The Tien Shan Early Paleozoic tectonics and geodynamics
... [9] Microcontinent, continental island arc. In the Paleozoic the Tien Shan rocks composed a few tectonic blocks, having an old continental crust and separated by oceanic basins. A continental block of this kind can be ranked as a microcontinent or as a continental island arc, volcanic or nonvolcanic ...
... [9] Microcontinent, continental island arc. In the Paleozoic the Tien Shan rocks composed a few tectonic blocks, having an old continental crust and separated by oceanic basins. A continental block of this kind can be ranked as a microcontinent or as a continental island arc, volcanic or nonvolcanic ...
Geology and volcanic setting of the Horne deposit, Rouyn
... faults are composite and show evidence of repeated movement (Wilson, 1941). Within the mine area, the zone of intense shearing along the Horne Creek fault varies from about 50 m to 150 m in thickness. The Andesite fault has ...
... faults are composite and show evidence of repeated movement (Wilson, 1941). Within the mine area, the zone of intense shearing along the Horne Creek fault varies from about 50 m to 150 m in thickness. The Andesite fault has ...
The geology around the city of Guanajuato is specially interesting
... The second day of the trip we return to the Mining District to study in more detail the different facies of the Calderones Formation, which is the principal subject of our present research in the region. We can see outcrops of vent structures as well as of proximal, medial and distal facies of the b ...
... The second day of the trip we return to the Mining District to study in more detail the different facies of the Calderones Formation, which is the principal subject of our present research in the region. We can see outcrops of vent structures as well as of proximal, medial and distal facies of the b ...
Intermediate Earth Science Teacher’s Manual
... Heat flow and movement of material in the mantle cause convection currents. Convection currents cause the plates to move. Earth at one point, was one giant landmass. Continental drift is the movement of the continents (due to convection currents in the mantle). Fossils, rock formations, mountain ran ...
... Heat flow and movement of material in the mantle cause convection currents. Convection currents cause the plates to move. Earth at one point, was one giant landmass. Continental drift is the movement of the continents (due to convection currents in the mantle). Fossils, rock formations, mountain ran ...
The magnetite-apatite ore of the Kiruna district, Northern Sweden
... and textures. Minerals like chlorite, zoisite, epidot, actinolite and albite in the mafic rocks indicate the greenschist-fazies. According to HARLOV (2002) the orebody is connect with extensive fault zone (Fig.6). It is an obvious change in the nature of the rock sequence about 1 km to the east of t ...
... and textures. Minerals like chlorite, zoisite, epidot, actinolite and albite in the mafic rocks indicate the greenschist-fazies. According to HARLOV (2002) the orebody is connect with extensive fault zone (Fig.6). It is an obvious change in the nature of the rock sequence about 1 km to the east of t ...
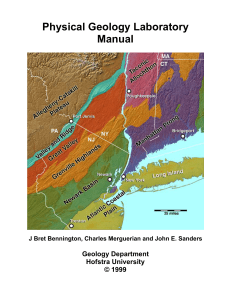
Bennington, J Bret, Merguerian, Charles, and Sanders, J.E., 1999
... not only grade your papers but "copy edit" them as well. It is our intention to help you become better at writing, perhaps the most important skill in almost any professional career. Format: Typed (or word processed), double spaced, ample margins all around, and written on one side of the paper only ...
... not only grade your papers but "copy edit" them as well. It is our intention to help you become better at writing, perhaps the most important skill in almost any professional career. Format: Typed (or word processed), double spaced, ample margins all around, and written on one side of the paper only ...
Activity— Foam Faults - Cascadia Earthscope Earthquake and
... drops downward or “subsides.” This relationship between extensional motion of geologic layers and downdropped fault blocks (graben or rift valley if the downdropped block is bounded on both sides by normal faults, as in this block model) produces normal faulting. It also represents the extensional ...
... drops downward or “subsides.” This relationship between extensional motion of geologic layers and downdropped fault blocks (graben or rift valley if the downdropped block is bounded on both sides by normal faults, as in this block model) produces normal faulting. It also represents the extensional ...
The Basin and Range Province: Origin and Tectonic Significance
... possible exceptionof the northern part of the East African rift system, it is unusual amongthe regions of any continent for high heat flow, thin lithosphere, the occurrence of low seismic velocities in the underlying upper mantle, a history of long-lived episodic magmatism,and a pronouncedlayer of l ...
... possible exceptionof the northern part of the East African rift system, it is unusual amongthe regions of any continent for high heat flow, thin lithosphere, the occurrence of low seismic velocities in the underlying upper mantle, a history of long-lived episodic magmatism,and a pronouncedlayer of l ...
