts, and deep ocean trenches are formed. Rock on the subducting plate becomes part of the asthenosphere. Oceanic crust is denser and thinner than continental crust, so all seafloor rock is eventually destroyed in this way. Thus, the oldest seafloor ...
earth: inside and out - American Museum of Natural History
... Life on Earth is possible because of the "Goldilocks effect": itʼs in just the right place (neither too close nor too far from the Sun) and is made of just the right stuff (water plus the six elements of which 95% of life consists). Everywhere on the planet that theyʼve looked, scientists have found ...
... Life on Earth is possible because of the "Goldilocks effect": itʼs in just the right place (neither too close nor too far from the Sun) and is made of just the right stuff (water plus the six elements of which 95% of life consists). Everywhere on the planet that theyʼve looked, scientists have found ...
Plate Tectonics and Sedimentation: Where do sediments
... crust heated from below, thermally expands and thins creation of tension fractures (= normal faults) extension causes collapse of thinned crust (= horsts & grabens) creation of long, narrow, fault-bounded central rift valley thick sequences of continental deposits due to rapid subsidence and high re ...
... crust heated from below, thermally expands and thins creation of tension fractures (= normal faults) extension causes collapse of thinned crust (= horsts & grabens) creation of long, narrow, fault-bounded central rift valley thick sequences of continental deposits due to rapid subsidence and high re ...
12/2 Sea Floor Spreading HW
... crack in the oceanic crust. At a mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. As the molten material cools, it forms a strip of solid rock in the center of the ridge. Then more molten material ...
... crack in the oceanic crust. At a mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. As the molten material cools, it forms a strip of solid rock in the center of the ridge. Then more molten material ...
Lecture 7. Marine Sediments
... basin, properties of rocks such as magnetism, occurrence of earthquakes. ...
... basin, properties of rocks such as magnetism, occurrence of earthquakes. ...
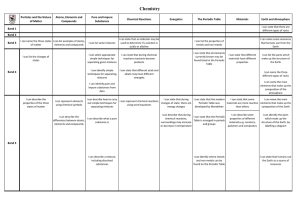
Chemistry - Edgbarrow School
... their properties metals and acids, as examples of Table carbon dioxide and breaking of bonds chemical reactions ...
... their properties metals and acids, as examples of Table carbon dioxide and breaking of bonds chemical reactions ...
convection-and-the-mantel-1st-one-of-week-5
... In the 1960’s scientist were able to dive to the ocean floor in Alvin a small submarine designed to take the enormous amount of pressures at the bottom of the ocean. – When they got down there they saw pillow shaped or they look like they just got squeezed from a tube of tooth past shaped ...
... In the 1960’s scientist were able to dive to the ocean floor in Alvin a small submarine designed to take the enormous amount of pressures at the bottom of the ocean. – When they got down there they saw pillow shaped or they look like they just got squeezed from a tube of tooth past shaped ...
Earth Structure and Plates
... Principles of Plate Tectonics • Earth’s outermost layer composed of thin ...
... Principles of Plate Tectonics • Earth’s outermost layer composed of thin ...
Chapter 15- Classification of Matter
... b. ____________________- change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter. i. Substance does not change __________________ when it undergoes a physical change. ii. __________________ is a process for separating a mixture by evaporating a liquid and condensing its vapor. c. ___________________ ...
... b. ____________________- change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter. i. Substance does not change __________________ when it undergoes a physical change. ii. __________________ is a process for separating a mixture by evaporating a liquid and condensing its vapor. c. ___________________ ...
Chapter 14 - AC Reynolds High
... • Redesigned equipment and processes • Fewer hazardous chemicals • Recycled or sold toxic chemical outputs • Began making nonpolluting products • Company saved $1.2 billion • Sparked cleaner production movement ...
... • Redesigned equipment and processes • Fewer hazardous chemicals • Recycled or sold toxic chemical outputs • Began making nonpolluting products • Company saved $1.2 billion • Sparked cleaner production movement ...
chapter14
... • Redesigned equipment and processes • Fewer hazardous chemicals • Recycled or sold toxic chemical outputs • Began making nonpolluting products • Company saved $1.2 billion • Sparked cleaner production movement ...
... • Redesigned equipment and processes • Fewer hazardous chemicals • Recycled or sold toxic chemical outputs • Began making nonpolluting products • Company saved $1.2 billion • Sparked cleaner production movement ...
Chapter 15
... • The earth’s crust consists of solid inorganic elements and compounds called minerals that can sometimes be used as resources. – Mineral resource: is a concentration of naturally occurring material in or on the earth’s crust that can be extracted and processed into useful materials at an affordable ...
... • The earth’s crust consists of solid inorganic elements and compounds called minerals that can sometimes be used as resources. – Mineral resource: is a concentration of naturally occurring material in or on the earth’s crust that can be extracted and processed into useful materials at an affordable ...
Lecture 14 – Marine Sediments (1) The CCD is: (a) the depth at
... (9) Saturation horizon is deepest in the Atlantic Ocean (~4500 m) relative to the Indian Ocean (~3500m) and shallowest in the Pacific (<3000 m). Why? Would you expect the CCD in the Atlantic to also be deeper explain why? The reason for that is that the pH due to respiration along the conveyer is lo ...
... (9) Saturation horizon is deepest in the Atlantic Ocean (~4500 m) relative to the Indian Ocean (~3500m) and shallowest in the Pacific (<3000 m). Why? Would you expect the CCD in the Atlantic to also be deeper explain why? The reason for that is that the pH due to respiration along the conveyer is lo ...
2017Geological Oceanography
... • These canyons cut into the continental shelf and slope, ending in a deep-sea fan • Sometimes they extend from the mouth of a river that drains sediment and fast flowing water out to sea – Created by erosion like canyons on land ...
... • These canyons cut into the continental shelf and slope, ending in a deep-sea fan • Sometimes they extend from the mouth of a river that drains sediment and fast flowing water out to sea – Created by erosion like canyons on land ...