Minerals of Uganda
... Industrial Minerals and Rocks of Uganda Industrial minerals and rocks and their geological provinces, carbonatites, sedimentary carbonate rocks, clays, phosphates, feldspars, kaolin, rock salt, gypsum, talc, silica sand, vermiculite, dimension stone, sand, volcanic rocks, ...
... Industrial Minerals and Rocks of Uganda Industrial minerals and rocks and their geological provinces, carbonatites, sedimentary carbonate rocks, clays, phosphates, feldspars, kaolin, rock salt, gypsum, talc, silica sand, vermiculite, dimension stone, sand, volcanic rocks, ...
Structural Controls on Massive Sulfide Deposition and Hydrothermal
... to the interaction of orthogonal synvolcanic faulting, and the regional east– west foliation. The average strikes of two distinct fracture sets are 040º and Fig. 4. Simplified section through the F Group structure, rotated approximately 45° to its ori355º (Fig. 9), a and b, respectively. A ginal att ...
... to the interaction of orthogonal synvolcanic faulting, and the regional east– west foliation. The average strikes of two distinct fracture sets are 040º and Fig. 4. Simplified section through the F Group structure, rotated approximately 45° to its ori355º (Fig. 9), a and b, respectively. A ginal att ...
PETROGENESIS OF THE MIOCENE SILICIC PYROCLASTIC
... I. Introduction, aims of the study Silicic (SiO2>65wt%) magmas evolve in shallow level magma reservoirs following the segregation of their parental melts from the source regions. Eruption of the felsic residual magmas, the erupted volume of the magma and the mechanism of the eruption are primarily ...
... I. Introduction, aims of the study Silicic (SiO2>65wt%) magmas evolve in shallow level magma reservoirs following the segregation of their parental melts from the source regions. Eruption of the felsic residual magmas, the erupted volume of the magma and the mechanism of the eruption are primarily ...
Ore deposits related to intermediate to felsic intrusions – Formation
... Py is the principal sulphide present but lesser amounts of cpy and even less commonly, bn may be present. ...
... Py is the principal sulphide present but lesser amounts of cpy and even less commonly, bn may be present. ...
Chapter 23: The Paleozoic Era
... are older than the Middle Ordovician of eastern New York are tilted at a different angle than those of the younger Silurian rocks. This means that something, such as a tectonic collision, tilted the rocks after the Middle Ordovician but before the Silurian. Volcanic activity also provides evidence o ...
... are older than the Middle Ordovician of eastern New York are tilted at a different angle than those of the younger Silurian rocks. This means that something, such as a tectonic collision, tilted the rocks after the Middle Ordovician but before the Silurian. Volcanic activity also provides evidence o ...
Geology 10L Manual - FOG - City College of San Francisco
... getting messy (hats and gloves and raingear recommended). Weather cancellations of field trips will occur only during storms. Bring good boots for walking along beaches and up and down hills. Bring writing utensils and lab manual and a hard writing surface, like a clipboard. You will be working! Pla ...
... getting messy (hats and gloves and raingear recommended). Weather cancellations of field trips will occur only during storms. Bring good boots for walking along beaches and up and down hills. Bring writing utensils and lab manual and a hard writing surface, like a clipboard. You will be working! Pla ...
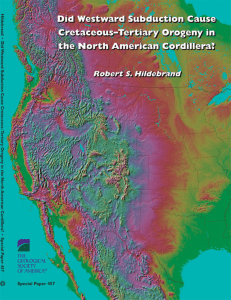
Did westward subduction cause Cretaceous
... During the early Mesozoic, Panthalassic Ocean crust was subducted westward beneath a ribbon continent named Rubia, where it created a generally low-standing continental arc. At about 124 Ma, the widespread deposition of intraformational gravels and conglomerates atop the passive margin marked the pa ...
... During the early Mesozoic, Panthalassic Ocean crust was subducted westward beneath a ribbon continent named Rubia, where it created a generally low-standing continental arc. At about 124 Ma, the widespread deposition of intraformational gravels and conglomerates atop the passive margin marked the pa ...
OCR Document
... Climate change is the long-term variability associated with the earth–ocean–climate system. The variability is caused by changes in certain boundary conditions, such as intensity of sunlight, arrangement of continents and oceans, and the composition of the atmosphere. Therefore, associated with the ...
... Climate change is the long-term variability associated with the earth–ocean–climate system. The variability is caused by changes in certain boundary conditions, such as intensity of sunlight, arrangement of continents and oceans, and the composition of the atmosphere. Therefore, associated with the ...
Scouting craton`s edge in paleo-Pacific Gondwana Carol A. Finn US
... West of the Gawler craton lies a buried granitic and gneissic continental fragment, the Coompana block (Shaw et al., 1996) (Figs. 1 and 2), that may have amalgamated with the Gawler craton by at least ~1450 Ma (Fitzsimons, 2003). The sources of the ovoid positive magnetic anomalies are not well det ...