Nappes of the southern Tien Shan
... The southern Tien Shan is a folded area with widespread Paleozoic nappes. The ensembles of nappes distributed in Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and China are described, and their structural similarity and distinctions in different parts of the area are shown. Nappes of the southern Tien Shan oc ...
... The southern Tien Shan is a folded area with widespread Paleozoic nappes. The ensembles of nappes distributed in Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and China are described, and their structural similarity and distinctions in different parts of the area are shown. Nappes of the southern Tien Shan oc ...
In: Zagros.Hindu Kush.Himalaya Geodynamic Evolution Edited by
... attempt to interpret their geological evolution. Notwithstanding many assumptions due to scarcity of data, eight tectono-plutonic phases are recognized from Precambrian to Pliocene, which are separated by relatively stable intervals. The elongated belt of the Precambrian calc-alkaline intrusives in ...
... attempt to interpret their geological evolution. Notwithstanding many assumptions due to scarcity of data, eight tectono-plutonic phases are recognized from Precambrian to Pliocene, which are separated by relatively stable intervals. The elongated belt of the Precambrian calc-alkaline intrusives in ...
Early Paleozoic Tectonic and Thermomechanical
... UHP metamorphic rocks was a mixture of continental and mafic/ultramafic materials, derived either from oceanic mélanges or pieces of a rifted continental margin tectonically incorporated into an oceanic subduction channel. These observations require that the North Qaidam UHP metamorphic rocks origin ...
... UHP metamorphic rocks was a mixture of continental and mafic/ultramafic materials, derived either from oceanic mélanges or pieces of a rifted continental margin tectonically incorporated into an oceanic subduction channel. These observations require that the North Qaidam UHP metamorphic rocks origin ...
Significance of seismic reflections beneath a tilted
... to obtain a consistentmodel for both the seismicand gravity data from the TehachapiMountains. The CALCRUST reflection profile aimed principally at there it was taken south, toward line 4 of the Consortium for addressingthe structuralrelationshipof the gneissand schist, Continental Reflection Profili ...
... to obtain a consistentmodel for both the seismicand gravity data from the TehachapiMountains. The CALCRUST reflection profile aimed principally at there it was taken south, toward line 4 of the Consortium for addressingthe structuralrelationshipof the gneissand schist, Continental Reflection Profili ...
`Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs)`: Definition, recommended
... Provinces (LIPs). The term LIP has been widely applied to large basaltic provinces such as the Deccan Traps, and the term Silicic Large Igneous Province (SLIP) to volcanic provinces of dominantly felsic composition, such as the Whitsunday Province. However, neither term (LIP, SLIP) has been applied ...
... Provinces (LIPs). The term LIP has been widely applied to large basaltic provinces such as the Deccan Traps, and the term Silicic Large Igneous Province (SLIP) to volcanic provinces of dominantly felsic composition, such as the Whitsunday Province. However, neither term (LIP, SLIP) has been applied ...
South coast of Arran
... Kildonan (NS 037 208), including the sea cliffs near Bennan Head. The exposures of the dyke swarm are principally on the shore (Figs 6.8 and 6.9); the composite sill is seen in the cliffs at Bennan Head and in small quarries to the north. The southern Arran dyke swarm in this area has a dominant NW– ...
... Kildonan (NS 037 208), including the sea cliffs near Bennan Head. The exposures of the dyke swarm are principally on the shore (Figs 6.8 and 6.9); the composite sill is seen in the cliffs at Bennan Head and in small quarries to the north. The southern Arran dyke swarm in this area has a dominant NW– ...
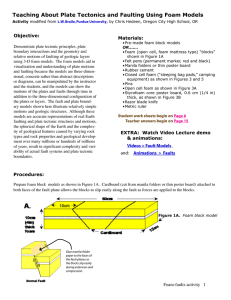
Teaching About Plate Tectonics and Faulting Using Foam
... as described above and then move the two outer blocks together as in Figure 1C. The inner block will be thrust upwards producing reverse faults and an uplifted block. In a plate tectonic setting, such compressional motion is associated with convergent plate boundaries (Table 1) where two lithosphe ...
... as described above and then move the two outer blocks together as in Figure 1C. The inner block will be thrust upwards producing reverse faults and an uplifted block. In a plate tectonic setting, such compressional motion is associated with convergent plate boundaries (Table 1) where two lithosphe ...
Subduction and the rock record: Concepts developed
... similar relationships in other high P-T belts. Wakabayashi and Unruh (1995) proposed that normal slip took place during one period of time along the ophiolite–Franciscan Complex contact and that tectonic wedging (and periodic thrust faulting along the contact) were operative during other periods (Fi ...
... similar relationships in other high P-T belts. Wakabayashi and Unruh (1995) proposed that normal slip took place during one period of time along the ophiolite–Franciscan Complex contact and that tectonic wedging (and periodic thrust faulting along the contact) were operative during other periods (Fi ...