... West of the Gawler craton lies a buried granitic and gneissic continental fragment, the Coompana block (Shaw et al., 1996) (Figs. 1 and 2), that may have amalgamated with the Gawler craton by at least ~1450 Ma (Fitzsimons, 2003). The sources of the ovoid positive magnetic anomalies are not well det ...
Plate Tectonics: Note 2 T. Seno (Earthquake Res Inst, Univ of Tokyo
... There are transform faults in the land area. The San Andreas fault, US, the Alpine Fault, New Zealand, and the North Anatolian fault, Turkey, are such examples. Although they are strike-slip faults in the continent, they are different from usual intraplate strike-slip faults, because they mark a bou ...
... There are transform faults in the land area. The San Andreas fault, US, the Alpine Fault, New Zealand, and the North Anatolian fault, Turkey, are such examples. Although they are strike-slip faults in the continent, they are different from usual intraplate strike-slip faults, because they mark a bou ...
Insights from the Azuero Peninsula, SW Panama
... enriched pattern, typical of plateau-like affinities (Fig. 2D). Chemistry of the Azuero Proto-arc ...
... enriched pattern, typical of plateau-like affinities (Fig. 2D). Chemistry of the Azuero Proto-arc ...
Plate tectonics and petroleum basins
... Philippine trench on the east, may be considered a mega-transcurrent setting. The fundamental shear is between the Indian Plate on the west and the Pacific Plate (including the Philippine Sea Plate) on the east. In the early Middle Tertiary the entire region experienced transtensional shear which br ...
... Philippine trench on the east, may be considered a mega-transcurrent setting. The fundamental shear is between the Indian Plate on the west and the Pacific Plate (including the Philippine Sea Plate) on the east. In the early Middle Tertiary the entire region experienced transtensional shear which br ...
Ba – Barium 71
... Ba in floodplain sediment The total Ba distribution in floodplain sediment, determined by XRF, varies from 15 to 4837 mg kg-1, with a median of 380 mg kg-1, and the aqua regia extractable from 7 to 2210 mg kg-1 Ba (median 82 mg kg-1). As with stream sediment, approximately half of the Ba is extracte ...
... Ba in floodplain sediment The total Ba distribution in floodplain sediment, determined by XRF, varies from 15 to 4837 mg kg-1, with a median of 380 mg kg-1, and the aqua regia extractable from 7 to 2210 mg kg-1 Ba (median 82 mg kg-1). As with stream sediment, approximately half of the Ba is extracte ...
47 In nature there is a wide variety of sedimentary rocks and each
... become better sorted (sands are said to become “cleaner’ as they lose their silt and clay fractions) and its’ particles become rounder and more spherical in shape (see the section on Grain Shape and consider the generalizations made here in light of all of the constraints on grain shape). A sediment ...
... become better sorted (sands are said to become “cleaner’ as they lose their silt and clay fractions) and its’ particles become rounder and more spherical in shape (see the section on Grain Shape and consider the generalizations made here in light of all of the constraints on grain shape). A sediment ...
volcanism and intrusions of the deccan traps, india: geochemistry
... The largest area (≈ 1200 km2) is the Chhota Udaipur sub-province (Gwalani et al., 1993) which has been divided into sectors based on their predominant lithology: 1) the Amba Dongar sector is characterised by a carbonatite-ring complex which intruded Cretaceous sediments (Bagh sandstone), the carbona ...
... The largest area (≈ 1200 km2) is the Chhota Udaipur sub-province (Gwalani et al., 1993) which has been divided into sectors based on their predominant lithology: 1) the Amba Dongar sector is characterised by a carbonatite-ring complex which intruded Cretaceous sediments (Bagh sandstone), the carbona ...
(Nyasa) Rift US Scientists Donna J. Shillingt
... defined in the upper crust by ~100-km-long border faults [Ebinger et al., 1987]. The length scales of segments together with flexure associated with faulting [Ebinger et al., 1991], occurrence of deep seismicity [Jackson and Blenkinsop, 1993; Foster and Jackson, 1998] and inferred mafic lower crust ...
... defined in the upper crust by ~100-km-long border faults [Ebinger et al., 1987]. The length scales of segments together with flexure associated with faulting [Ebinger et al., 1991], occurrence of deep seismicity [Jackson and Blenkinsop, 1993; Foster and Jackson, 1998] and inferred mafic lower crust ...
DNR San Juan Islands Brandon
... All other occurrences are less than several hundred meters across and are too small to show in Figure 1. Isotopic dates cluster between 286 and 219 Ma (Armstrong and Misch, 1987), indicating Permian or Triassic metamorphism. Thus, metamorphism of the Vedder coincided with volcanism and chert deposit ...