M.Sc. Geology Revised Syllabus June 2013 I Semester Code Paper
... folding in shield zones, fold systems. Joints Classification and their importance in Construction projects. Mechanics of faulting. Classification and recognition of faults. Strike slip faults, normal faults. Unconformities and basement cover relations. 15 hours Unit – III Tectonic aspects of Igneous ...
... folding in shield zones, fold systems. Joints Classification and their importance in Construction projects. Mechanics of faulting. Classification and recognition of faults. Strike slip faults, normal faults. Unconformities and basement cover relations. 15 hours Unit – III Tectonic aspects of Igneous ...
full text pdf
... bulbous cauliflower-like margins. A few cognate lava clasts occur within the siliceous layers, revealing that lithic inclusions are not always diagnostic of a pyroclastic origin [38]. They consist of phenocrysts and rounded ...
... bulbous cauliflower-like margins. A few cognate lava clasts occur within the siliceous layers, revealing that lithic inclusions are not always diagnostic of a pyroclastic origin [38]. They consist of phenocrysts and rounded ...
Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon
... under the appropriate conditions. Watson and Harrison (1983) demonstrated that their empirical relationship applies over a wide range of conditions and melt compositions. Solubility is largely insensitive to pressure and appears to deviate from their equation only for dry (,;1.5 wt% H2O) or peralkal ...
... under the appropriate conditions. Watson and Harrison (1983) demonstrated that their empirical relationship applies over a wide range of conditions and melt compositions. Solubility is largely insensitive to pressure and appears to deviate from their equation only for dry (,;1.5 wt% H2O) or peralkal ...
The role of crustal heterogeneity in controlling vertical coupling
... strength, thickness and density give insights into lateral and vertical strain propagation during Late Cretaceous shortening and Early Tertiary left-lateral shearing related to the early development of the North America– Caribbean plate boundary in southern Mexico. Analogue models reproduce a two-ph ...
... strength, thickness and density give insights into lateral and vertical strain propagation during Late Cretaceous shortening and Early Tertiary left-lateral shearing related to the early development of the North America– Caribbean plate boundary in southern Mexico. Analogue models reproduce a two-ph ...
article in press - Centro de Geociencias
... of the type Cosoltepec Formation (Fig. 2). The Salada, Cosoltepec (s.s.) and Cuatlaco units all contain mafic lenses of tholeiitic, within-plate affinity (Keppie et al., 2007; Grodzicki et al., in press). Compared with the Ordovician units, concordant detrital zircons in the Salada, Cosoltepec (s.s) ...
... of the type Cosoltepec Formation (Fig. 2). The Salada, Cosoltepec (s.s.) and Cuatlaco units all contain mafic lenses of tholeiitic, within-plate affinity (Keppie et al., 2007; Grodzicki et al., in press). Compared with the Ordovician units, concordant detrital zircons in the Salada, Cosoltepec (s.s) ...
There are possible iron oxide-copper
... Eder, 1983; Hoffmann, 1990; Porada, 1989). Katangan rocks host the Copperbelt world-class Cu and Co deposits. Alkaline magmatism took place during the rifting phase. Widespread (calcalkaline ?) magmatism seems to have occurred after the closure of the basin, during a subduction-related event and lat ...
... Eder, 1983; Hoffmann, 1990; Porada, 1989). Katangan rocks host the Copperbelt world-class Cu and Co deposits. Alkaline magmatism took place during the rifting phase. Widespread (calcalkaline ?) magmatism seems to have occurred after the closure of the basin, during a subduction-related event and lat ...
CRCT Earth Science Review 6
... waves, and returns to its original shape. C Rock changes shape, but does not release significant amounts of energy. D Rock becomes compacted under pressure and realigns its mineral grains. ...
... waves, and returns to its original shape. C Rock changes shape, but does not release significant amounts of energy. D Rock becomes compacted under pressure and realigns its mineral grains. ...
Clarification of Pasha Rift Structure in Pasha-Ladoga
... smoothing in either a vertical or horizontal direction; in the ZondMT software this corresponds to a smoothing ratio value of 1. The regularization (Tikhonov) parameter controls the trade-off between fitting the AMT data and producing a spatially smooth model. In the ZondMT software it can be set in ...
... smoothing in either a vertical or horizontal direction; in the ZondMT software this corresponds to a smoothing ratio value of 1. The regularization (Tikhonov) parameter controls the trade-off between fitting the AMT data and producing a spatially smooth model. In the ZondMT software it can be set in ...
Earth,Tests,Ch10
... A) the hanging wall block below an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block B) the footwall block below an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block C) the hanging wall block above an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block D) the ...
... A) the hanging wall block below an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block B) the footwall block below an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block C) the hanging wall block above an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block D) the ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.