... All other occurrences are less than several hundred meters across and are too small to show in Figure 1. Isotopic dates cluster between 286 and 219 Ma (Armstrong and Misch, 1987), indicating Permian or Triassic metamorphism. Thus, metamorphism of the Vedder coincided with volcanism and chert deposit ...
Activity–Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
... of coastal blocks with respect to stable North America (yellow arrows). The southern Cascade volcanic arc (red triangles) erupts along the trailing edge of Oregon block in a region of crustal extension. Orange areas, representing young volcanic rocks erupted in the last 2 million years, are more vol ...
... of coastal blocks with respect to stable North America (yellow arrows). The southern Cascade volcanic arc (red triangles) erupts along the trailing edge of Oregon block in a region of crustal extension. Orange areas, representing young volcanic rocks erupted in the last 2 million years, are more vol ...
Chapter 4-Volcanoes-w-2017
... islands. In fact, with the exception of the volcanic islands that form above subduction zones, most other oceanic islands are either single shield volcanoes, or more often the combination of two or more shields built upon massive amounts of pillow lavas. Examples include the Canary Islands, the Hawa ...
... islands. In fact, with the exception of the volcanic islands that form above subduction zones, most other oceanic islands are either single shield volcanoes, or more often the combination of two or more shields built upon massive amounts of pillow lavas. Examples include the Canary Islands, the Hawa ...
Copy of A View of Earth`s Past Fill in Notes
... ______ are large areas of exposed Precambrian Rocks. Most are highly deformed & contain few fossils. B. Precambrian Life __________ are layered, reef-like deposits that contain cyanobacteria. Fossils are rare from this time probably because life that existed lacked parts that can be made into fossil ...
... ______ are large areas of exposed Precambrian Rocks. Most are highly deformed & contain few fossils. B. Precambrian Life __________ are layered, reef-like deposits that contain cyanobacteria. Fossils are rare from this time probably because life that existed lacked parts that can be made into fossil ...
The Paleozoic Era - AC Reynolds High
... are older than the Middle Ordovician of eastern New York are tilted at a different angle than those of the younger Silurian rocks. This means that something, such as a tectonic collision, tilted the rocks after the Middle Ordovician but before the Silurian. Volcanic activity also provides evidence o ...
... are older than the Middle Ordovician of eastern New York are tilted at a different angle than those of the younger Silurian rocks. This means that something, such as a tectonic collision, tilted the rocks after the Middle Ordovician but before the Silurian. Volcanic activity also provides evidence o ...
fault - Science Partnership
... Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Seismographs are instruments that detect and record earthquakes. The principle behind the seismograph is that inertia tends to keep the suspended mass motionless while the recording surface vibrates with the bedrock. Thus the seismograph measures the displacem ...
... Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Seismographs are instruments that detect and record earthquakes. The principle behind the seismograph is that inertia tends to keep the suspended mass motionless while the recording surface vibrates with the bedrock. Thus the seismograph measures the displacem ...
tectonic evolution of the japanese island arc system
... surveying, and trench excavation have continued for the past ∼30 years. The resulting collection of maps was published by Research Group of the Active Faults in Japan (1991) and, more recently, a marine portion was presented by Tokuyama et al (1999). The important findings of these results are revie ...
... surveying, and trench excavation have continued for the past ∼30 years. The resulting collection of maps was published by Research Group of the Active Faults in Japan (1991) and, more recently, a marine portion was presented by Tokuyama et al (1999). The important findings of these results are revie ...
f.y.b.a geography
... features like mountains, plateau and plains, rivers, lakes, sea, oceans and human settlements are found on the crust. It is the most significant zone of the solid earth with an average thickness of 17 kilometer. The base of the crust is sharply defined where it contacts the mantle. This surface of s ...
... features like mountains, plateau and plains, rivers, lakes, sea, oceans and human settlements are found on the crust. It is the most significant zone of the solid earth with an average thickness of 17 kilometer. The base of the crust is sharply defined where it contacts the mantle. This surface of s ...
Could Iceland be a modern analogue for the Earth`s early
... whereas underplated basalts tend to remain dry, as recorded in deep enclaves from Kerguelen, which have re-equilibrated under granulite facies conditions (Grégoire et al., 1998). In Iceland, the partially hydrated lava pile progressively subsides because of loading and drifts away from the ridge-ax ...
... whereas underplated basalts tend to remain dry, as recorded in deep enclaves from Kerguelen, which have re-equilibrated under granulite facies conditions (Grégoire et al., 1998). In Iceland, the partially hydrated lava pile progressively subsides because of loading and drifts away from the ridge-ax ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.